Study the following output for Principal component analysis on "heptathlon" data and answer the following questions.
Output:
Importance of components:
PC1PC2PC3PC4PC5PC6
Standard deviation2.11191.09280.721810.676140.495240.27010
Proportion of Variance0.63720.17060.074430.065310.035040.01042
Cumulative Proportion0.63720.80780.882230.947540.982580.99300
PC7
Standard deviation0.2214
Proportion of Variance0.0070
Cumulative Proportion1.0000
1) If you want to take into account almost 95% variability in the data then how many principal components will you choose?
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
2) Now if you use Kaiser's criterion of selecting optimal number of Principal components then how many principal components will you choose?
a)1 b) 2 c) 3 d) 4
3) In principal component analysis what is the angle between principal components'?
a)00 b) 450 c) 900 d) >450
4) In order to perform factor analysis on a dataset having dispersion matrix ?, we must have,
a) ? = I, b) ? ? I c) ? can be anything d) None.
5) What can you say about Promax and Varimax rotations in Factor Analysis?
a) Factors obtained in both rotation methods are orthogonal (perpendicular).
b) Factors obtained in both rotation methods are not orthogonal.
c) Factors obtained in Promax rotation are orthogonal whereas factors obtained in Varimax rotation are not.
d) Factors obtained in Varimax rotation are orthogonal whereas factors obtained in Promax rotation are not.
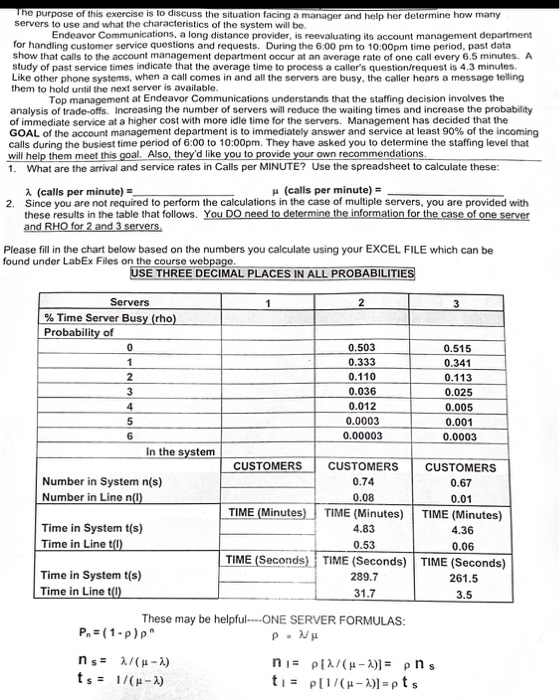
Remaining Time: 22 minutes, 27 seconds. Question Completion Status 0 0.01656 QUESTION 5 The service time for customers coming through a checkout counter has mean 1 5 minutes and variance 1 minutes. Find the probability that the average (mean) service time for 100 customers to get service will be less than 1 2 minutes. O 0.0017 O 0.0712 0 0,0028 0 0.0013 QUESTION 6 The following information represents age x.(In months) and weight y,(In lbs) of 12 children. 057After reading chapters 1 and 2, answer the following questions: 1. Give a concise and precise definition of economics? 2. Explain why it is necessary to study economics? 3. What are the two branches of economics? Explain their differences. 4. Define positiveormative economics and give an example of each. 5. Is resource limitation an economic problem for the United States and its citizens? 6. Name the four economic resources and their respective remuneration. 7. Why do economists disagree? Explain using normative and positive economics. 8. What is the importance of assumptions in the study of economics? Use a word-processing software, such as Microsoft Word, to type your assignments.The purpose of this exercise is to discuss the situation facing a manager and help her determine how many servers to use and what the characteristics of the system will be. Endeavor Communications, a long distance provider, is reevaluating its account management department for handling customer service questions and requests. During the 6:00 pm to 10:00pm time period, past data hat calls to the account management department occur at an average rate of one call every 6.5 minutes. A study of past service times indicate that the average time to process a caller's question/request is 4.3 minutes. Like other phone systems, when a call comes in and all the servers are busy, the caller hears a message telling them to hold until the next server is available Top management at Endeavor Communications understands that the staffing decision involves the analysis of trade-offs. Increasing the number of servers will reduce the waiting times and increase the probability of immediate service at a higher cost with more idle time for the servers. Management has decided that the GOAL of the account management department is to immediately answer and service at least 90% of the incoming calls during the busiest time period of 6:00 to 10:00pm. They have asked you to determine the staffing level that will help them meet this goal. Also, they'd like you to provide your own recommendations. 1. What are the arrival and service rates in Calls per MINUTE? Use the spreadsheet to calculate these: A. (calls per minute) = (calls per minute) = 2. Since you are not required to perform the calculations in the case of multiple servers, you are provided with these results in the table that follows. You DO need to determine the information for the case of one server and RHO for 2 and 3 servers, Please fill in the chart below based on the numbers you calculate using your EXCEL FILE which can be found under LabEx Files on the course webpage. USE THREE DECIMAL PLACES IN ALL PROBABILITIES Servers 2 3 % Time Server Busy (rho) Probability of 0.503 0.515 0.333 0.341 0.110 JAWN-O 0.113 0.036 0.025 0.012 0.005 0.0003 0.001 0.00003 0.0003 In the system CUSTOMERS CUSTOMERS CUSTOMERS Number in System n(s) 0.74 0.67 Number in Line n(0) 0.08 0.01 TIME (Minutes) TIME (Minutes) TIME (Minutes) Time in System t(s) 4.83 4.36 Time in Line t() 0.53 0.06 TIME (Seconds) TIME (Seconds) TIME (Seconds) Time in System ((s) 289.7 261.5 Time in Line t() 31.7 3.5 These may be helpful----ONE SERVER FORMULAS: Pa = (1-p)p P. Vu ns= 2/(p=1) ni= p[2/ (H-X)]= phs ts = 1/ (H-1) to= p[1/ (H-X)]=ptsb. A survey was conducted on 2000 people to nd their personality traits. Participants self- reported their personality traits from the three available traits \"extravert\Question 6 (1 point) Sarah's Texas location has a server that is starting to give her trouble. It is needing to be restarted frequently and seems to be very slow. The server is on the replacement schedule and has just overheated, stopped and will not restart. What plan should direct the recovery for this single server? Business impact analysis plan Business continuity plan Disaster recovery plan Recovery point plan