

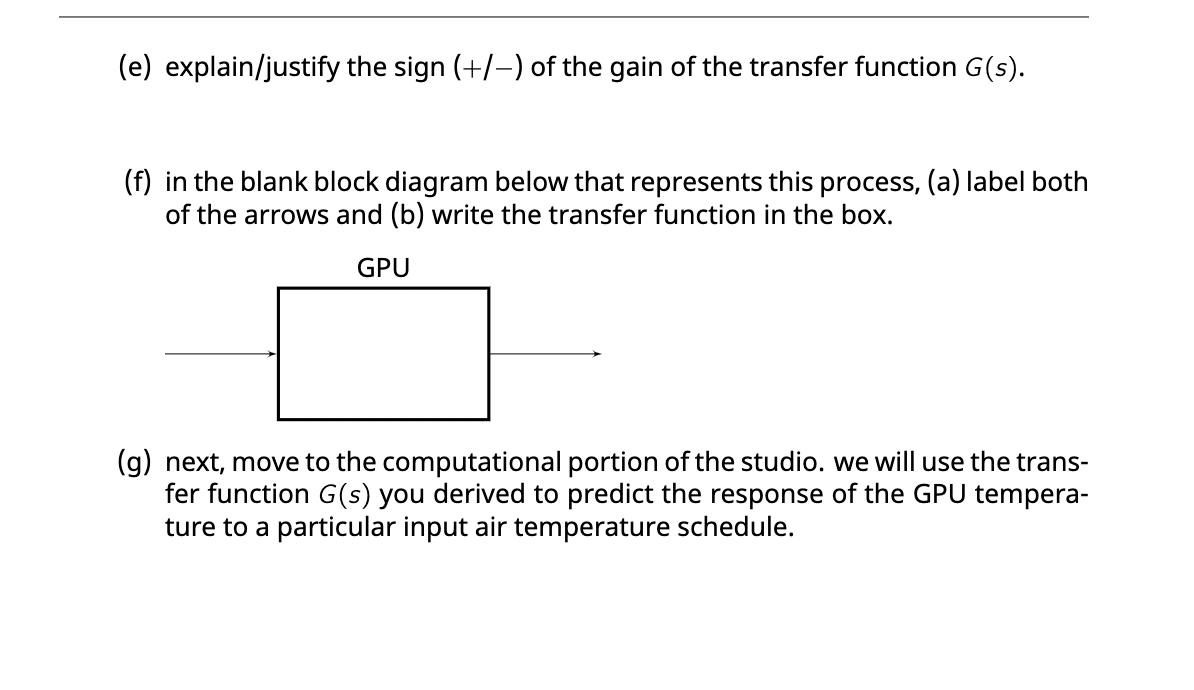
Tall let 0 = (t) [C] be the temperature of a graphics processing unit (GPU), a component of a computer. the computations performed by the GPU generate heat at a rate q=g(t) [J/s]. to prevent the temperature of the GPU from rising enough to damage its components, a fan is used to blow air, which is at temperature a = 0.(t) [C], across the GPU at a constant speed. owing to heat transfer from the (hotter) GPU to the (colder) air, the air cools the GPU. OK cool air 9 JIS fan GPU Figure 1: GPU cooling. two inputs: (1) the temperature of the air, oa(t), and (2) the heat generated by the computations, q(t). both inputs affect one output: the tem- perature of the GPU, 0(t). 1. to develop a simple dynamic model for 0 = 0(t), what three physical parameters must be know? what are their units? (hint: invoke Newton's "law" of cooling] 2. develop a dynamic model governing the dynamics of the output 0 = e(t) in re- sponse to changes in the inputs a = 0.(t) and q = 9(t). 3. suppose the user of the computer is playing a video game that places a constant demand on the GPU for rendering. then, the rate at which heat is generated is constant q(t) = g. however, the air temperature 0 (t) is not constant; rather, it can deviate from its steady-state value on. thus, we have reduced this to a single- input (@a(t)), single-output (@(t)) problem. (a) given the steady-state value of the air temperature 7, and the fixed value of the heat generation rate , write an equation that the steady-state GPU temperature 7 must satisfy. (b) define new input and output variables in deviation form (denoted by *): 0(t):= * (t) = (c) write your dynamic model for e(t) in terms of the deviation variables. (d) derive the transfer function G(s) that describes how the temperature of the GPU (t) responds to changes in the air temperature Of(t). assume the GPU temperature as initially at its steady state temperature, so e(t = 0) = 7. write the transfer function in standard gain/time-constant form. (e) explain/justify the sign (+/-) of the gain of the transfer function G(s). (f) in the blank block diagram below that represents this process, (a) label both of the arrows and (b) write the transfer function in the box. GPU (g) next, move to the computational portion of the studio. we will use the trans- fer function G(s) you derived to predict the response of the GPU tempera- ture to a particular input air temperature schedule. Tall let 0 = (t) [C] be the temperature of a graphics processing unit (GPU), a component of a computer. the computations performed by the GPU generate heat at a rate q=g(t) [J/s]. to prevent the temperature of the GPU from rising enough to damage its components, a fan is used to blow air, which is at temperature a = 0.(t) [C], across the GPU at a constant speed. owing to heat transfer from the (hotter) GPU to the (colder) air, the air cools the GPU. OK cool air 9 JIS fan GPU Figure 1: GPU cooling. two inputs: (1) the temperature of the air, oa(t), and (2) the heat generated by the computations, q(t). both inputs affect one output: the tem- perature of the GPU, 0(t). 1. to develop a simple dynamic model for 0 = 0(t), what three physical parameters must be know? what are their units? (hint: invoke Newton's "law" of cooling] 2. develop a dynamic model governing the dynamics of the output 0 = e(t) in re- sponse to changes in the inputs a = 0.(t) and q = 9(t). 3. suppose the user of the computer is playing a video game that places a constant demand on the GPU for rendering. then, the rate at which heat is generated is constant q(t) = g. however, the air temperature 0 (t) is not constant; rather, it can deviate from its steady-state value on. thus, we have reduced this to a single- input (@a(t)), single-output (@(t)) problem. (a) given the steady-state value of the air temperature 7, and the fixed value of the heat generation rate , write an equation that the steady-state GPU temperature 7 must satisfy. (b) define new input and output variables in deviation form (denoted by *): 0(t):= * (t) = (c) write your dynamic model for e(t) in terms of the deviation variables. (d) derive the transfer function G(s) that describes how the temperature of the GPU (t) responds to changes in the air temperature Of(t). assume the GPU temperature as initially at its steady state temperature, so e(t = 0) = 7. write the transfer function in standard gain/time-constant form. (e) explain/justify the sign (+/-) of the gain of the transfer function G(s). (f) in the blank block diagram below that represents this process, (a) label both of the arrows and (b) write the transfer function in the box. GPU (g) next, move to the computational portion of the studio. we will use the trans- fer function G(s) you derived to predict the response of the GPU tempera- ture to a particular input air temperature schedule









