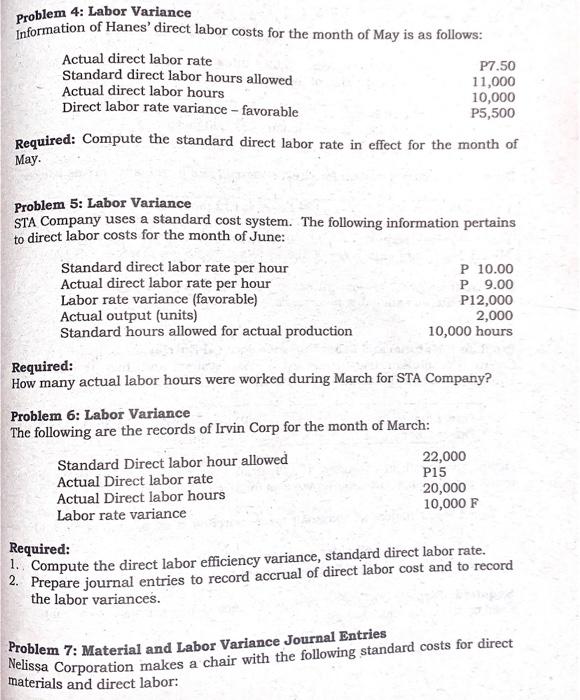
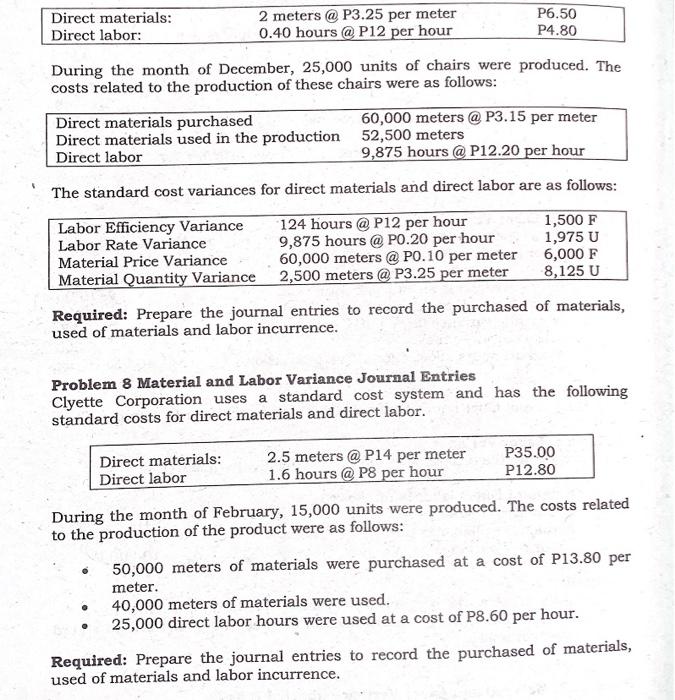
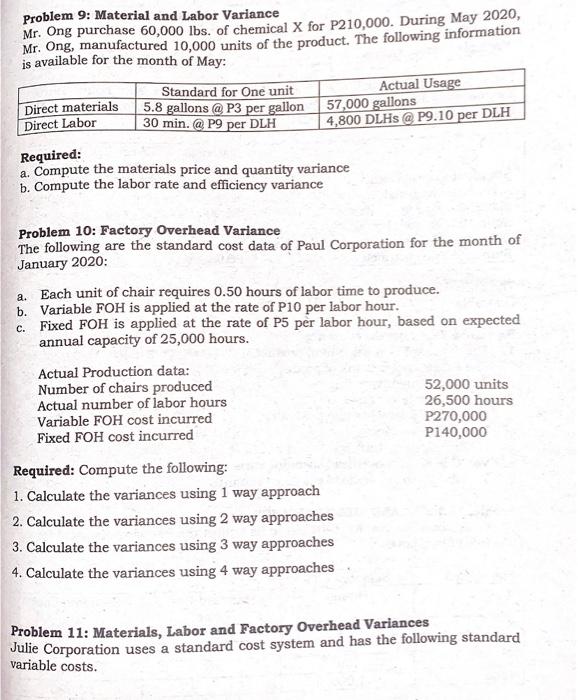
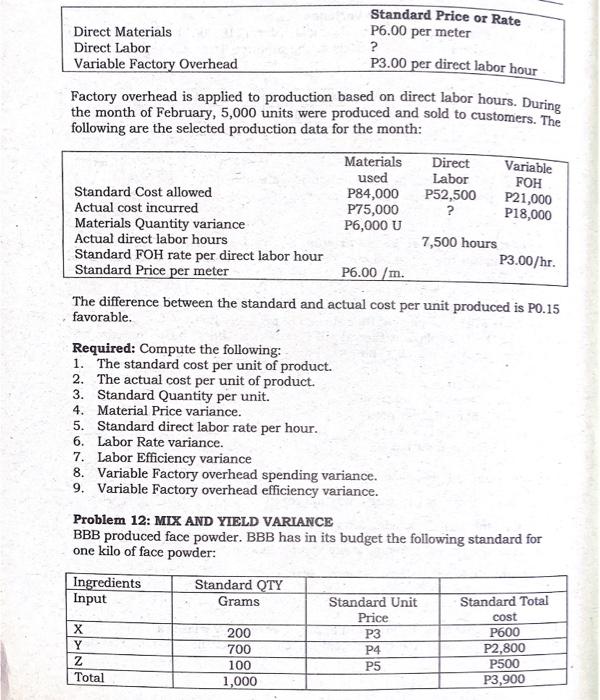
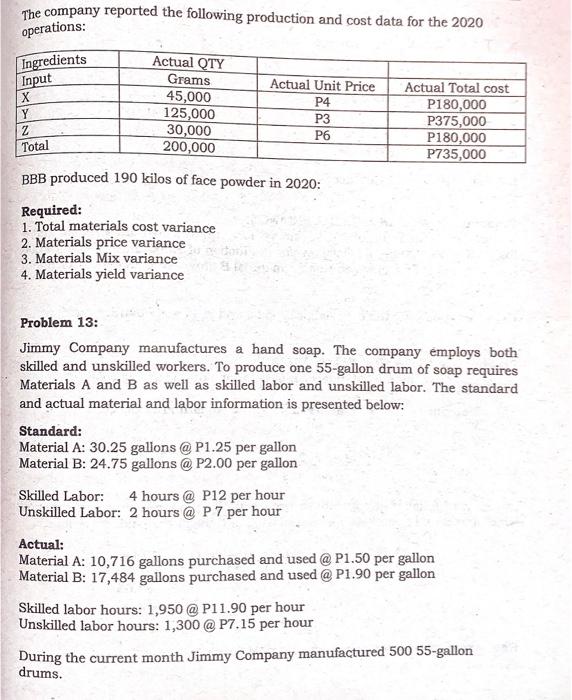
STRAIGHT PROBLEMS Problem 1: Material Variance Information on Dulce's direct material costs for May is as follows: Actual quantity of direct materials purchased and used 30,000 lbs. Actual cost of direct materials P84,000 Unfavorable direct material usage variance P 3,000 Standard quantity of direct materials allowed for May production 29,000 lbs. Required: Compute the direct material price variance. Problem 2: Material Variance Katrina Company's direct material costs are as follows: Standard unit price P 3.60 Actual quantity purchased 1,600 Standard quantity allowed for actual production 1,450 Materials purchase price variance - favorable P 240 Required: Compute the actual purchase price per unit, rounded to the nearest centavos. Problem 3 Material Variance Irish Corporation produces chairs. The standard direct material cost to produce one unit of chairs is 4 meters of raw materials at P5.00 per meter. During 2020, 8,400 meters of raw materials were purchased at a cost of P20,160. All the purchased materials were actually used to produce 2,000 units of chairs. Required: 1. Compute the actual price per meter material price and quantity variance and prepare journal entry to record the variance, assuming the price variance is determined at the time of usage. 2. Assume that Irish purchased is 8,500 meters of materials for P20,400 but used only 8,400. Compute the material purchase price variance, quantity variance and prepare journal entries to record the variance, assuming the variance is determined at the earliest possible time. Information of Hanes' direct labor costs for the month of May is as follows: Problem 4: Labor Variance Actual direct labor rate P7.50 Standard direct labor hours allowed Actual direct labor hours 11,000 Direct labor rate variance - favorable 10,000 P5,500 Required: Compute the standard direct labor rate in effect for the month of . Problem 5: Labor Variance STA Company uses a standard cost system. The following information pertains to direct labor costs for the month of June: Standard direct labor rate per hour P 10.00 Actual direct labor rate per hour P 9.00 Labor rate variance (favorable) P12,000 Actual output (units) 2,000 Standard hours allowed for actual production 