Question: . Task 1: Communication with a Web server in the local network (HTTP protocol) (2 mark) Open the previous PT (Packet Tracer-Lab 2). Make sure


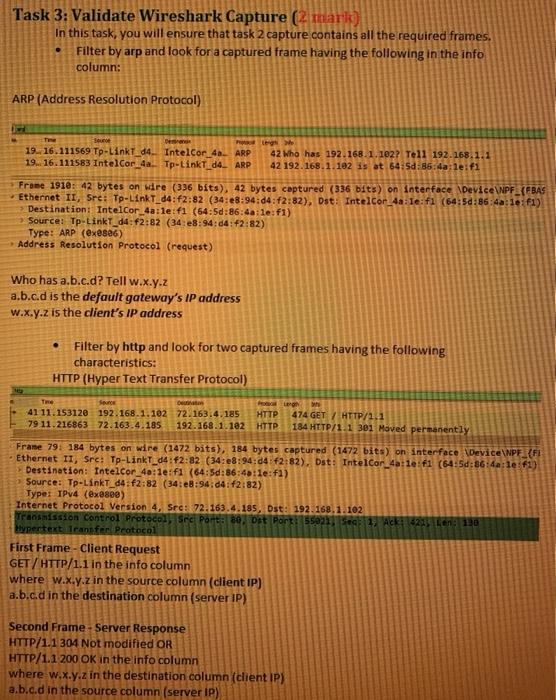
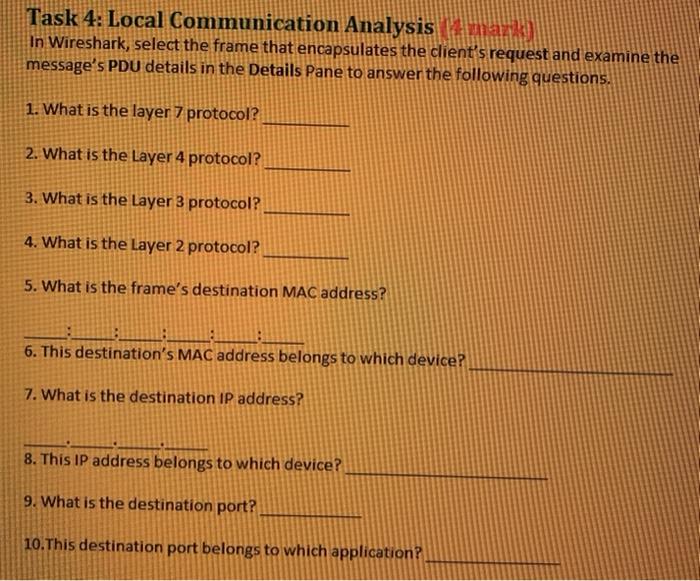
. Task 1: Communication with a Web server in the local network (HTTP protocol) (2 mark) Open the previous PT (Packet Tracer-Lab 2). Make sure PCO can ping servero, with the right IP address, otherwise this part will not work When you open the PT, by default, you are in Realtime mode. Now click on PCO and Desktop and then Web Browser tab In the URL box type http://192.168.5.10 (web server IP address), click Go . You see an HTTP web page opens from the server (blue). You are connected to a Web server and requested a web page (Welcome Cisco Packet racer). Minimize the PCO screen for now. In PT, change Realtime mode to Simulation mode, by clicking on the simulation icon . In simulation mode click on Edit Filters and then on the Misc tab You will see many protocols with check marks. Make sure they are unchecked except HTTP . Still in simulation mode, open PCO page again (web browser page), click on Go to capture the HTTP packets in simulation mode. Make sure to click on the Capture/Forward tab to capture the PDU. To stop capturing PDU, just click on Capture/Forward again. . Now click on PCO, Switch OPDU to see inside a packet Questions: Which layer of Osi model show the MAC address? What is the Ethernet Header? What protocol did you capture? This protocol used by which layer of the OSI model? What is the SRC (PCO) and DES IP (Servero) address? What is the destination port? Save to a file namedi lab3_PT_task1.pkt Task 2: Accessing Local Resources (your laptop) (2 mark) In this task, you will capture the network traffic between a web client and a web server, each running on the same network segment. Do not proceed until all previous tasks have succeeded! On your laptop, start the WS. Make sure you capture traffic on the correct interface! Refer back to lab 2 if you are not sure or do not remember how to do this! To ensure you are capturing on the correct interface, ping the default gateway and verify the frames are being captured in Wireshark. . Delete the ARP cache. On your laptop, run CMD as Administrator. From the Command Prompt, enter the following command: arpa If there are some arp cache in the memory, then you have to delete them. To delete the Arp cache in the Windows CMD prompt, just type arp-d* You must make sure that no errors resulted from the execution of the command! . In the CMD prompt screen, type ping cisco.com and press enter. The DNS on the Cisco server would resolve the URL cisco.com to an IP address. (72.163.4.185) C:\WINDOWS\system32>ping cisco.com Pinging cisco.com (72.163.4.185) Now you have an IP address for Cisco server. Open a web browser in your laptop. Enter the following URL in the browser's address bar: http://a.b.cd replace a.b.c.d with the web server's IP address (72.163.4.185). Do not proceed to the next step until the web page successfully displays in the web browser. Stop the Wireshark. Save the captures to a file named: lab3_WS_task2.pcapng . Task 3: Validate Wireshark Capture (2 mark) In this task, you will ensure that task 2 capture contains all the required frames. Filter by arp and look for a captured frame having the following in the info column: . ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) 19.. 16.111569 Tp-LinkT_d4. IntelCor 40_ ARP 19.. 