Question
Sudoku Solver Question Example of Sudoku puzzle (not exact one that will be solved) INTRODUCTION: Sudoku is just a puzzle, but the backtracking technique for
Sudoku Solver Question
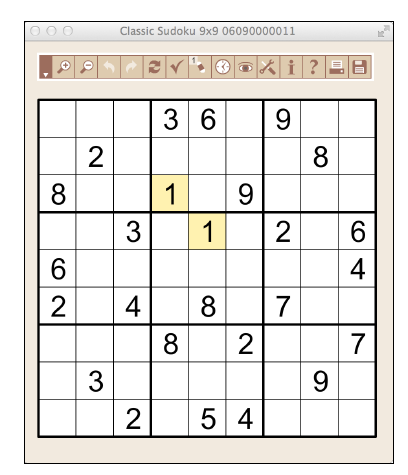
Example of Sudoku puzzle (not exact one that will be solved)
INTRODUCTION: Sudoku is just a puzzle, but the backtracking technique for solving it is used in many important application domains. To solve a Sudoku without backtracking, you could generate every possible solution, then evaluate all of them and collect the legal ones. But there are 9^81 ways to fill in a Sudoku grid. 9^81 is ~= 2*10^77. If you could evaluate a billion grids per second, it would take 2*10^68 seconds. The universe is less than 10^18 seconds old. For this homework, you will learn the power of backtracking by writing a Sudoku solver that finds answers in just a few seconds.
SUDOKU Rules: A puzzle looks like the one on the previous page: a 9x9 grid with some numbers filled in. The challenge is to fill in each empty space with a digit 1 through 9, so that no digit is repeated in any row, column or block. Block is my name for the nine 3x3 blocks outlined in thicker black lines in the picture.
Your Assignment: In the Eclipse workspace of your choice, create a new Java project containing package sudoku. Import the 4 starter files that you downloaded with this assignment: Evaluation.java, Grid.java, Solver.java, and TestGridSupplier.java. You won't need to change Evaluation.java or TestGridSupplier.java. Your assignment is to finish Grid.java and Solver.java.
Grid: This class models a Sudoku puzzle that is unsolved, partially solved, or completely solved. The class has a 9x9 array of ints, called values. If a Sudoku square is empty, the corresponding cell in values is zero; otherwise the cell in values contains the number in the Sudoku square. The starter class has a ctor and a toString() method that you should not change. It also has 4 empty methods that you need to write: next9Grids(), isLegal(), isFull(), and equals(). Do not change their names, arg lists, or return types. The comments on the unfinished methods tell you all you need to know about what they should do. Its ok to add more methods to this class.
You dont need to provide this class with hashCode() or compareTo() methods. The equals() method is just so that you can compare your puzzle solutions to solutions in TestGridSupplier. (That is, you wont be collecting Grid instances into a hash set a tree set.)
Solver: Most of this class has already been written. Complete the solveRecurse() method using the backtracking technique you saw in lecture and lab. Also complete the evaluate() method. The main() method is for you to use while testing your code with the puzzles and solutions in TestGridSupplier.
Evaluation: You saw this enum in lecture and lab. It contains 3 values that represent the 3 possible outcomes of the evaluate() method of the Grid class. Look at the source code. Sometimes enums can be complicated, but this one is not. You might need to write a simple enum for the next midterm.
TestGridSupplier: This class contains static methods that return Grid instances. Some of them are puzzles, some are solutions, and some are for testing your code.
