Subnet the given address space without VLSM You are asked to subnet the given network such that each network segment (subnet) has a block of
Subnet the given address space without VLSM
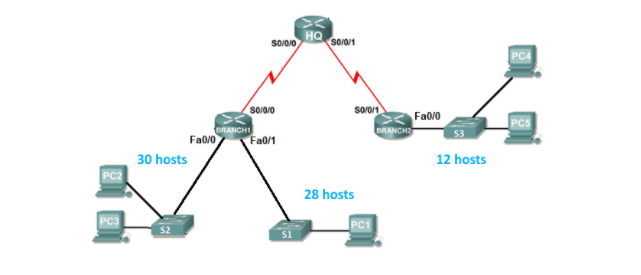

You are asked to subnet the given network such that each network segment (subnet) has a block of IPs that are on different networks. Routers separate subnets and are used to connect devices on different subnets.
Determine the #of subnets and custom subnet mask
-
How many bits to borrow to create the required # of subnets? (subnet bits, S):
-
Number of resulting subnets (max. # of subnets possible) = 2S =
-
After borrowing, each of the resulting subnets has:
-
# Network bits N = network bits + subnet bits =
-
# host bits H =
-
Number of usable hosts (host addresses) per subnet = 2H 2 =
-
Custom subnet mask (of resulting subnets):
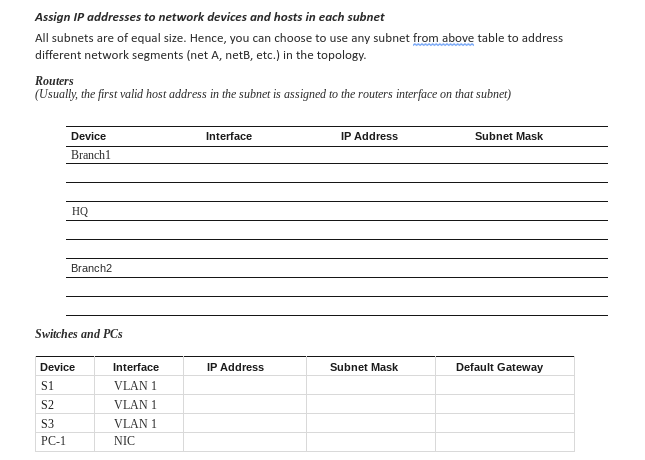
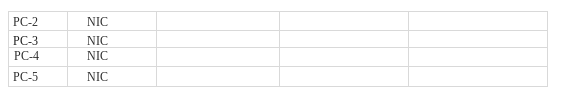
You will now subnet the given address space and allocate to the different network segments (subnets) in the topology. For convenience, you can name the network segments (subnets) as netA, netBetc. You can also choose numbers to identify the subnets, such as 1, 2, 3etc.
IP addressing scheme
Now that we have determined the subnet mark, the IP addressing mask, the network addressing scheme can be created. The addressing scheme includes the subnet numbers, the subnet broadcast address, and the range of IP addresses assignable to hosts.
Divide the address space in to the required number of subnets and complete the table below to show the address boundaries of each subnet.
You are asked to subnet the given network such that each network segment (subnet) has a block of IPs that are on different networks. Routers separate subnets and are used to connect devices on different subnets.
Determine the #of subnets and custom subnet mask
-
How many bits to borrow to create the required # of subnets? (subnet bits, S):
-
Number of resulting subnets (max. # of subnets possible) = 2S =
-
After borrowing, each of the resulting subnets has:
-
# Network bits N = network bits + subnet bits =
-
# host bits H =
-
Number of usable hosts (host addresses) per subnet = 2H 2 =
-
Custom subnet mask (of resulting subnets):
You will now subnet the given address space and allocate to the different network segments (subnets) in the topology. For convenience, you can name the network segments (subnets) as netA, netBetc. You can also choose numbers to identify the subnets, such as 1, 2, 3etc.

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


