Task 1.
a) balance the chemical equation of complete combustion of your assigned compound.
b) Estimate the enthalpy of complete combustion (Hcombustion) of exactly 1 mole of hex-1-yne using bond dissociation energies (see table below .
b) 386.9g of your hex-1-yne is completely combusted to heat up exactly 6 tons of gasoline, which has a specific heat capacity of 2.00 J/gC, starting at room temperature (25.0C). What is the final temperature of gasoline?
Task 2. Use the attached tables for Hf unless otherwise specified.
a) Find out the H (in kJ/mol) of freezing potassium, K(l) K(s). Show thinking process.
b) Estimate the Hf of your assigned compound (assume it is a liquid) using the determined Hcombustion in Task 1 (assume it is measured at SATP) and the tabled Hf values of CO2(g) and H2O(g). To obtain lv 4, derive the answer using Hesss Law and the chemical equations of Hf for each reactant and product. For example,
H2(g) + O2(g) H2O (g) Hf = 241.8 kJ/mol
c) The H of freezing of your assigned compound is -PP/100 kJ/mol. What is the Hf of your compound in its solid form
TABLES PROVIDED:
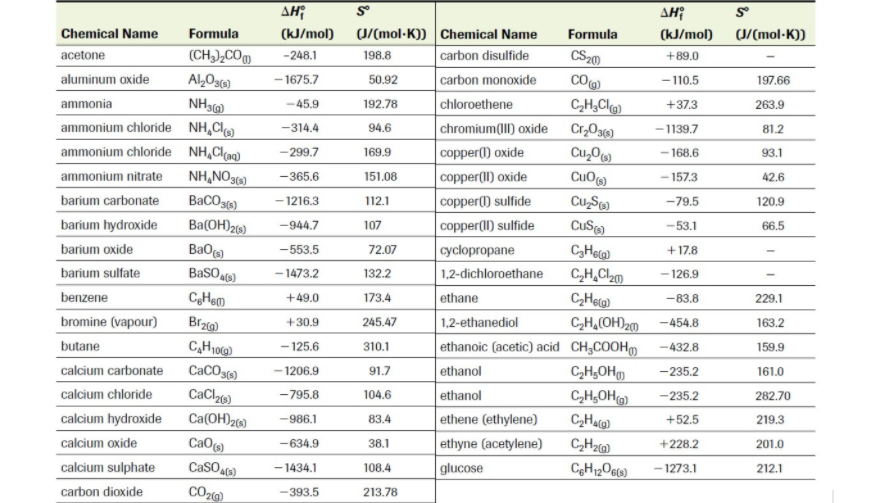
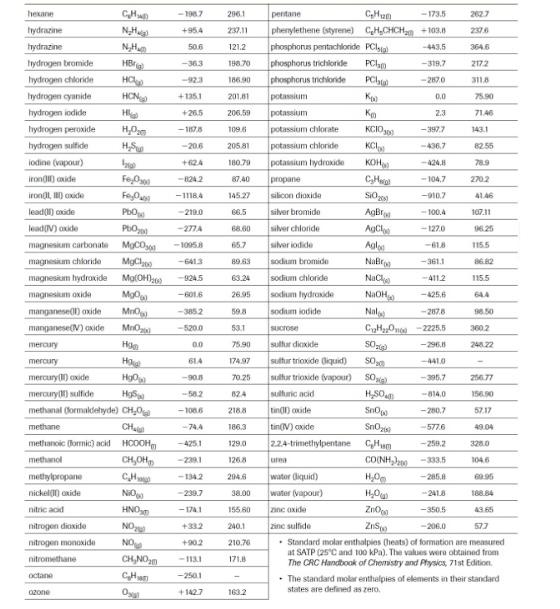
TABLE 7.1 Average Bond Dissociation Energies, D (kJ/mol) H-H 436 C-H 410 N-H 390 0-H 460 H-C 410 C-C 350 N-C 300 0-C 350 H-F 570 C-F 450 N-F 270 O-F 180 H-C1 432 C-C1330 N-C 200 0-CI 200 H-Br 366 C-Br 270 N-Br 240 0-Br 210 H-1 2989 C-I 240 N-I 0-1 220 H-N 390 CN 300 N-N 240 0-N 200 H-O 460 C-O 350 N-0 200 0-0 180 H-S 340 C-s 260 NS 0-5 Multiple covalent bonds C=C 611 C=C 835 C=0 732 O=0 498 - so AH; (kJ/mol) AH; (kJ/mol) +89.0 (J/(mol-K)) -248.1 CS20 COQ - 1675.7 -110,5 197.66 263.9 NH3 -45.9 +37.3 - 314.4 - 1139.7 81.2 - 168.6 93.1 - 299.7 -365.6 - 157.3 42.6 NH, NO 3ts BaCO3(8) - 1216.3 -79.5 120.9 -944.7 -53.1 66.5 -553.5 Chemical Name Formula acetone (CH3),COM aluminum oxide Al O3(s) ammonia ammonium chloride NH CHO ammonium chloride NHCl(aq) ammonium nitrate barium carbonate barium hydroxide Ba(OH)2(8) barium oxide BaO(s). barium sulfate BaSO468) benzene bromine (vapour) butane calcium carbonate calcium chloride calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)258) calcium oxide CaO (8) calcium sulphate Caso carbon dioxide s (J/(mol-K)) Chemical Name Formula 198.8 carbon disulfide 50.92 carbon monoxide 192.78 chloroethene CH2CH) 94.6 chromium(III) oxide Cr,031) 169.9 copper(I)oxide CuO) 151.08 copper(II)oxide CO) 112.1 copper(I) sulfide Cus) 107 copper(II) sulfide Cus) 72.07 cyclopropane CHEC 132.2 1.2-dichloroethane CH.C120 173.4 ethane