Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
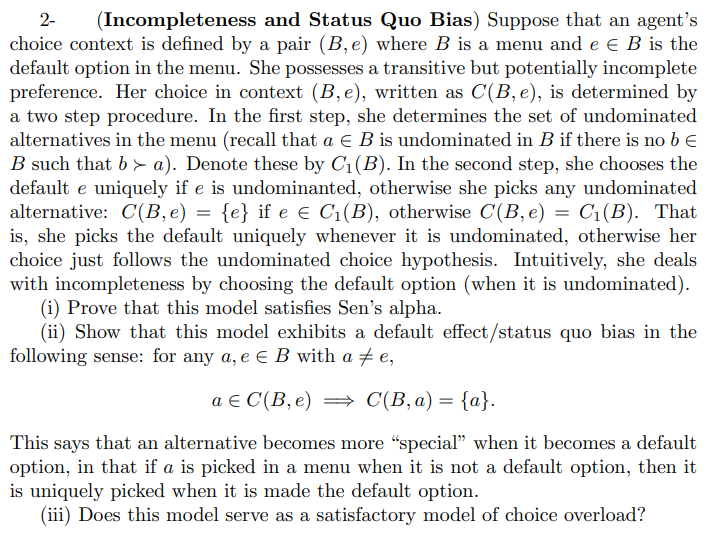
Suppose that an agent s 2 - ( Incompleteness and Status Quo Bias ) Suppose that an agent's choice context is defined by a pair
Suppose that an agentsIncompleteness and Status Quo Bias Suppose that an agent's
choice context is defined by a pair where is a menu and einB is the
default option in the menu. She possesses a transitive but potentially incomplete
preference. Her choice in context written as is determined by
a two step procedure. In the first step, she determines the set of undominated
alternatives in the menu recall that ainB is undominated in if there is no bin
such that Denote these by In the second step, she chooses the
default uniquely if is undominanted, otherwise she picks any undominated
alternative: if otherwise That
is she picks the default uniquely whenever it is undominated, otherwise her
choice just follows the undominated choice hypothesis. Intuitively, she deals
with incompleteness by choosing the default option when it is undominated
i Prove that this model satisfies Sen's alpha.
ii Show that this model exhibits a default effectstatus quo bias in the
following sense: for any einB with
ainC
This says that an alternative becomes more "special" when it becomes a default
option, in that if is picked in a menu when it is not a default option, then it
is uniquely picked when it is made the default option.
iii Does this model serve as a satisfactory model of choice overload?
choice context is defined by a pair B e where B is a menu and e in B is the
default option in the menu. She possesses a transitive but potentially incomplete
preference. Her choice in context B e written as CB e is determined by
a two step procedure. In the first step, she determines the set of undominated
alternatives in the menu recall that a in B is undominated in B if there is no b in
B such that b a Denote these by CB In the second step, she chooses the
default e uniquely if e is undominanted, otherwise she picks any undominated
alternative: CB ee if e in CB otherwise CB e CB That
is she picks the default uniquely whenever it is undominated, otherwise her
choice just follows the undominated choice hypothesis. Intuitively, she deals
with incompleteness by choosing the default option when it is undominated
i Prove that this model satisfies Sens alpha.
ii Show that this model exhibits a default effectstatus quo bias in the
following sense: for any a e in B with a e
a in CB e CB aa
This says that an alternative becomes more special when it becomes a default
option, in that if a is picked in a menu when it is not a default option, then it
is uniquely picked when it is made the default option.
iii Does this model serve as a satisfactory model of choice overload?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