10,000 hours Required: How many actual labor hours were worked during March for STA Company? Problem 6: Labor Variance The following are the records of Irvin Corp for the month of March: Standard Direct labor hour allowed 22,000 Actual Direct labor rate P15 Actual Direct labor hours 20,000 Labor rate variance 10,000 F Required: 1. Compute the direct labor efficiency variance, standard direct labor rate. 2. Prepare journal entries to record accrual of direct labor cost and to record the labor variances. Problem 7: Material and Labor Variance Journal Entries Nelissa Corporation makes a chair with the following standard costs for direct materials and direct labor: Direct materials: 2 meters @ P3.25 per meter P6.50 Direct labor: 0.40 hours @ P12 per hour P4.80 During the month of December, 25,000 units of chairs were produced. The costs related to the production of these chairs were as follows: Direct materials purchased 60,000 meters @ P3.15 per meter Direct materials used in the production 52,500 meters Direct labor 9,875 hours @ P12.20 per hour The standard cost variances for direct materials and direct labor are as follows: Labor Efficiency Variance 124 hours @ P12 per hour 1,500 F Labor Rate Variance 9,875 hours @ PO.20 per hour 1,975 U Material Price Variance 60,000 meters @ PO.10 per meter 6,000 F Material Quantity Variance 2,500 meters @ P3.25 per meter 8,125 U Required: Prepare the journal entries to record the purchased of materials, used of materials and labor incurrence. Problem 8 Material and Labor Variance Journal Entries Clyette Corporation uses a standard cost system and has the following standard costs for direct materials and direct labor. Direct materials: Direct labor 2.5 meters @ P14 per meter 1.6 hours @ P8 per hour P35.00 P12.80 During the month of February, 15,000 units were produced. The costs related to the production of the product were as follows: 50,000 meters of materials were purchased at a cost of P13.80 per meter. 40,000 meters of materials were used. 25,000 direct labor hours were used at a cost of P8.60 per hour. Required: Prepare the journal entries to record the purchased of materials, used of materials and labor incurrence. Problem 9: Material and Labor Variance Mr. Ong purchase 60,000 lbs. of chemical X for P210,000. During May 2020, Mr. Ong, manufactured 10,000 units of the product. The following information is available for the month of May: Standard for