STRATEGY: Plan your work before you start. The Solver class needs the Grid class to be working properly, so start with Grid. First write the simple methods isFull(), and equals(). Add a main method that tests these methods with instances from TestGridSupplier. If you get unexpected results, use the debugger or println statements to step through your code and see exactly where the problem is. Then write isLegal(), which is complicated. Youll have to check 9 rows, 9 columns, and 9 blocks. You might write a method called containsNonZeroRepeat(), whose input is an array of 9 ints. For each row, column, and block, build and array of 9 ints, containing the values in that row/col/block; then let containsNonZeroRepeat() figure out if your grid is legal or illegal.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Grid.java
package sudoku;
import java.util.*;
public class Grid { private int[][] values;
// // DON'T CHANGE THIS. // // Constructs a Grid instance from a string[] as provided by TestGridSupplier. // See TestGridSupplier for examples of input. // Dots in input strings represent 0s in values[][]. // public Grid(String[] rows) { values = new int[9][9]; for (int j=0; j
// // DON'T CHANGE THIS. // public String toString() { String s = ""; for (int j=0; j
// // DON'T CHANGE THIS. // Copy ctor. Duplicates its source. Youll call this 9 times in next9Grids. // Grid(Grid src) { values = new int[9][9]; for (int j=0; j
// // COMPLETE THIS // // // Finds an empty member of values[][]. Returns an array list of 9 grids that look like the current grid, // except the empty member contains 1, 2, 3 .... 9. Returns null if the current grid is full. Dont change // this grid. Build 9 new grids. // // // Example: if this grid = 1........ // ......... // ......... // ......... // ......... // ......... // ......... // ......... // ......... // // Then the returned array list would contain: // // 11....... 12....... 13....... 14....... and so on 19....... // ......... ......... ......... ......... ......... // ......... ......... ......... ......... ......... // ......... ......... ......... ......... ......... // ......... ......... ......... ......... ......... // ......... ......... ......... ......... ......... // ......... ......... ......... ......... ......... // ......... ......... ......... ......... ......... // ......... ......... ......... ......... ......... // public ArrayList
// Find x,y of an empty cell.
// Construct array list to contain 9 new grids. ArrayList
// Create 9 new grids as described in the comments above. Add them to grids.
return grids; }
// // COMPLETE THIS // // Returns true if this grid is legal. A grid is legal if no row, column, or // 3x3 block contains a repeated 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9. // public boolean isLegal() { // Check every row. If you find an illegal row, return false.
// Check every column. If you find an illegal column, return false.
// Check every block. If you find an illegal block, return false.
// All rows/cols/blocks are legal. return true; }
// // COMPLETE THIS // // Returns true if every cell member of values[][] is a digit from 1-9. // public boolean isFull() {
}
// // COMPLETE THIS // // Returns true if x is a Grid and, for every (i,j), // x.values[i][j] == this.values[i][j]. // public boolean equals(Object x) {
} }
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Solver.java
package sudoku;
import java.util.*;
public class Solver { private Grid problem; private ArrayList
public Solver(Grid problem) { this.problem = problem; }
public void solve() { solutions = new ArrayList(); solveRecurse(problem); }
// // FINISH THIS. // // Standard backtracking recursive solver. // private void solveRecurse(Grid grid) { Evaluation eval = evaluate(grid);
if (eval == Evaluation.ABANDON) { // Abandon evaluation of this illegal board. } else if (eval == Evaluation.ACCEPT) { // A complete and legal solution. Add it to solutions. } else { // Here if eval == Evaluation.CONTINUE. Generate all 9 possible next grids. Recursively // call solveRecurse() on those grids. } }
