Question
Table 2.4 in Berk and DeMarzo (2020) provide key financial ratios for large US firms updated in Spring of 2018. Within this table, the authors
Table 2.4 in Berk and DeMarzo (2020) provide key financial ratios for large US firms updated in Spring of 2018. Within this table, the authors highlight the 25%, median, and 75% quartiles for each type of ratio. Using examples of firms, explain why there are significant differences between the 25% and 75% quartiles for large companies specifically focusing on the Net Profit Margin, Asset Turnover, and the Equity Multiplier. How would you explain the differences between firms in the lower and upper quartiles (hint: see the DuPont identity for guidance)? Include at least two citations that support your response.
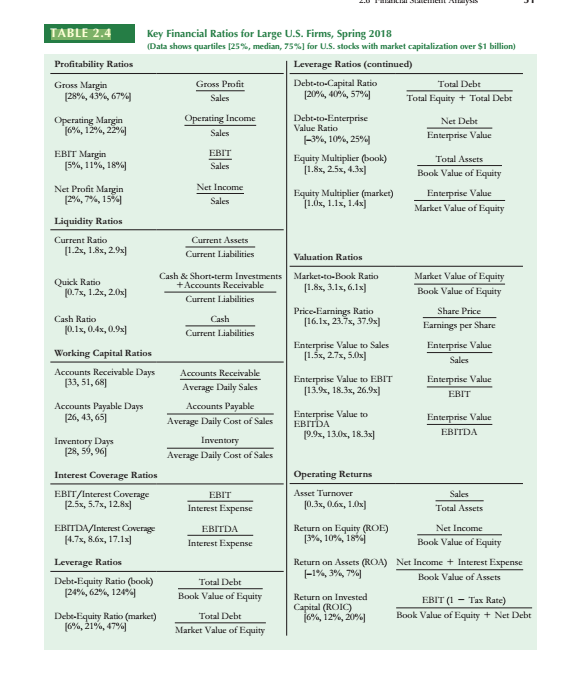
TABLE 2.4 Profitability Ratios Gross Margin [28%, 43%, 67% Operating Margin [6%, 12%, 22%] EBIT Margin [5%, 11%, 18%] Net Profit Margin [2%, 7%, 15%] Liquidity Ratios Current Ratio [1.2x, 1.8x, 2.9x] Quick Ratio [0.7x, 1.2x, 2.0x] Cash Ratio [0.1x, 0.4x, 0.9x] Working Capital Ratios Accounts Receivable Days [33,51,68] Accounts Payable Days [26, 43,65] Key Financial Ratios for Large U.S. Firms, Spring 2018 (Data shows quartiles [25%, median, 75%] for U.S. stocks with market capitalization over $1 billion) Leverage Ratios (continued) Inventory Days [28, 59,96] Interest Coverage Ratios EBIT/Interest Coverage [2.5x, 5.7x, 12.8x] EBITDA/Interest Coverage [4.7x, 8.6x, 17.1x] Leverage Ratios Debt-Equity Ratio (book) [24%, 62%, 124% Debt-Equity Ratio (market) [6%, 21%, 47%] Gross Profit Sales Operating Income Sales EBIT Sales Net Income Sales Current Assets Current Liabilities Cash & Short-term Investments +Accounts Receivable Current Liabilities Cash Current Liabilities Accounts Receivable Average Daily Sales Accounts Payable Average Daily Cost of Sales Inventory Average Daily Cost of Sales EBIT Interest Expense EBITDA Interest Expense Total Debt Book Value of Equity Total Debt Market Value of Equity Debt-to-Capital Ratio [20%, 40%, 57%] Debt-to-Enterprise Value Ratio -3%, 10%, 25% Equity Multiplier (book) [1.8x, 2.5x, 4.3x] Equity Multiplier (market) [1.0x, 1.1x, 1.4x] Valuation Ratios Market-to-Book Ratio [1.8x, 3.1x, 6.1x] Price-Earnings Ratio [16.1x, 23.7x, 37.9x] Enterprise Value to Sales [1.5x, 2.7x, 5.0x] Enterprise Value to EBIT [13.9x, 18.3x, 26.9x] Enterprise Value to EBITDA [9.9x, 13.0x, 18.3x] Operating Returns Asset Turnover [0.3x, 0.6x, 1.0x] Return on Equity (ROE) [3%, 10%, 18% Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) Total Debt Total Equity + Total Debt [6%, 12%, 20%] Net Debt Enterprise Value Total Assets Book Value of Equity Enterprise Value Market Value of Equity Market Value of Equity Book Value of Equity Share Price Earnings per Share Enterprise Value Sales Enterprise Value EBIT Enterprise Value EBITDA Sales Total Assets Return on Assets (ROA) Net Income + Interest Expense -1%, 3%, 7%] Book Value of Assets Net Income Book Value of Equity EBIT (1 - Tax Rate) Book Value of Equity + Net Debt
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
There are several reasons why there are significant differences between the 25 and 75 quartiles for ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


