Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
struct node //Definition of a node. double data; struct node *next; b; struct node* makeNode (double d) struct node *nodePtr; nodePtr-(struct node*) malloc (sizeof(struct node));
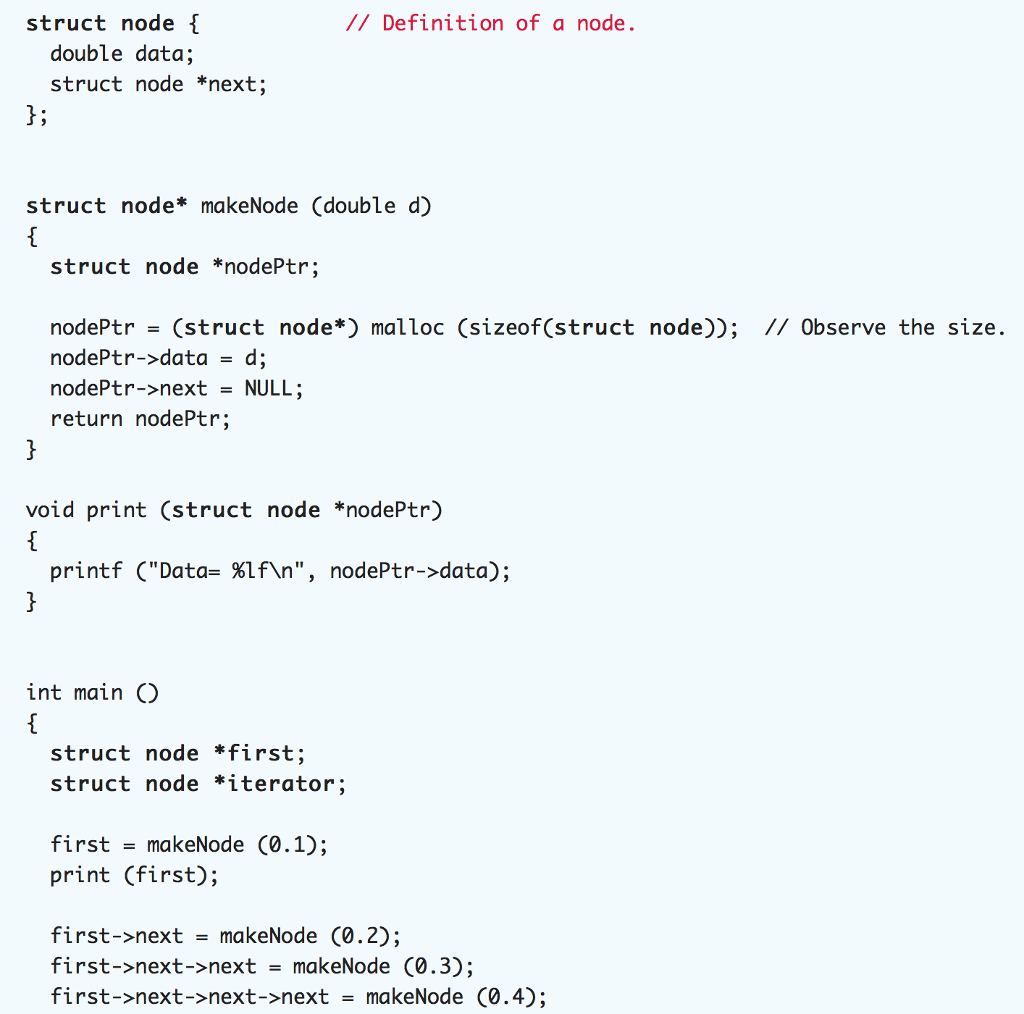


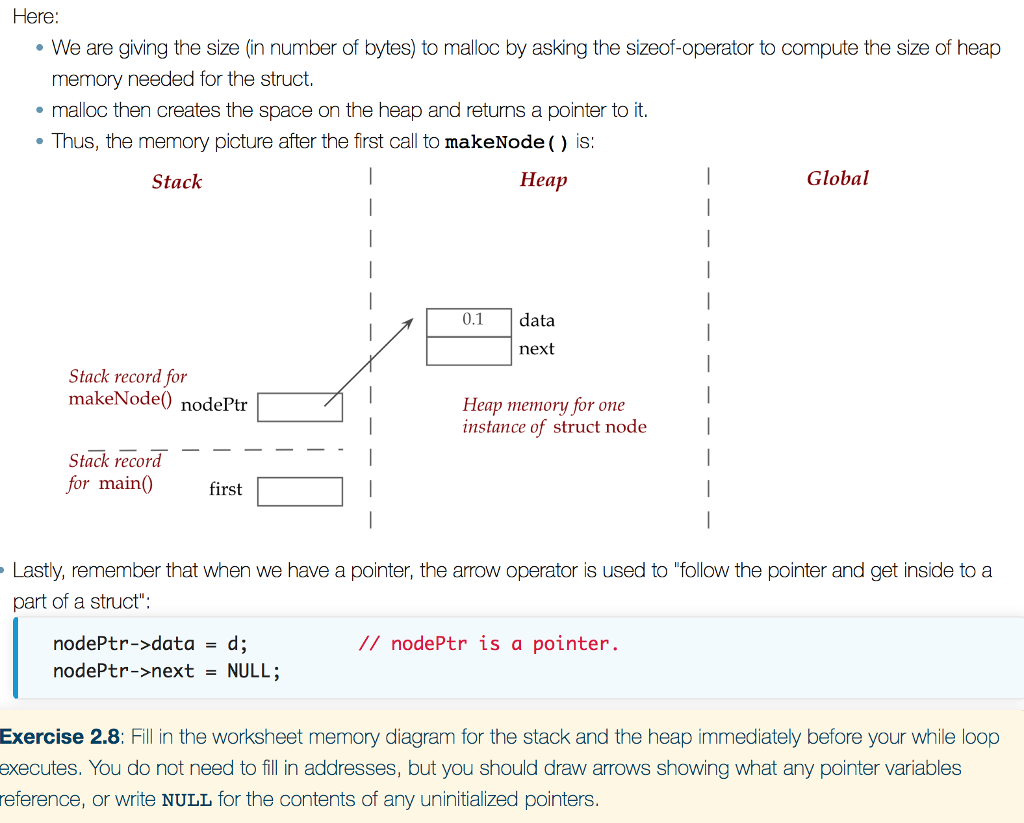
struct node //Definition of a node. double data; struct node *next; b; struct node* makeNode (double d) struct node *nodePtr; nodePtr-(struct node*) malloc (sizeof(struct node)); // Observe the size. nodePtr->data = d; nodePtr->next = NULL; return nodePtr; void print (struct node *nodePtr) printf ("Data-xfNn", nodePtr->data); int main O struct node *first; struct node *iterator; first - makeNode (0.1); print (first); first->next = makeNode (0.2); first->next->next = makeNode (0.3); first->next->next->next - makeNode (0.4)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