16.111583 IntelCor.4 Tp-LinkTd4 ARP 42 Who has 192.168.1.102? Tell 192.168.1.1 42 192.168.1.102 is at 64:50:85:4a:le.fi Frane 1910: 42 bytes on wre (336 bits), 42 bytes captured (336 bits) on interface Device\PF_{BAS Ethernet II, Sre: Tp-LinkT_04:62:82 (34:48:94:04:12:82), Dst: IntelCor_4a: Te:fi (64:50:86:4:le: f1) > Destination: Intel Cor 4a:le: f1 (64:5d:86:40:le:fi) Source: Tp-LinkT_04:42:82 (34:e8:94:04:42:82) Type: ARP (ex0886) Address Resolution Protocol (request) Who has a.b.c.d? Tell w.x.y.z a.b.c.d is the default gateway's IP address W.x.y.z is the client's IP address Filter by http and look for two captured frames having the following characteristics: HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) De 41 11.153120 192.168.1.102 72.163.4.185 HTTP 79 11.216863 72.163.4.185 192.168.1.182 HTTP 474 GET / HTTP/1.1 184 HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently Frame 79: 184 bytes on wire (1472 bits), 184 bytes captured (1472 bits) on interface Device\NPF_{FI Ethernet 11, Src: Tp-LinkT_04:42:32 (34:e8:94:04 2:82), Dst: Intel Cor_4a: le f1 (64:5d:36:4a: le f1) Destination: Intelcor_40:1e:fl (64:50:56:40:le:fi) Source: Tp-LinkT_d4f2:82 (34:e8:94:04:42:82) Type: IPv4 (@x2890) Internet Protocol Version 4, Sre: 72.163.4.185, Dst: 192.168.1.102 Transmission Control Protocol See Port: 80 Dst Port 55021, S: 1. Ack 422 Len: 190 Hypertext Transfer Protocol First Frame - Client Request GET/HTTP/1.1 in the info column where w.x.y.z in the source column (dient IP) a.b.c.d in the destination column (server IP) Second Frame - Server Response HTTP/1.1 304 Not modified OR HTTP/1.1 200 OK in the info column where w.x.y.z in the destination column (client IP) a.b.c.d in the source column (server IP) Task 4: Local Communication Analysis mark In Wireshark, select the frame that encapsulates the client's request and examine the message's PDU details in the Details Pane to answer the following questions. 1. What is the layer 7 protocol? 2. What is the Layer 4 protocol? 3. What is the Layer 3 protocol? 4. What is the Layer 2 protocol? 5. What is the frame's destination MAC address? 6. This destination's MAC address belongs to which device? 7. What is the destination IP address? 8. This IP address belongs to which device? 9. What is the destination port? 10. This destination port belongs to which application? . Task 1: Communication with a Web server in the local network (HTTP protocol) (2 mark) Open the previous PT (Packet Tracer-Lab 2). Make sure PCO can ping servero, with the right IP address, otherwise this part will not work When you open the PT, by default, you are in Realtime mode. Now click on PCO and Desktop and then Web Browser tab In the URL box type http://192.168.5.10 (web server IP address), click Go . You see an HTTP web page opens from the server (blue). You are connected to a Web server and requested a web page (Welcome Cisco Packet racer). Minimize the PCO screen for now. In PT, change Realtime mode to Simulation mode, by clicking on the simulation icon . In simulation mode click on Edit Filters and then on the Misc tab You will see many protocols with check marks. Make sure they are unchecked except HTTP . Still in simulation mode, open PCO page again (web browser page), click on Go to capture the HTTP packets in simulation mode. Make sure to click on the Capture/Forward tab to capture the PDU. To stop capturing PDU, just click on Capture/Forward again. . Now click on PCO, Switch OPDU to see inside a packet Questions: Which layer of Osi model show the MAC address? What is the Ethernet Header? What protocol did you capture? This protocol used by which layer of the OSI model? What is the SRC (PCO) and DES IP (Servero) address? What is the destination port? Save to a file namedi lab3_PT_task1.pkt Task 2: Accessing Local Resources (your laptop) (2 mark) In this task, you will capture the network traffic between a web client and a web server, each running on the same network segment. Do not proceed until all previous tasks have succeeded! On your laptop, start the WS. Make sure you capture traffic on the correct interface! Refer back to lab 2 if you are not sure or do not remember how