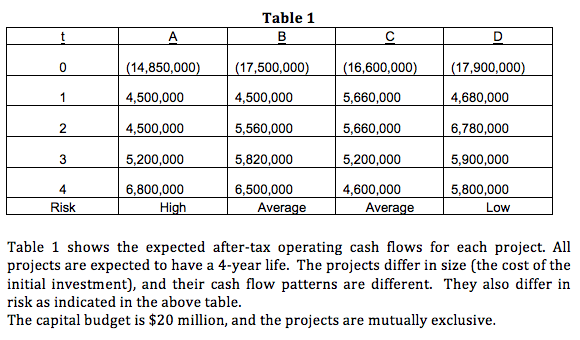
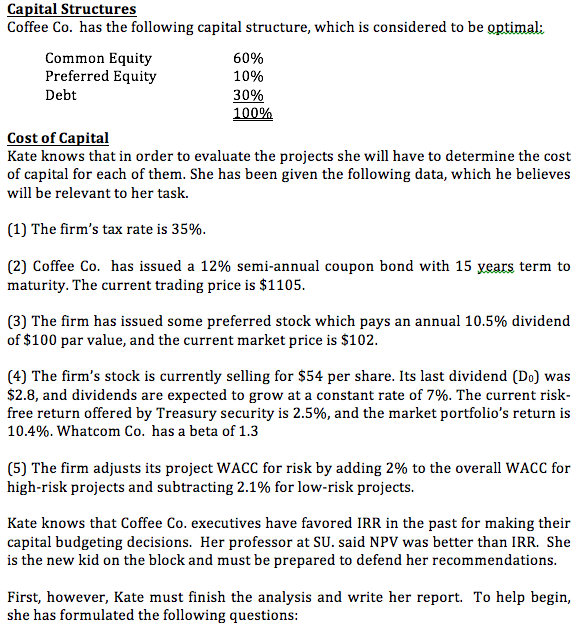

Table 1 B A 0 (14,850,000) (17,500,000) (16,600,000) (17,900,000) 1 4,500,000 4,500,000 5,660,000 4,680,000 2 4,500,000 5,560,000 5,660,000 6,780,000 3 5,200,000 5,820,000 5,200,000 5,900,000 4 Risk 6,800,000 High 6,500,000 Average 4,600,000 Average 5,800,000 Low Table 1 shows the expected after-tax operating cash flows for each project. All projects are expected to have a 4-year life. The projects differ in size (the cost of the initial investment), and their cash flow patterns are different. They also differ in risk as indicated in the above table. The capital budget is $20 million, and the projects are mutually exclusive. Capital Structures Coffee Co. has the following capital structure, which is considered to be optimali Common Equity 60% Preferred Equity 10% Debt 30% 100% Cost of Capital Kate knows that in order to evaluate the projects she will have to determine the cost of capital for each of them. She has been given the following data, which he believes will be relevant to her task. (1) The firm's tax rate is 35%. (2) Coffee Co. has issued a 12% semi-annual coupon bond with 15 years term to maturity. The current trading price is $1105. (3) The firm has issued some preferred stock which pays an annual 10.5% dividend of $100 par value, and the current market price is $102. (4) The firm's stock is currently selling for $54 per share. Its last dividend (De) was $2.8, and dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate of 7%. The current risk- free return offered by Treasury security is 2.5%, and the market portfolio's return is 10.4%. Whatcom Co. has a beta of 1.3 (5) The firm adjusts its project WACC for risk by adding 2% to the overall WACC for high-risk projects and subtracting 2.1% for low-risk projects. Kate knows that Coffee Co. executives have favored IRR in the past for making their capital budgeting decisions. Her professor at SU. said NPV was better than IRR. She is the new kid on the block and must be prepared to defend her recommendations. First, however, Kate must finish the analysis and write her report. To help begin, she has formulated the following questions: 1. What is the firm's cost of debt? 2. What is the firm's cost of preferred stock? 3. Cost of common equity (1) What is the estimated cost of common equity using the CAPM approach? (2) What is the estimated cost of common equity using the DCF approach? (3) What is the final estimate for cost of equity? 4. What is Coffee Co.'s overall WACC? 5. Do you think the firm should use the single overall WACC as the hurdle rate for each of its projects? Explain. 6. What is the WACC for each project? 7. Calculate all relevant capital budgeting measures for each project and place your numerical solutions in Table 2. Table 2 B A D NPV IRR 8. Comment on the commonly used capital budgeting measures. What is the underlying cause of ranking conflicts? Which criterion is the best one, and why? 9. Which of the projects are unacceptable and why? 10. Rank the projects that are acceptable, according to Kates' criterion of choice