Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Suppose that during April, RiteAde produces 12,500 cases of powdered drink mix and sells 14,500 cases. Sale price, variable cost per case, and total fixed
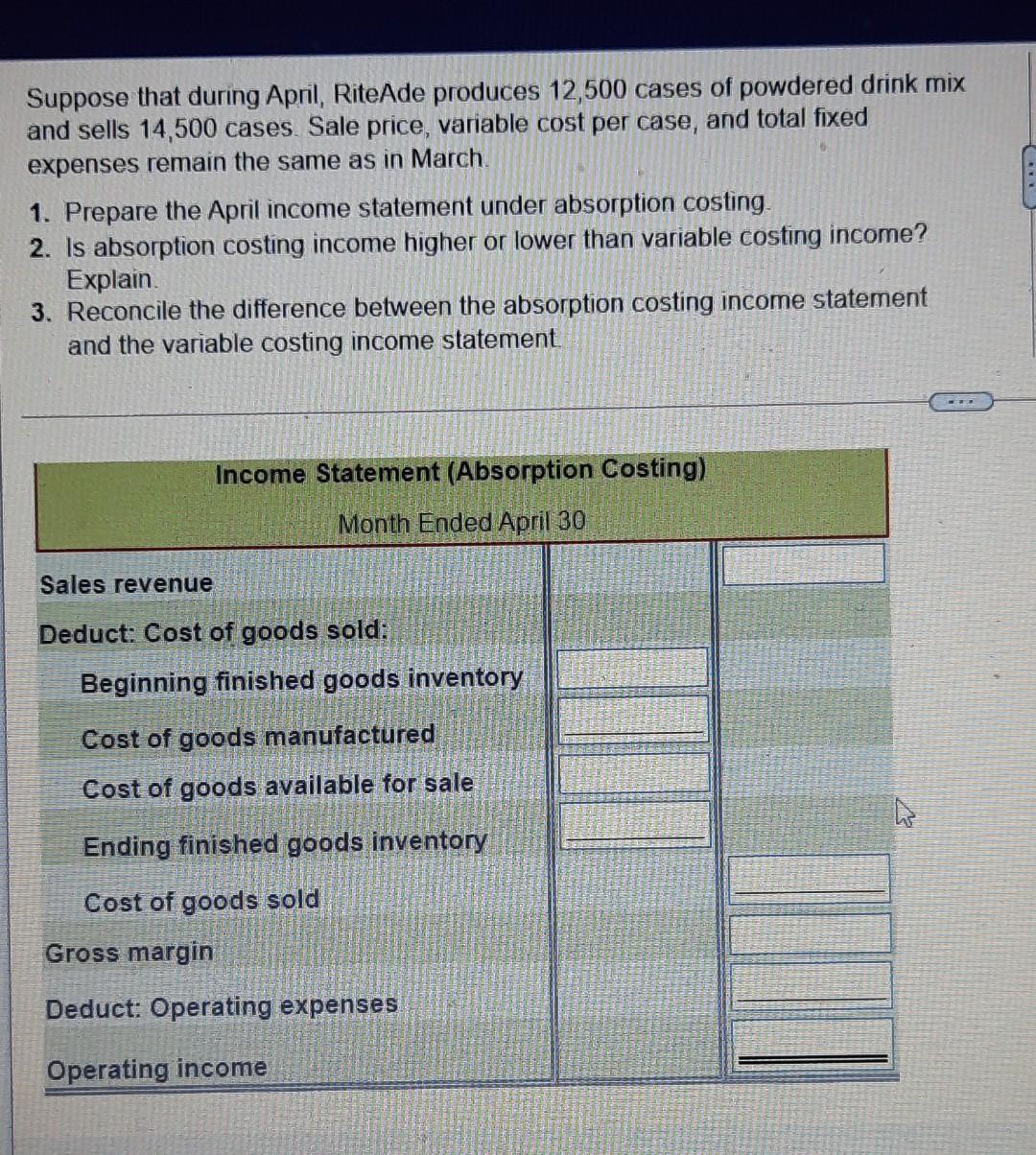
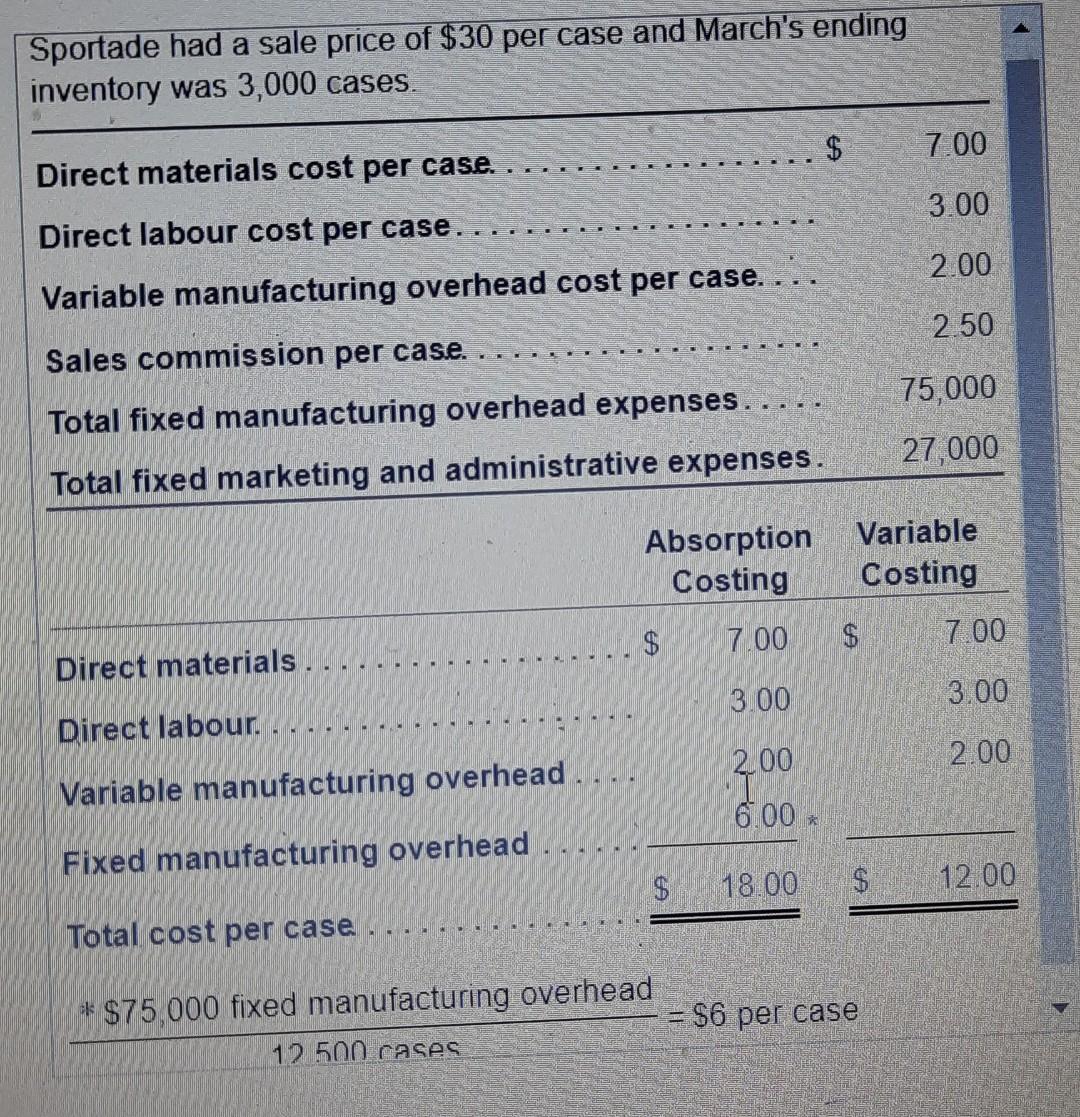
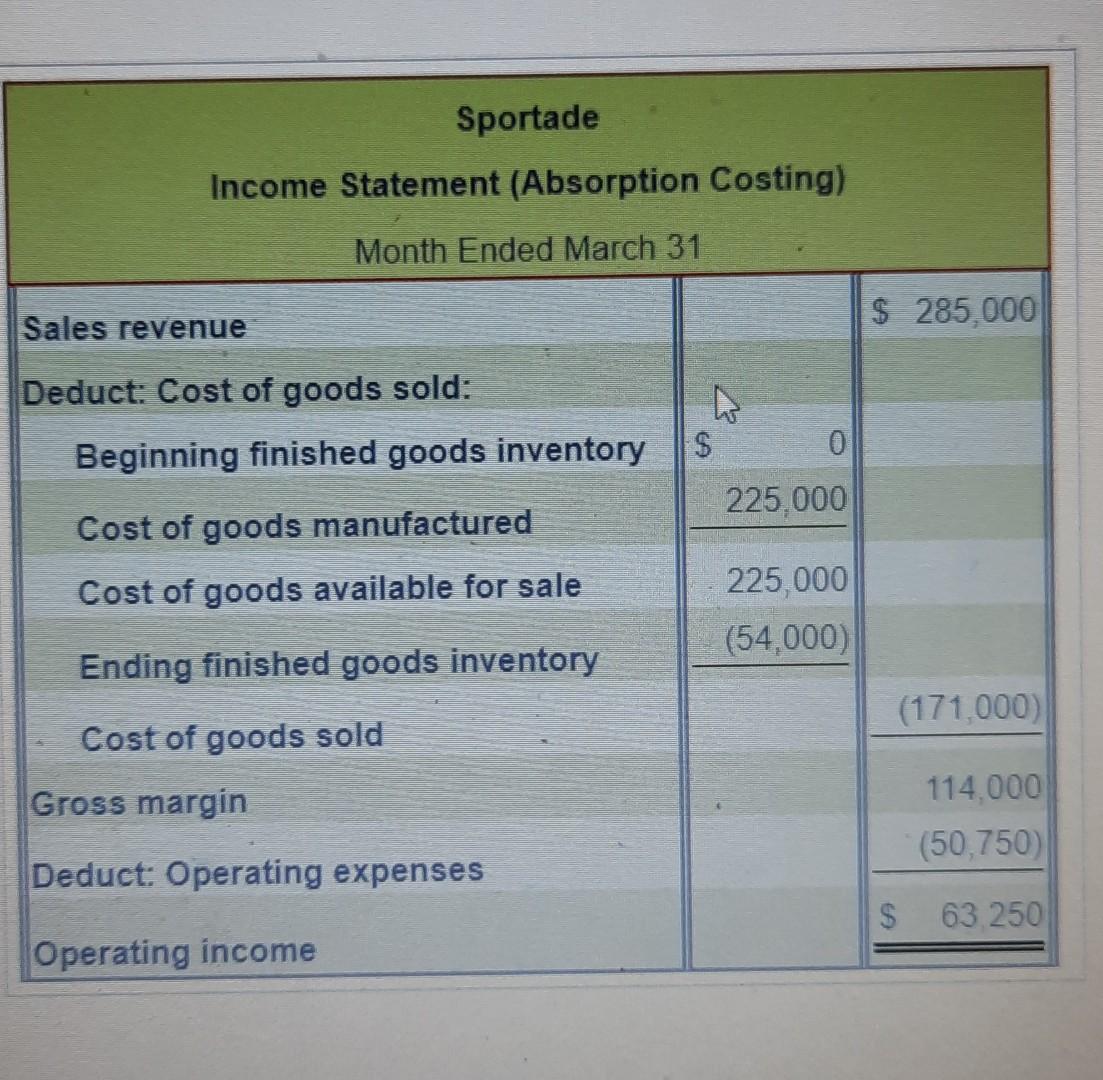
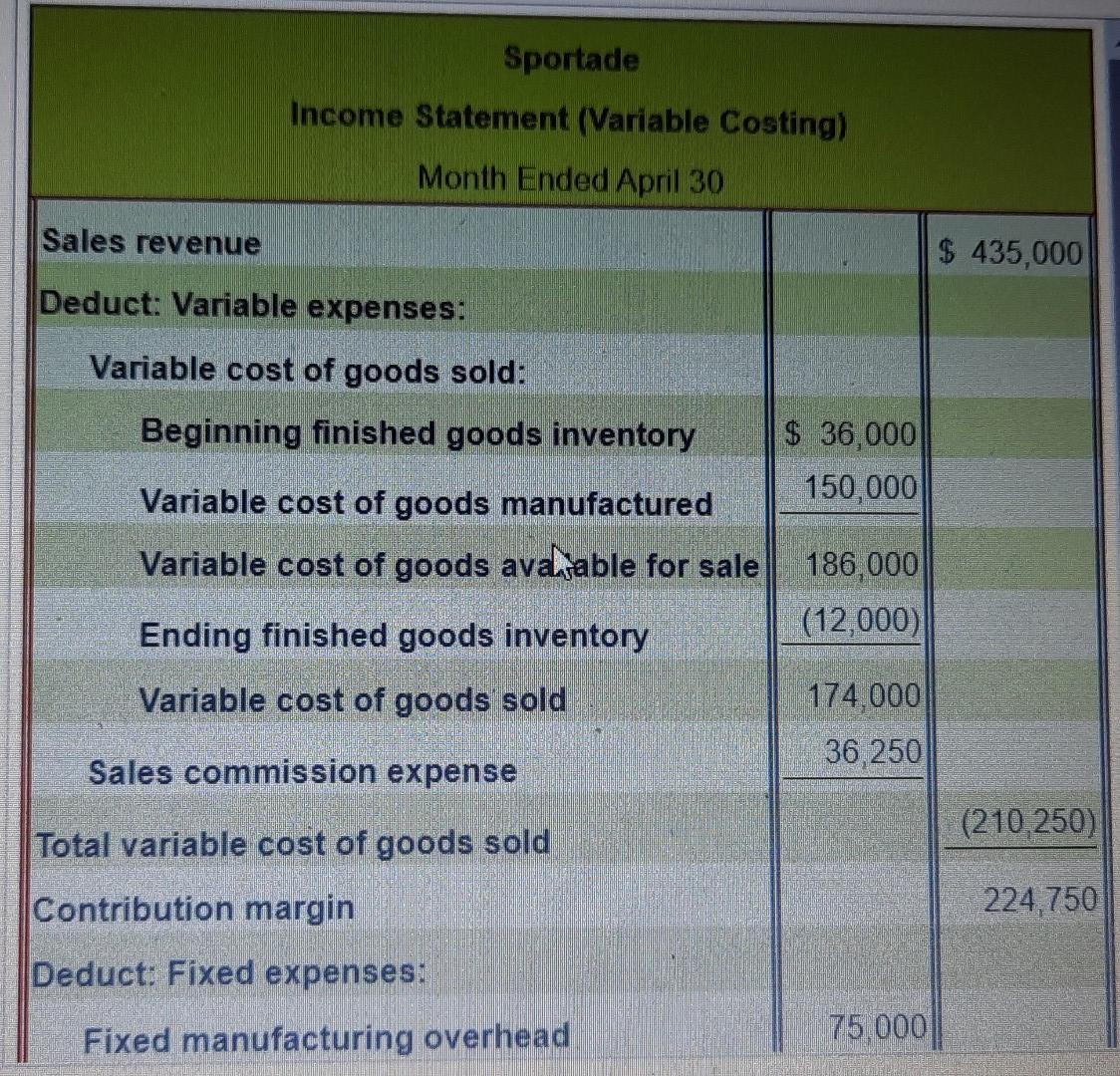
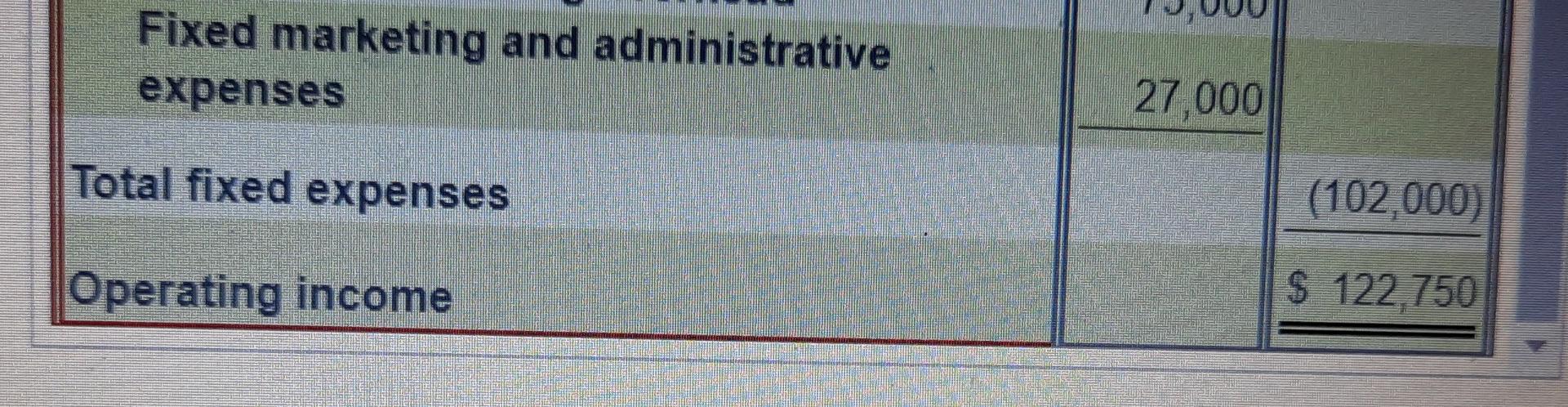
Suppose that during April, RiteAde produces 12,500 cases of powdered drink mix and sells 14,500 cases. Sale price, variable cost per case, and total fixed expenses remain the same as in March. 