// // COMPLETE THIS // // Returns Evaluation.ABANDON if the grid is illegal. // Returns ACCEPT if the grid is legal and complete. // Returns CONTINUE if the grid is legal and incomplete. // public Evaluation evaluate(Grid grid) {
}
public ArrayList
public static void main(String[] args) { Grid g = TestGridSupplier.getPuzzle1(); // or any other puzzle Solver solver = new Solver(g); System.out.println(Will solve + g); solver.solve();
// Print out your solution, or test if it equals() the solution in TestGridSupplier. } }
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Evaluation.java
package sudoku;
enum Evaluation { ACCEPT, ABANDON, CONTINUE; }
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
TestGridSupplier.java
package sudoku;
// // All puzzles modeled here are copyright 2016. //
public class TestGridSupplier { // // A simple puzzle and its solution. Took less than 1 second on my MacBook Pro. // private final static String[] PUZZLE_1 = { "..3.1.5..", "8..395..1", "15.....27", ".8..7..5.", "62.9.4.13", ".9..2..7.", "91.....34", "2..748..9", "..6.3.2.." };
private final static String[] SOLUTION_1 = { "463217598", "872395641", "159486327", "384671952", "627954813", "591823476", "918562734", "235748169", "746139285" };
static Grid getPuzzle1() { return new Grid(PUZZLE_1); } static Grid getSolution1() { return new Grid(SOLUTION_1); }
private final static String[] PUZZLE_2 = { ".........", "8.1...9.7", "..75493..", "7..9.2..8", "....1....", "1..3.8..5", "..84312..", "2.5...1.9", "........." };
private final static String[] SOLUTION_2 = { "439187562", "851623947", "627549381", "763952418", "582714693", "194368725", "978431256", "245876139", "316295874" };
static Grid getPuzzle2() { return new Grid(PUZZLE_2); } static Grid getSolution2() { return new Grid(SOLUTION_2); }
private final static String[] PUZZLE_3 = { ".97..1.6.", "2....7..5", "....9...3", "85.......", "..9...5..", ".......32", "3...7....", "5..6....1", ".4.1..37." };
private final static String[] SOLUTION_3 = { "497351268", "236847195", "185296743", "853924617", "629713584", "714568932", "361472859", "578639421", "942185376" };
static Grid getPuzzle3() { return new Grid(PUZZLE_3); } static Grid getSolution3() { return new Grid(SOLUTION_3); }
// // You can use these to test your Grid's evaluate() method. // private final static String[] REJECT_1 = { "11.......", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", "........." };
private final static String[] REJECT_2 = { "2........", "2........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", "........." };
private final static String[] REJECT_3 = { "3........", "..3......", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", "........." };
private final static String[] REJECT_4 = { ".........", ".........", ".........", "....4....", ".....4...", ".........", ".........", ".........", "........." };
private final static String[] CONTINUE = { "123456789", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", ".........", "........." };
static Grid getReject1() { return new Grid(REJECT_1); } static Grid getReject2() { return new Grid(REJECT_2); } static Grid getReject3() { return new Grid(REJECT_3); } static Grid getReject4() { return new Grid(REJECT_4); } static Grid getContinue() { return new Grid(CONTINUE); } static Grid getAccept() { return getSolution1(); } }
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SudokuGrader.java
(used to check if code works, out of 100 points)
package sudoku;
import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.GridLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map;
import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JDialog; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JSlider; import javax.swing.JTextArea;
public class SudokuGrader { private final static Class>[] EMPTY_ARGSLIST = { }; private final static Class>[] OBJECT_ARGSLIST = { Object.class }; private final static Class>[] Grid_ARGSLIST = { Grid.class }; //private final static String PACKAGE = "sudokusolution"; private final static String PACKAGE = "sudoku";
private String gradersNotes; private int commentDeduction; private int styleDeduction; private Map