to do this! To ensure you are capturing on the correct interface, ping the default gateway and verify the frames are being captured in Wireshark. . Delete the ARP cache. On your laptop, run CMD as Administrator. From the Command Prompt, enter the following command: arpa If there are some arp cache in the memory, then you have to delete them. To delete the Arp cache in the Windows CMD prompt, just type arp-d* You must make sure that no errors resulted from the execution of the command! . In the CMD prompt screen, type ping cisco.com and press enter. The DNS on the Cisco server would resolve the URL cisco.com to an IP address. (72.163.4.185) C:\WINDOWS\system32>ping cisco.com Pinging cisco.com (72.163.4.185) Now you have an IP address for Cisco server. Open a web browser in your laptop. Enter the following URL in the browser's address bar: http://a.b.cd replace a.b.c.d with the web server's IP address (72.163.4.185). Do not proceed to the next step until the web page successfully displays in the web browser. Stop the Wireshark. Save the captures to a file named: lab3_WS_task2.pcapng . Task 3: Validate Wireshark Capture (2 mark) In this task, you will ensure that task 2 capture contains all the required frames. Filter by arp and look for a captured frame having the following in the info column: . ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) 19.. 16.111569 Tp-LinkT_d4. IntelCor 40_ ARP 19.. 16.111583 IntelCor.4 Tp-LinkTd4 ARP 42 Who has 192.168.1.102? Tell 192.168.1.1 42 192.168.1.102 is at 64:50:85:4a:le.fi Frane 1910: 42 bytes on wre (336 bits), 42 bytes captured (336 bits) on interface Device\PF_{BAS Ethernet II, Sre: Tp-LinkT_04:62:82 (34:48:94:04:12:82), Dst: IntelCor_4a: Te:fi (64:50:86:4:le: f1) > Destination: Intel Cor 4a:le: f1 (64:5d:86:40:le:fi) Source: Tp-LinkT_04:42:82 (34:e8:94:04:42:82) Type: ARP (ex0886) Address Resolution Protocol (request) Who has a.b.c.d? Tell w.x.y.z a.b.c.d is the default gateway's IP address W.x.y.z is the client's IP address Filter by http and look for two captured frames having the following characteristics: HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) De 41 11.153120 192.168.1.102 72.163.4.185 HTTP 79 11.216863 72.163.4.185 192.168.1.182 HTTP 474 GET / HTTP/1.1 184 HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently Frame 79: 184 bytes on wire (1472 bits), 184 bytes captured (1472 bits) on interface Device\NPF_{FI Ethernet 11, Src: Tp-LinkT_04:42:32 (34:e8:94:04 2:82), Dst: Intel Cor_4a: le f1 (64:5d:36:4a: le f1) Destination: Intelcor_40:1e:fl (64:50:56:40:le:fi) Source: Tp-LinkT_d4f2:82 (34:e8:94:04:42:82) Type: IPv4 (@x2890) Internet Protocol Version 4, Sre: 72.163.4.185, Dst: 192.168.1.102 Transmission Control Protocol See Port: 80 Dst Port 55021, S: 1. Ack 422 Len: 190 Hypertext Transfer Protocol First Frame - Client Request GET/HTTP/1.1 in the info column where w.x.y.z in the source column (dient IP) a.b.c.d in the destination column (server IP) Second Frame - Server Response HTTP/1.1 304 Not modified OR HTTP/1.1 200 OK in the info column where w.x.y.z in the destination column (client IP) a.b.c.d in the source column (server IP) Task 4: Local Communication Analysis mark In Wireshark, select the frame that encapsulates the client's request and examine the message's PDU details in the Details Pane to answer the following questions. 1. What is the layer 7 protocol? 2. What is the Layer 4 protocol? 3. What is the Layer 3 protocol? 4. What is the Layer 2 protocol? 5. What is the frame's destination MAC address? 6. This destination's MAC address belongs to which device? 7. What is the destination IP address? 8. This IP address belongs to which device? 9. What is the destination port? 10. This destination port belongs to which application
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


