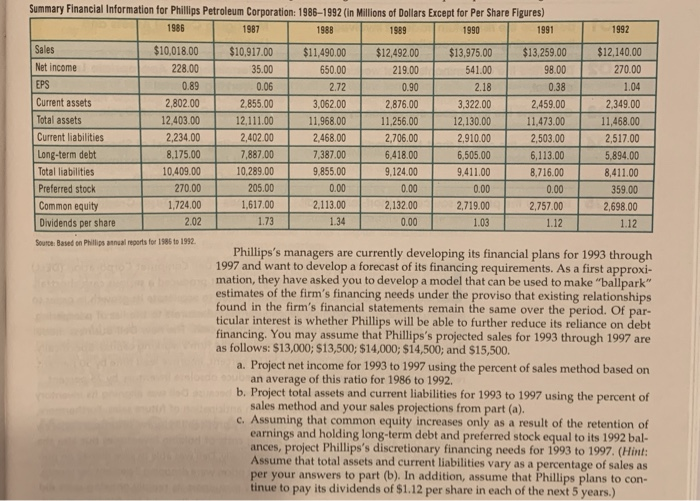
Summary Financial Information for Phillips Petroleum Corporation: 1986-1992 (in Millions of dollars Except for Per Share Figures) 1986 1987 I 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 Sales $10,018.00 $10,917.00 $11.490.00 $12.492.00 $13,975.00 $13,259.00 $12,140.00 Net income 228.00 35.00 650.00 219.00 541.00 98.00 270.00 EPS 0.89 0.06 2.72 0.90 2.18 0.38 1.04 Current assets 2,802.00 2.855.00 3,062.00 2,876.00 3,322.00 2,459.00 2,349.00 Total assets 12,403.00 12,111.00 11,968.00 11.256.00 12,130.00 11,473.00 11,468.00 Current liabilities 2,234.00 2,402.00 2,468.00 2,706.00 2,910.00 2,503.00 2,517.00 Long-term debt 8,175.00 7,887.00 7,387.00 6.418.00 6,505.00 6,113.00 5.894.00 Total liabilities 10,409.00 10,289.00 9,855.00 9,124.00 9,411.00 8.716.00 8,411.00 Preferred stock 270.00 205. 00 0 . 00 0 .00 0.00 0.00 359.00 Common equity 1,724.00 1.617.00 2,113.00 2,132.00 2,719.00 2,757.00 2.698.00 Dividends per share 2. 02 1 .73 1. 34 0 .00 1.03 1.12 1.12 Source Based on Phillips anual reports for 1986 to 1992 Phillips's managers are currently developing its financial plans for 1993 through 1997 and want to develop a forecast of its financing requirements. As a first approxi- mation, they have asked you to develop a model that can be used to make "ballpark" estimates of the firm's financing needs under the proviso that existing relationships found in the firm's financial statements remain the same over the period. Of par. ticular interest is whether Phillips will be able to further reduce its reliance on debt financing. You may assume that Phillips's projected sales for 1993 through 1997 are as follows: $13,000; $13,500, $14,000; $14,500; and $15,500. a. Project net income for 1993 to 1997 using the percent of sales method based on an average of this ratio for 1986 to 1992. b. Project total assets and current liabilities for 1993 to 1997 using the percent of sales method and your sales projections from part (a). c. Assuming that common equity increases only as a result of the retention of earnings and holding long-term debt and preferred stock equal to its 1992 bal- ances, project Phillips's discretionary financing needs for 1993 to 1997. (Hint: Assume that total assets and current liabilities vary as a percentage of sales as per your answers to part (b). In addition, assume that Phillips plans to con tinue to pay its dividends of $1.12 per share in each of the next 5 years.) Summary Financial Information for Phillips Petroleum Corporation: 1986-1992 (in Millions of dollars Except for Per Share Figures) 1986 1987 I 1988 1989 1990 1991 1992 Sales $10,018.00 $10,917.00 $11.490.00 $12.492.00 $13,975.00 $13,259.00 $12,140.00 Net income 228.00 35.00 650.00 219.00 541.00 98.00 270.00 EPS 0.89 0.06 2.72 0.90 2.18 0.38 1.04 Current assets 2,802.00 2.855.00 3,062.00 2,876.00 3,322.00 2,459.00 2,349.00 Total assets 12,403.00 12,111.00 11,968.00 11.256.00 12,130.00 11,473.00 11,468.00 Current liabilities 2,234.00 2,402.00 2,468.00 2,706.00 2,910.00 2,503.00 2,517.00 Long-term debt 8,175.00 7,887.00 7,387.00 6.418.00 6,505.00 6,113.00 5.894.00 Total liabilities 10,409.00 10,289.00 9,855.00 9,124.00 9,411.00 8.716.00 8,411.00 Preferred stock 270.00 205. 00 0 . 00 0 .00 0.00 0.00 359.00 Common equity 1,724.00 1.617.00 2,113.00 2,132.00 2,719.00 2,757.00 2.698.00 Dividends per share 2. 02 1 .73 1. 34 0 .00 1.03 1.12 1.12 Source Based on Phillips anual reports for 1986 to 1992 Phillips's managers are currently developing its financial plans for 1993 through 1997 and want to develop a forecast of its financing requirements. As a first approxi- mation, they have asked you to develop a model that can be used to make "ballpark" estimates of the firm's financing needs under the proviso that existing relationships found in the firm's financial statements remain the same over the period. Of par. ticular interest is whether Phillips will be able to further reduce its reliance on debt financing. You may assume that Phillips's projected sales for 1993 through 1997 are as follows: $13,000; $13,500, $14,000; $14,500; and $15,500. a. Project net income for 1993 to 1997 using the percent of sales method based on an average of this ratio for 1986 to 1992. b. Project total assets and current liabilities for 1993 to 1997 using the percent of sales method and your sales projections from part (a). c. Assuming that common equity increases only as a result of the retention of earnings and holding long-term debt and preferred stock equal to its 1992 bal- ances, project Phillips's discretionary financing needs for 1993 to 1997. (Hint: Assume that total assets and current liabilities vary as a percentage of sales as per your answers to part (b). In addition, assume that Phillips plans to con tinue to pay its dividends of $1.12 per share in each of the next 5 years.)