private enum Category { // For each category, student can't lose > maxDeductions. // Grid evaluation Grid(45), next9Grids(15), isLegal(10), isFull(10), equals(10), // Solver evaluation evaluate(10), Solver(35), // Comments and style Style(5), Comments(5);
private int maxDeductions;
Category(int maxDeductions) { this.maxDeductions = maxDeductions; }
int getMaxDeductions() { return maxDeductions; } }
private void grade() { gradeGrid(); gradeSolver(); testSubjective(); int score = 100; for (Category cat: catToDeductions.keySet()) { if (cat == Category.Style || cat == Category.Comments) continue; ArrayList
public void gradeGrid() { String err; Class> className = getClass(PACKAGE + ".Grid"); if (className == null) { sop("No Grid Class"); } //check the return type of "isLegal","isFull","next9Grids" methods String[] methodNames = {"isLegal","isFull","next9Grids"}; for (String name: methodNames) { try { Method m = className.getDeclaredMethod(name, EMPTY_ARGSLIST); if (name.equals("next9Grids")) { if(!ArrayList.class.isAssignableFrom(m.getReturnType())) deduct(Category.Grid, name + "() does not return Arraylist", 10); } else if(name.equals("isLegal")) { if(m.getReturnType()!= boolean.class) { sop(m.getReturnType()); deduct(Category.Grid, name + "() does not return Boolean", 2); } } else if(name.equals("isFull")) { if(m.getReturnType()!= boolean.class) deduct(Category.Grid, name + "() does not return Boolean", 2); }
} catch (NoSuchMethodException x) { deduct(Category.Grid, "No " + name + "() method", 10); } // check if equal is present try { Method m = className.getDeclaredMethod("equals", OBJECT_ARGSLIST); if(m.getReturnType()!= boolean.class) deduct(Category.Grid, "equals() does not return Boolean", 2); } catch (NoSuchMethodException x) { deduct(Category.Grid, "No " + name + "() method", 10); } }
//check if the equals returns correct result Grid g1 = TestGridSupplier.getPuzzle1(); Grid g2 = TestGridSupplier.getPuzzle1(); // a grid which is having one String[] puzzleTestEqual = { "..3.1.5..", "8..395..1", "14.....27", ".8..7..5.", "62.9.4.13", ".9..2..7.", "91.....34", "2..748..9", "..6.3.2.." }; Grid g3 = new Grid(puzzleTestEqual); if(!g1.equals(g2)) { err = "equals returned false for the same Grid"; deduct(Category.Grid, err, 5); } if(g1.equals(g3)) { err = "equals returned true for the different Grid"; deduct(Category.Grid, err, 5); } // check if isLegal correct String[] puzzleTestisLegalRow = { "..3.3.5..", "8..395..1", "14.....27", ".8..7..5.", "62.9.4.13", ".9..2..7.", "91.....34", "2..748..9", "..6.3.2.." }; String[] puzzleTestisLegalCol = { "..3.1.5..", "8..395..1", "14.....27", ".8..7..5.", "62.9.4.13", ".9..2..7.", "91.....34", "2..748..9", "8.6.3.2.." }; if(!g1.isLegal()) { deduct(Category.Grid, "isLegal() does not return False for a correct Grid", 2); } if(new Grid(puzzleTestisLegalRow).isLegal()) { deduct(Category.Grid, "isLegal() returns True for an incorrect Grid", 2); } if(new Grid(puzzleTestisLegalCol).isLegal()) { deduct(Category.Grid, "isLegal() returns True for an incorrect Grid", 2); } //check for isFull String[] testisFull = { "463217598", "872395641", "159486327", "384671952", "627954813", "591823476", "918562734", "235748169", "746139285" }; if(g1.isFull()) { deduct(Category.Grid, "isFull() return True for an incomplete Grid", 3); } if(!new Grid(testisFull).isFull()) { deduct(Category.Grid, "isFull() return False for a complete Grid", 3); } //check size of the arrayList returned by next9Grids if(g1.next9Grids().size()!=9) { deduct(Category.Grid, "next9Grids() does not return Arraylist of size 9", 5); } } public void gradeSolver() { Class> className = getClass(PACKAGE + ".Solver"); if (className == null) { sop("No Solver Class"); } //check evaluate() Grid g1 = TestGridSupplier.getPuzzle1(); String[] puzzleTestisLegalRow = { "..3.3.5..", "8..395..1", "14.....27", ".8..7..5.", "62.9.4.13", ".9..2..7.", "91.....34", "2..748..9", "..6.3.2.." }; String[] puzzleTestisLegalCol = { "..3.1.5..", "8..395..1", "14.....27", ".8..7..5.", "62.9.4.13", ".9..2..7.", "91.....34", "8..748..9", "..6.3.2.." }; String[] puzzleTestisLegalGrid = { "3.3.1.5..", "8..395..1", "14.....27", ".8..7..5.", "62.9.4.13", ".9..2..7.", "91.....34", "8..748..9", "..6.3.2.." }; //String[] methodNames = {"evalute","solve"}; Grid g2 = new Grid(puzzleTestisLegalRow); Grid g3 =new Grid(puzzleTestisLegalCol); Grid g4 = new Grid(puzzleTestisLegalGrid); Grid g5 = TestGridSupplier.getSolution1(); try { Method m = className.getDeclaredMethod("evaluate", Grid_ARGSLIST); if (m.getReturnType() != Evaluation.class) { deduct(Category.Solver, "evaluate() does not return Evaluation", 5); } Solver s = new Solver(g1); if (s.evaluate(g1)==Evaluation.ABANDON) { deduct(Category.Solver, "evaluate() returns ABANDON for a legal Grid", 5); } if (s.evaluate(g2)!