Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Suppose the cash flow in year 3 is only $416,000. Redraw Figure 8.3. How would the IRR change? figure 8-3: not excel form solution required.
 Suppose the cash flow in year 3 is only $416,000. Redraw Figure 8.3. How would the IRR change?
Suppose the cash flow in year 3 is only $416,000. Redraw Figure 8.3. How would the IRR change?
figure 8-3:
not excel form solution required.
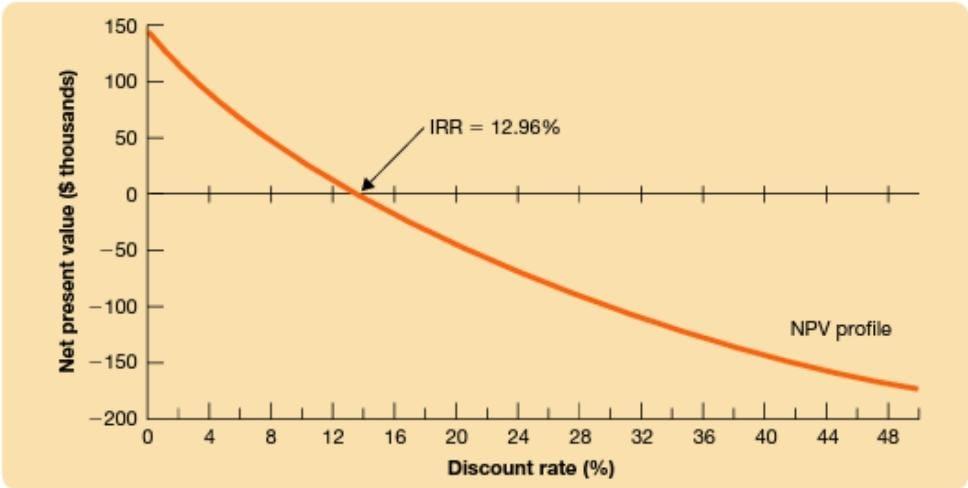
46 679 s #### 1827:55 Let's calculate the IRR for the revised office project. If you rent out the office block for 3 years, the cash flows are as follows: + + Year: 1 2 3 Cash flows -$350,000 +$16,000 +$15,000 +S465,000 The IRR is the discount rate at which these cash flows would have zero NPV. Thus, $16,000 NPV =-$350,000+ $16.000 $466,000 = 0 I+IRR. (1+IRR)2 (+ IRRY There is no simple general method for solving this equation. You have to rely on a little trial and error. Let us arbitrarily try a zero discount rate. This gives an NPV of S148,000: $16,000 $16.000 $466,000 NPV =-$350,000+ =$148,000 1.0 (1.0) (1.07 With a zero discount rate the NPV is positive. So the IRR must be greater than zero. The next step might be to try a discount rate of 50%. In this case NPV is -$194,000: NPV = -$350,000+ $16,000 $16,000 $466,000 = -5194,000 1.50 (1.50) (1.50) + + The investment in the project is therefore-G--(-$350,000), or $350.000 Text Net Present Value and Other Investment Criteria The McGraw-HR Companies 2009 Part Two Value 2 150 100 50 IRR - 12.95% 0 -50 -100 NPV profile - 150 150 -200 LLLLLLLL 0 4 8 12 16 32 36 40 44 48 20 24 28 Discount rate (%) NPV is now negative. So the IRR must lie somewhere between zero and 50%. In Figure 8-3 we have plotted the net present values for a range of discount rates. You can see that a discount rate of 12.96% gives an NPV of zero. Therefore, the IRR is 12.96%. You can always find the IRR by plotting an NPV profile, as in Figure 8-3, but it is quicker and more accurate to let a spreadsheet or specially programmed finan- cial calculator do the trial and error for you. The nearby boxes illustrate how to do so. The rate of return rule tells you to accept a project if the rate of return exceeds the opportunity cost of capital. You can see from Figure 8-3 why this makes Because the NPV profile is downward-sloping the project has a positive NPV a as the opportunity cost of capital is less than the project's 12.96% IRR. If the op nity cost of capital is higher than the 12.96% IRR, NPV is negative. Therefore we compare the project IRR with the opportunity cost of capital, we are effect asking whether the project has a positive NPV. This was true for our one-period office project. It is also true for our three-period office project. We conclude that the rate of 150 100 IRR = 12.96% 50 0 Net present value ($ thousands) -50 - -100 NPV profile -150 -200 0 4 8 12 16 32 36 40 44 48 20 24 28 Discount rate (%) 46 679 s #### 1827:55 Let's calculate the IRR for the revised office project. If you rent out the office block for 3 years, the cash flows are as follows: + + Year: 1 2 3 Cash flows -$350,000 +$16,000 +$15,000 +S465,000 The IRR is the discount rate at which these cash flows would have zero NPV. Thus, $16,000 NPV =-$350,000+ $16.000 $466,000 = 0 I+IRR. (1+IRR)2 (+ IRRY There is no simple general method for solving this equation. You have to rely on a little trial and error. Let us arbitrarily try a zero discount rate. This gives an NPV of S148,000: $16,000 $16.000 $466,000 NPV =-$350,000+ =$148,000 1.0 (1.0) (1.07 With a zero discount rate the NPV is positive. So the IRR must be greater than zero. The next step might be to try a discount rate of 50%. In this case NPV is -$194,000: NPV = -$350,000+ $16,000 $16,000 $466,000 = -5194,000 1.50 (1.50) (1.50) + + The investment in the project is therefore-G--(-$350,000), or $350.000 Text Net Present Value and Other Investment Criteria The McGraw-HR Companies 2009 Part Two Value 2 150 100 50 IRR - 12.95% 0 -50 -100 NPV profile - 150 150 -200 LLLLLLLL 0 4 8 12 16 32 36 40 44 48 20 24 28 Discount rate (%) NPV is now negative. So the IRR must lie somewhere between zero and 50%. In Figure 8-3 we have plotted the net present values for a range of discount rates. You can see that a discount rate of 12.96% gives an NPV of zero. Therefore, the IRR is 12.96%. You can always find the IRR by plotting an NPV profile, as in Figure 8-3, but it is quicker and more accurate to let a spreadsheet or specially programmed finan- cial calculator do the trial and error for you. The nearby boxes illustrate how to do so. The rate of return rule tells you to accept a project if the rate of return exceeds the opportunity cost of capital. You can see from Figure 8-3 why this makes Because the NPV profile is downward-sloping the project has a positive NPV a as the opportunity cost of capital is less than the project's 12.96% IRR. If the op nity cost of capital is higher than the 12.96% IRR, NPV is negative. Therefore we compare the project IRR with the opportunity cost of capital, we are effect asking whether the project has a positive NPV. This was true for our one-period office project. It is also true for our three-period office project. We conclude that the rate of 150 100 IRR = 12.96% 50 0 Net present value ($ thousands) -50 - -100 NPV profile -150 -200 0 4 8 12 16 32 36 40 44 48 20 24 28 Discount rate (%)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


