Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
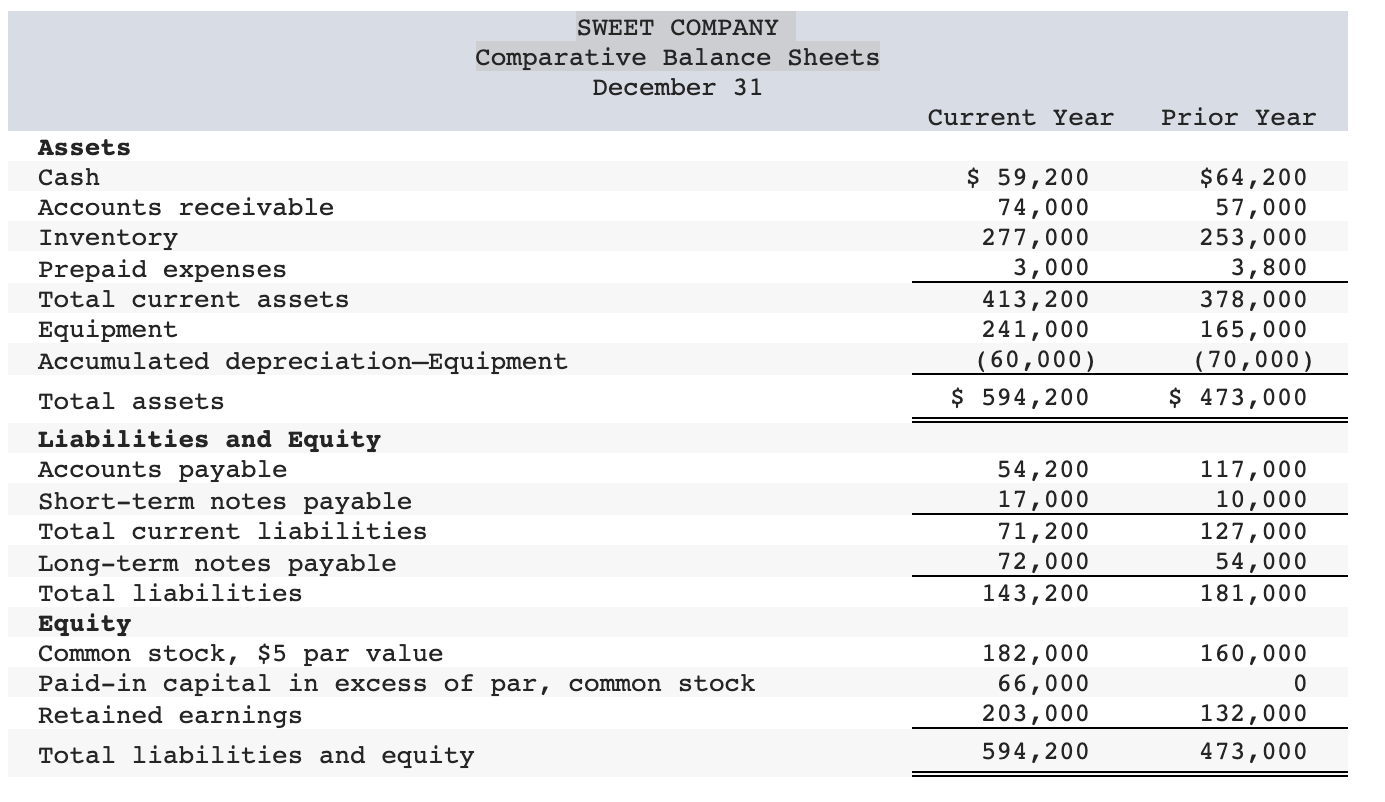
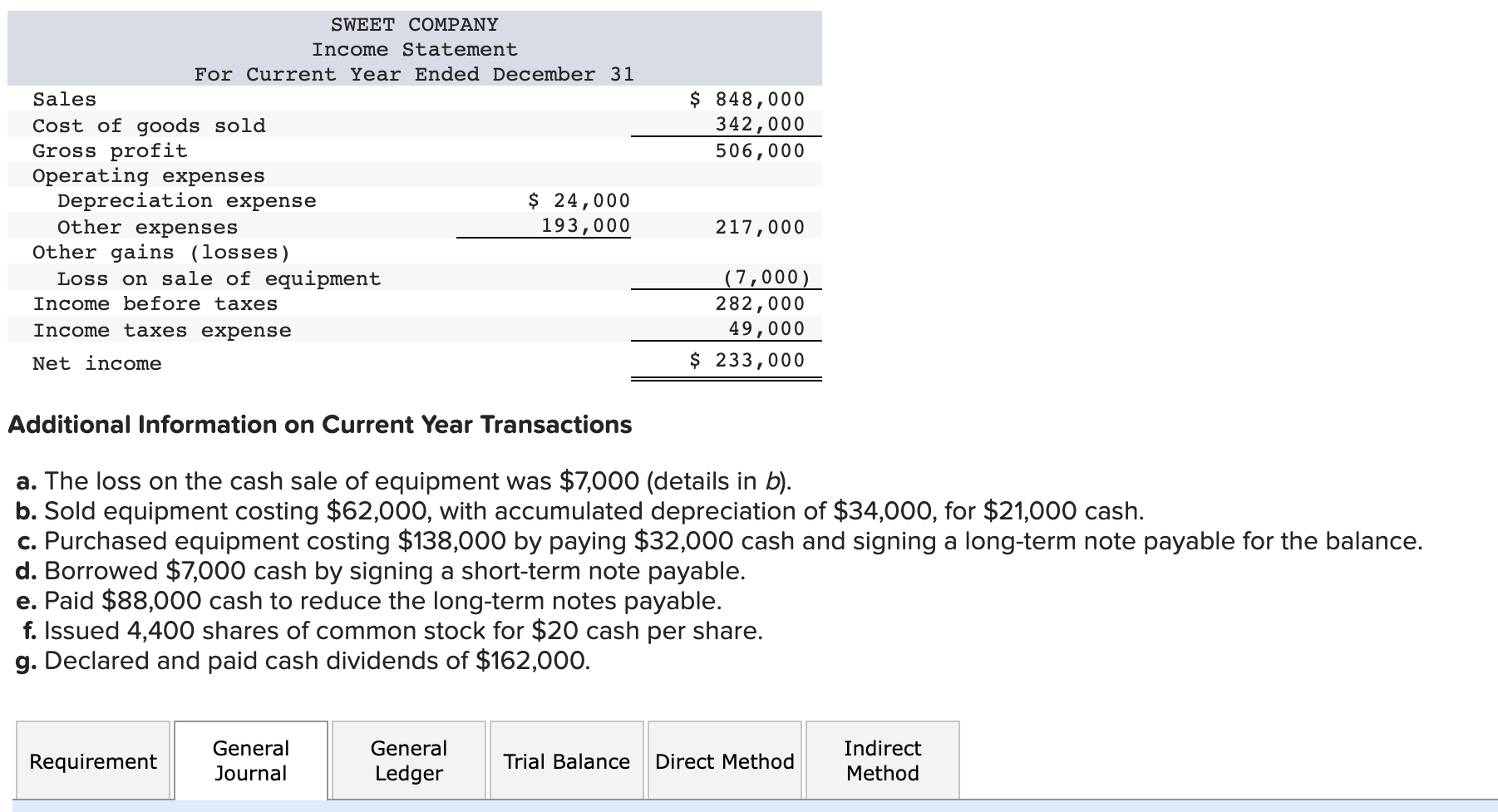
Sweet Company's current year income statement, comparative balance sheets, and additional information follow. For the year, (1) all sales are credit sales, (2) all credits
Sweet Company's current year income statement, comparative balance sheets, and additional information follow. For the year, (1) all sales are credit sales, (2) all credits to Accounts Receivable reflect cash receipts from customers, (3) all purchases of inventory are on credit, (4) all debits to Accounts Payable reflect cash payments for inventory, and (5) Other Expenses are paid in advance and are initially debited to Prepaid Expenses.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