CHE) 245.47 1.2-ethanediol C,H,OH)2 310,1 ethanoic (acetic) acid CH3COOH) 91.7 ethanol C,H,OH, 104.6 ethanol C,H,OH) 83.4 ethene (ethylene) CHACO 38.1 ethyne (acetylene) CH260 108.4 glucose CH 2016) 213.78 + 17.8 - 126.9 -83.8 -454.8 CHem Br2 CHOCO CaCO3(s) CaC128) -1473.2 +49.0 +30.9 - 125.6 - 1206.9 -795.8 -432.8 229.1 163.2 159.9 161.0 282.70 219.3 -235.2 -235.2 --986.1 +52.5 -634.9 +228.2 201.0 -1434.1 4(S) - 1273.1 212.1 CO20) -393.5 2961 -1987 +95.4 237.11 50.6 121.2 3646 -363 198.70 PC 2172 1860 PC +1351 201.51 78.50 7146 206.59 109.5 -1108 pertane C. Hun - 173.5 phenylethene styrene C.H.CHCHA+103.15 phosphorus pentachonide PC phosphorus trichloride -319,7 phosphorus trichode -2020 potakim ko 0,0 potassium 23 potassium chlorate -3927 potassium chloride KCH -436.7 potassium Hydroxide propane CH -104.7 silicon dioxide -9107 silver bromide - 100.4 silver chloride AC -1270 silveriodide KCIO 1431 -2006 205.81 8255 180.79 789 -242 87,40 2702 -11104 145.27 SO AB 107.11 --2100 -2724 58.00 -10958 Als 1155 -6413 89.83 -361.1 63.24 1155 sodium bromide sodium chloride sodium Hydroxide sodium iodide -6016 hane CH Tyde N. hydrazine N.HU tydrogen bromide HB Hydrogen chloride Irydrogen cyanide HCN hydrogen indide H hydrogen peroxide H,02 hydrogen sulfide HS lodine (vapour) ironicide Fe. TOOL) FO lead ride PO lead(V) oxide PLO magnesium carbonate MgCO3 magnesium chloride MOCH magnesium hydroacide Mo(OH)2 magnesium oxide Mo mange (1) oxide MO mangan(V)oxide MO Mercury Han mercury mercury (1) oxide mercury) silide HOS methanal formaldehyde) CH.0 methane CH metuniomic acid HCOOH methanol CH, OH methylpropane CH nickeloride NO nitric acid HNO nitrogen dioxide NOU nitrogen monoxide nitromethane CH.NO octane CH 2one Oy 644 NaCl - 4112 NAOH Nole -2078 CuHavigai - , -352 59.8 380 --5200 53.1 SUCOS 3602 00 75.90 sulfur dioxide 248.22 Some SO Ha 614 17497 -901 70.25 824 --502 -1006 -744 2188 186.3 Sno 129.0 1208 204.6 -1342 suur trioxide quid - 4410 sur tronde vapour) S03) -395.7 sulfuric acid HO -314,0 15.50 tin cuide Sno -2007 52.17 tin(V) oxide -5776 4904 2.2.4-trimethylpentane CH -259,2 NH no 1046 waterdiquid HO water vapout) 1400 -2418 nc oxide ZOO -350.5 zine sulfide ZS - 206.0 573 Standard molar enthalpies theats) of formation are measured SATP (25C and 100 kPa). The values were obtained from The CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 71st Edition The standard molar enthalpies of elements in their standard states are defined as zero. 36.00 -1741 15580 240.1 NO 210.76 -1131 171.5 -2501 +1427 1632