One unit Actual Usage Direct materials 5.8 gallons @ P3 per gallon 57,000 gallons Direct Labor 30 min. @ P9 per DLH 4,800 DLHS @ P9.10 per DLH Required: a. Compute the materials price and quantity variance b. Compute the labor rate and efficiency variance Problem 10: Factory Overhead Variance The following are the standard cost data of Paul Corporation for the month of January 2020: a. Each unit of chair requires 0.50 hours of labor time to produce. b. Variable FOH is applied at the rate of P10 per labor hour. c. Fixed FOH is applied at the rate of P5 per labor hour, based on expected annual capacity of 25,000 hours. Actual Production data: Number of chairs produced 52,000 units Actual number of labor hours 26,500 hours Variable FOH cost incurred P270,000 Fixed FOH cost incurred P140,000 Required: Compute the following: 1. Calculate the variances using 1 way approach 2. Calculate the variances using 2 way approaches 3. Calculate the variances using 3 way approaches 4. Calculate the variances using 4 way approaches Problem 11: Materials, Labor and Factory Overhead Variances Julie Corporation uses a standard cost system and has the following standard variable costs. Variable FOH P21,000 Standard Price or Rate Direct Materials P6.00 per meter Direct Labor ? Variable Factory Overhead P3.00 per direct labor hour Factory overhead is applied to production based on direct labor hours. During the month of February, 5,000 units were produced and sold to customers. The following are the selected production data for the month: Materials Direct used Labor Standard Cost allowed P84,000 P52,500 Actual cost incurred P75,000 ? P18,000 Materials Quantity variance P6,000 U Actual direct labor hours 7,500 hours Standard FOH rate per direct labor hour P3.00/hr. Standard Price per meter P6.00 /m. The difference between the standard and actual cost per unit produced is P0.15 favorable. Required: Compute the following: 1. The standard cost per unit of product. 2. The actual cost per unit of product. 3. Standard Quantity per unit. 4. Material Price variance. 5. Standard direct labor rate per hour. 6. Labor Rate variance. 7. Labor Efficiency variance 8. Variable Factory overhead spending variance. 