=Evaluation.ABANDON ||s.evaluate(g3)!=Evaluation.ABANDON||s.evaluate(g4)!=Evaluation.ABANDON ) { deduct(Category.Solver, "evaluate() does not return ABANDON for an illegal Grid", 5); } if(s.evaluate(g5)!=Evaluation.ACCEPT ) { deduct(Category.Solver, "evaluate() does not return ACCEPT for a full Grid", 5); } if(s.evaluate(g1)==Evaluation.ACCEPT ) { deduct(Category.Solver, "evaluate() return ACCEPT for an incomplete Grid", 5); } } catch (NoSuchMethodException x) { deduct(Category.Solver, "No evaluate() method", 10); } // check for solver class Grid g = TestGridSupplier.getPuzzle1(); Solver solver = new Solver(g); solver.solve(); Grid soln = solver.getSolutions().get(0); if(!soln.equals(TestGridSupplier.getSolution1())) { deduct(Category.Solver, "Solve does not give correct solution", 35); } } private class Deduction { private String reason; private int pointsOff;
Deduction(String reason, int pointsOff) { this.reason = reason; this.pointsOff = pointsOff; }
public String toString() { return reason + ": -" + pointsOff; } } private void deduct(Category cat, String reason, int pointsOff) { ArrayList
private Class> getClass(String name) { if (!name.startsWith(PACKAGE)) name = PACKAGE + "." + name; try { return Class.forName(name); } catch (ClassNotFoundException x) { return null; } } private static void sop(Object x) { System.out.println(x); } private void testSubjective() { SubjectiveDialog dia = new SubjectiveDialog(); dia.setModal(true); dia.setVisible(true);
gradersNotes = dia.getSubjectivePanel().getNotes(); int readabilityScore = dia.getSubjectivePanel().getReadabilityScore(); styleDeduction = Category.Style.getMaxDeductions() - readabilityScore; int commentsScore = dia.getSubjectivePanel().getCommentsScore(); commentDeduction = Category.Comments.getMaxDeductions() - commentsScore; }
private class SubjectivePanel extends JPanel { private ArrayList
SubjectivePanel() { sliders = new ArrayList(); setLayout(new BorderLayout()); setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 3)); Category[] cats = { Category.Style, Category.Comments }; for (Category cat: cats) { JPanel pan = new JPanel(new BorderLayout()); pan.add(new JLabel(cat.name()), BorderLayout.NORTH); JSlider slider = new JSlider(0, cat.getMaxDeductions(), cat.getMaxDeductions()); slider.setMajorTickSpacing(1); slider.setPaintTicks(true); slider.setPaintLabels(true); slider.setSnapToTicks(true); pan.add(slider, BorderLayout.SOUTH); sliders.add(slider); add(pan); } notesTA = new JTextArea(10, 25); JPanel commentsPan = new JPanel(new BorderLayout()); commentsPan.add(new JLabel("Your notes"), BorderLayout.NORTH); commentsPan.add(notesTA, BorderLayout.CENTER); add(commentsPan); }
int getReadabilityScore() { return sliders.get(0).getValue(); }
int getCommentsScore() { return sliders.get(1).getValue(); }
String getNotes() { return notesTA.getText().trim(); } }
private class SubjectiveDialog extends JDialog implements ActionListener { private SubjectivePanel subjPan;
SubjectiveDialog() { subjPan = new SubjectivePanel(); add(subjPan, BorderLayout.CENTER); JPanel okPan = new JPanel(); JButton okBtn = new JButton("Ok"); okBtn.addActionListener(this); okPan.add(okBtn); add(okPan, BorderLayout.SOUTH); pack(); }
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { setVisible(false); }
SubjectivePanel getSubjectivePanel() { return subjPan; } } public static void main(String[] args) { /ew Grader().testSubjective(); new SudokuGrader().grade(); } }
Classic Sudoku 9x9 06090000011 3 6 9 2 8 3126 4 6 2 487 3 Classic Sudoku 9x9 06090000011 3 6 9 2 8 3126 4 6 2 487 3Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


