Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
a. Use strain energy increments in the OWL Table Reference (see References button, Strain Energy Increments) to calculate the energy difference between the two


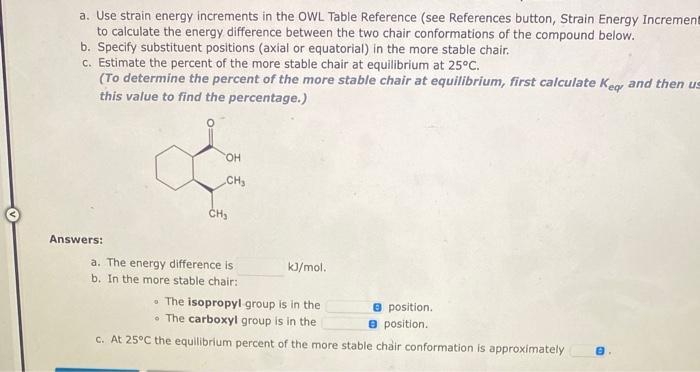
a. Use strain energy increments in the OWL Table Reference (see References button, Strain Energy Increments) to calculate the energy difference between the two chair conformations of the compound below. b. Specify substituent positions (axial or equatorial) in the more stable chair. c. Estimate the percent of the more stable chair at equilibrium at 25C. (To determine the percent of the more stable chair at equilibrium, first calculate Kear and then use this value to find the percentage.) Answers: CH eje HC a. The energy difference is b. In the more stable chair: OH kJ/mol. The isopropyl group is in the i The carboxyl group is in the c. At 25C the equilibrium percent of the more stable chair conformation is approximately 8 position. 8 position. Use the Rfrences to access important values if needed for this question. a. Use strain energy increments in the OWL Table Reference (see References button, Strain Energy Increments) to calculate the energy difference between the two chair conformations of the compound below. b. Specify substituent positions (axial or equatorial) in the more stable chair. c. Estimate the percent of the more stable chair at equilibrium at 25C. (To determine the percent of the more stable chair at equilibrium, first calculate Key and then use this value to find the percentage.) Answers: H C=CH CH a. The energy difference is b. In the more stable chair: kJ/mol. The vinyl(ethenyl) group is in the The methyl group is in the e position. a position. c. At 25C the equilibrium percent of the more stable chair conformation is approximately 8 a. Use strain energy increments in the OWL Table Reference (see References button, Strain Energy Increment to calculate the energy difference between the two chair conformations of the compound below. b. Specify substituent positions (axial or equatorial) in the more stable chair. c. Estimate the percent of the more stable chair at equilibrium at 25C. (To determine the percent of the more stable chair at equilibrium, first calculate Key and then us this value to find the percentage.) Answers: OH CH CH a. The energy difference is. b. In the more stable chair: kJ/mol. The isopropyl group is in the The carboxyl group is in the c. At 25C the equilibrium percent of the more stable chair conformation is approximately e position. e position. G
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.47 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
acHay Energies CH Cving This com be written as two conforr...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