1. Prepare the April income statement under absorption costing. 2. Is absorption costing income higher or lower than variable costing income? Explain 3. Reconcile the difference between the absorption costing income statement and the variable costing income statement Income Statement (Absorption Costing) Month Ended April 30 Sales revenue Deduct: Cost of goods sold: Beginning finished goods inventory Cost of goods manufactured Cost of goods available for sale Ending finished goods inventory Cost of goods sold Gross margin Deduct: Operating expenses Operating income Sportade had a sale price of $30 per case and March's ending inventory was 3,000 cases. $ 7.00 Direct materials cost per case. 3.00 Direct labour cost per case. 2.00 Variable manufacturing overhead cost per case. 2.50 Sales commission per case. 75,000 KO Total fixed manufacturing overhead expenses. Total fixed marketing and administrative expenses. 27,000 Absorption Costing Variable Costing $ 7.00 $ 7.00 Direct materials. 3.00 3.00 Direct labour. 200 2.00 Variable manufacturing overhead 6.00 Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 18.00 $ 12.00 Total cost per case * $75,000 fixed manufacturing overhead = $6 per case 12.500 cases Sportade Income Statement (Absorption Costing) Month Ended March 31 Sales revenue $ 285,000 Deduct: Cost of goods sold: Beginning finished goods inventory S 0 225,000 Cost of goods manufactured Cost of goods available for sale 225,000 (54,000) Ending finished goods inventory (171,000) Cost of goods sold Gross margin 114.000 (50,750 Ded ct: Opera expenses $ 63 250 Operating income Sportade Income Statement (Variable Costing) Month Ended April 30 Sales revenue $ 435,000 Deduct: Variable expenses: Variable cost of goods sold: Beginning finished goods inventory $ 36,000 150,000 Variable cost of goods manufactured Variable cost of goods avahable for sale 186,000 (12,000) Ending finished goods inventory Variable cost of goods sold 174,000 Sales commission expense 36,250 (210,250) Total variable cost of goods sold Contribution margin 224,750 Deduct: Fixed expenses: Fixed manufacturing overhead 75 000 Fixed marketing and administrative expenses 27,000 Total fixed expenses (102,000) Operating income $ 122,750
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


