Question
# Students should implement the following four functions in Solution_Q1.R: # generateData: takes as input the test results number, probability of positive results, and name

# Students should implement the following four functions in Solution_Q1.R: # generateData: takes as input the test results number, probability of positive results, and name of the test results file, and outputs the results file # loadData: takes as input the test results file and outputs the results as a dataframe # bayesianInference: takes as input the dataframe, prior, false positive rate, and hit rate, and outputs the vector of posterior probabilities # plotProsterior: takes as input the vector of posterior probabilities and name of the figure (where x axis is the number of data and y axis the corresponding posterior probabilities), and outputs the figure
source("Solution_Q1.R")
# Test results file testResultsFile = "testResults.csv" # Test results number testRusultsNum = 100 # Positive test results probability PosTestResultsProb = 0.9 # Posterior probabilitites figure posteriorsFig = "posteriorsFig"
# Probabilities prior = 0.001 # Prior probabilities fpr = 0.05 # False positive rate hr = 0.99 # Hit rate
# Takes as input the test results number, probability of positive results, and name of the test results file, and outputs the results file generateData
# Takes as input the test results file and outputs the results as a dataframe testResults = loadData(testResultsFile)
# Takes as input the dataframe, prior, false positive rate, and hit rate, and outputs the vector of posterior probabilities posteriors = bayesianInference(testResults, prior, fpr, hr)
# Takes as input the vector of posterior probabilities and name of the figure (where x axis is the number of data and y axis the corresponding posterior probabilities), and outputs the figure plotPosteriors(posteriors, posteriorsFig)
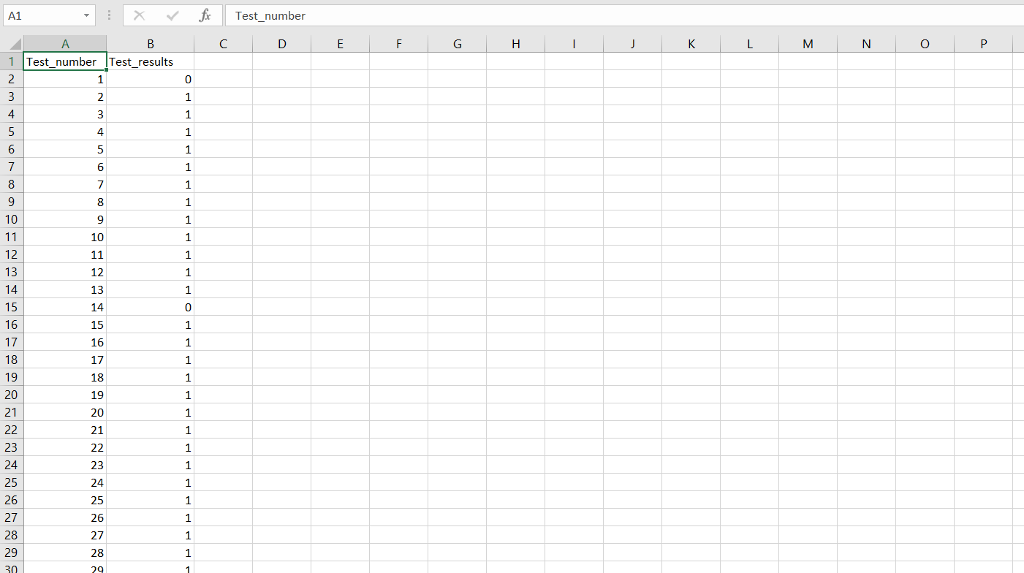
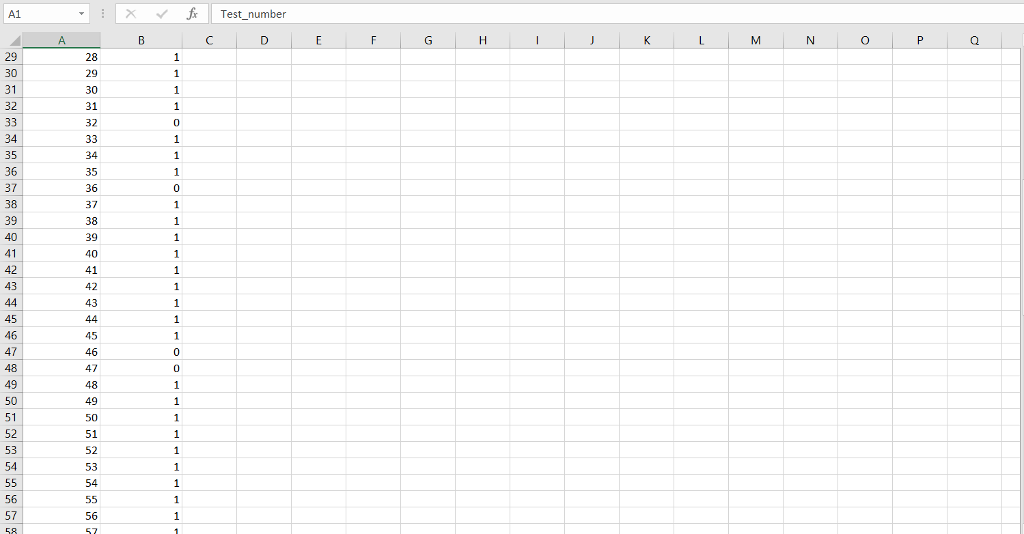
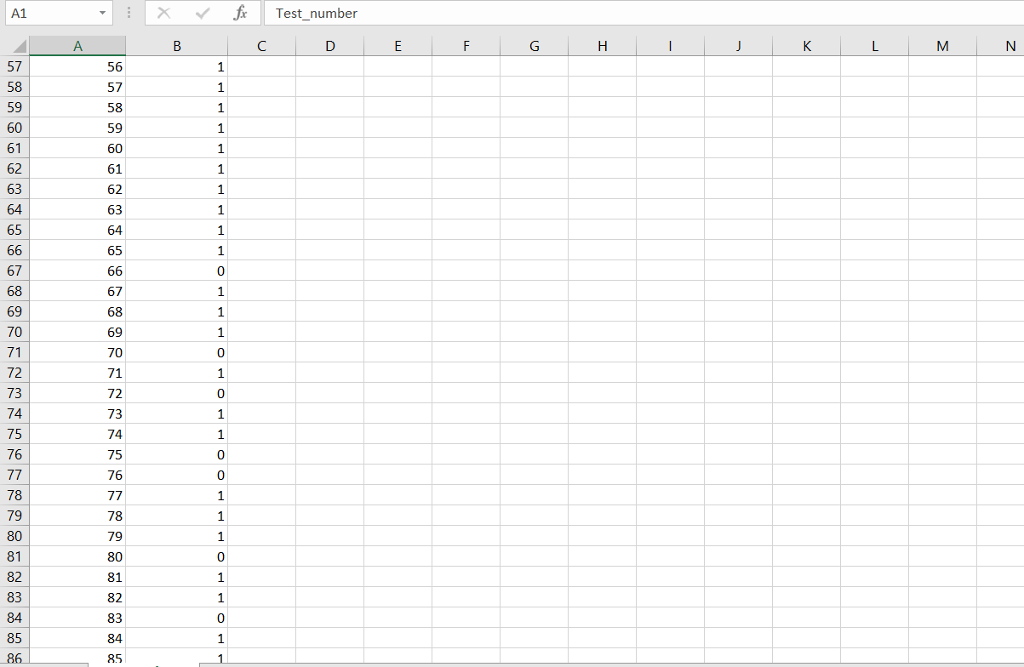
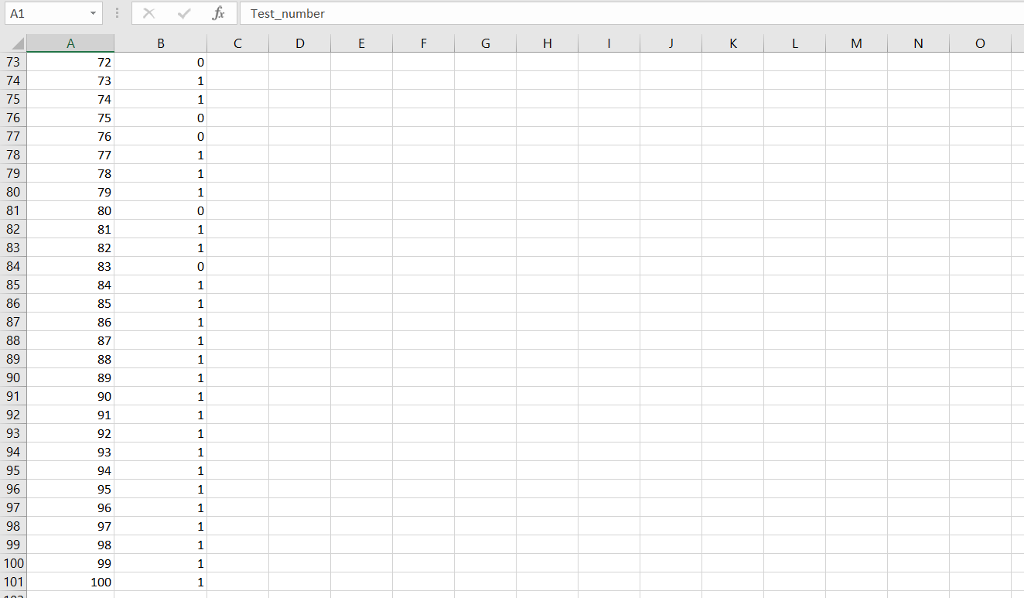
Input File:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