9. Variable Factory overhead efficiency variance. Problem 12: MIX AND YIELD VARIANCE BBB produced face powder. BBB has in its budget the following standard for one kilo of face powder: Ingredients Standard QTY Input Grams Standard Unit Standard Total Price 200 P3 P600 700 P4 P2,800 100 P5 P500 1,000 P3,900 cost Y 2 Total The company reported the following production and cost data for the 2020 operations: Ingredients Input X Y z Total Actual QTY Grams 45,000 125,000 30,000 200,000 Actual Unit Price P4 P3 P6 Actual Total cost P180,000 P375,000 P180,000 P735,000 BBB produced 190 kilos of face powder in 2020: Required: 1. Total materials cost variance 2. Materials price variance 3. Materials Mix variance 4. Materials yield variance Problem 13: Jimmy Company manufactures a hand soap. The company employs both skilled and unskilled workers. To produce one 55-gallon drum of soap requires Materials A and B as well as skilled labor and unskilled labor. The standard and actual material and labor information is presented below: Standard: Material A: 30.25 gallons @ P1.25 per gallon Material B: 24.75 gallons @ P2.00 per gallon Skilled Labor: 4 hours @ P12 per hour Unskilled Labor: 2 hours @ P7 per hour Actual: Material A: 10,716 gallons purchased and used @ P1.50 per gallon Material B: 17,484 gallons purchased and used @ P1.90 per gallon Skilled labor hours: 1,950 @ P11.90 per hour Unskilled labor hours: 1,300 @ P7.15 per hour During the current month Jimmy Company manufactured 500 55-gallon drums. Required: Compute the following (Round all answers to the nearest whole peso) a. Total Material price variance b. Total Material mix variance Total Material yield variance d. Total Labor rate variance Total Labor Mix variance f. Total Labor yield variance C. e. Problem 14: MIX AND YIELD VARIANCE Production of each unit of 001 requires 8 lbs. of B at a cost of P9 per lb. and 4 lbs. of X at P11.20 per lb. However, for production of 1,000 units of 001 10,000 lbs. were used, 75% of which was for material B at a cost of P8 per lb. for B and P9 per lb. for X. Required: Compute the material price, mix, and yield and quantity variance. Problem 15: MIX AND YIELD VARIANCE Marie Corp has material standards inputs for one unit is as follows Material Quantity in lbs. Standard Price per lb. X 400 40.00 Y 400 80.00 z 200 30.00 Total 1,000 lbs. 20 units of finished product have been actually produced during the period which the actual quantities of material used and the prices paid are as follows: Material Quantity used in lb. Price X 10,000 38.00 Y 8,500 84.00 Z 4,500 32.50 Total 23,000 lbs. Required: Compute the price, mix and yield variances