Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Summarize this information in a paragraph. Can be as many sentences as needed. Electrical current is the movement of electric charge carriers through any material,
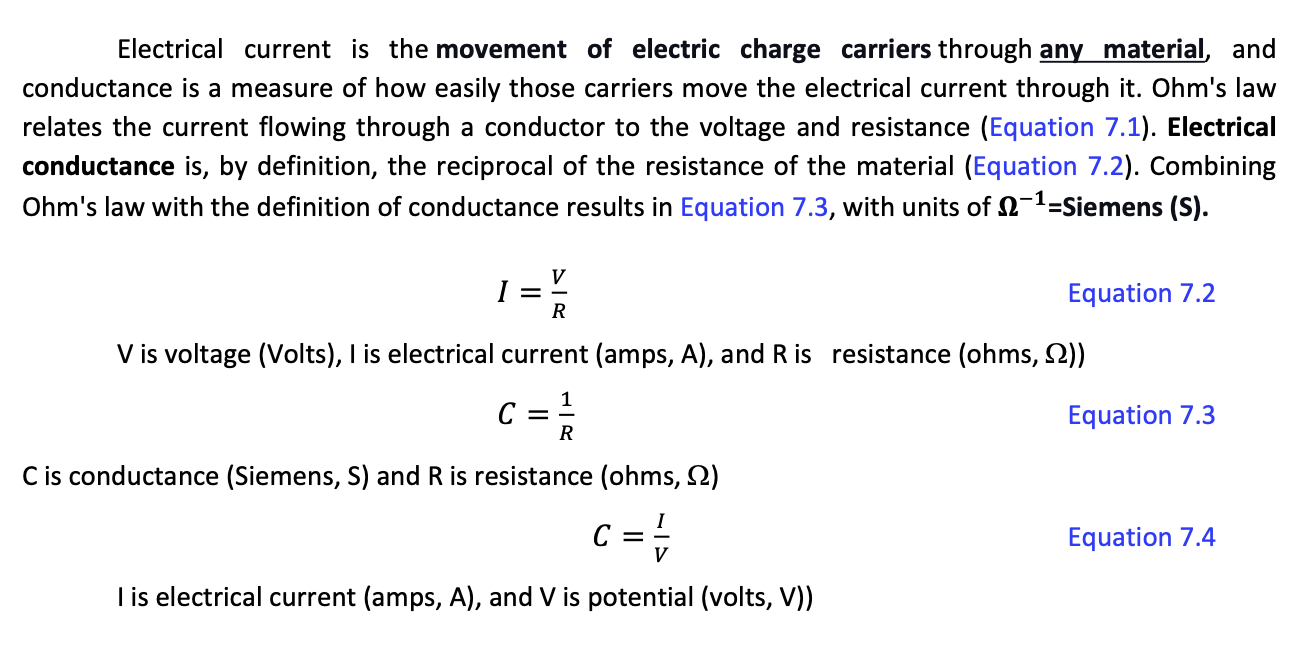

Summarize this information in a paragraph.
Can be as many sentences as needed.
Electrical current is the movement of electric charge carriers through any material, and conductance is a measure of how easily those carriers move the electrical current through it. Ohm's law relates the current flowing through a conductor to the voltage and resistance (Equation 7.1). Electrical conductance is, by definition, the reciprocal of the resistance of the material (Equation 7.2). Combining Ohm's law with the definition of conductance results in Equation 7.3, with units of 1= Siemens (S). I=RV Equation 7.2 V is voltage (Volts), I is electrical current (amps, A), and R is resistance (ohms, )) C=R1 Equation 7.3 C is conductance (Siemens, S) and R is resistance (ohms, ) C=VI Equation 7.4 I is electrical current (amps, A), and V is potential (volts, V)) What does all this have to do with aqueous solutions? Electrolytic Conductivity, also called Conductivity, are synonymous terms specifically associated with the ability of solutions, mainly aqueous, to carry electrical current. In a metal wire, the charge carriers are electrons, and the electric current measures the quantity of charge passing any point of the wire per unit of time. Pure liquid water (H2O) molecules are essentially electrically neutral and, therefore, a very poor conductor of electricity (re-read pages 15 and 16 in this Manual). However, even micrograms-per-liter of dissolved ionic compounds give water electrolytic conductor properties; therefore, a current measured in an aqueous solution is evidence of the presence of dissolved ions. The basic design principle of Conductivity measuring devices consists of applying an A.C. voltage to two electrodes separated by a fixed distance and measuring the resulting current through a volume of solution located between them (Figure 7.1 a); that is, the solution acts as a resistance in the circuit. More advanced conductivity cells use four electrodes (Figure 7.1 b). Electrolytic conductivity depends on the cell geometry (the area of the electrodes and the distance between them); for this reason, commercial devices are standardized internally using a "cell constant." The cell constant is equal to the space in cm between the probe's electrodes divided by the surface area of the electrodes in cm2. The product of Electrolytic conductivity (E.C.) by the cell constant (1/cm) is called Electrolytic Conductivity or Conductivity and it has units of Siemens-per-unit of length (S/m or S/cm, and other). The USGS (2019) states that "Specific Conductance" is correctly defined as the electrical conductance of 1 cubic centimeter of a solution at 25C. If the electrical conductance is measured at another temperature, the value is corrected to what it would be at 25C and reported as Specific Conductance at 25CStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


