Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
% Test 4: R21 % Find the rotation matrix from frame {1} to the frame moving with the rectangular plate. % Test 5: cyl_to_sty_2




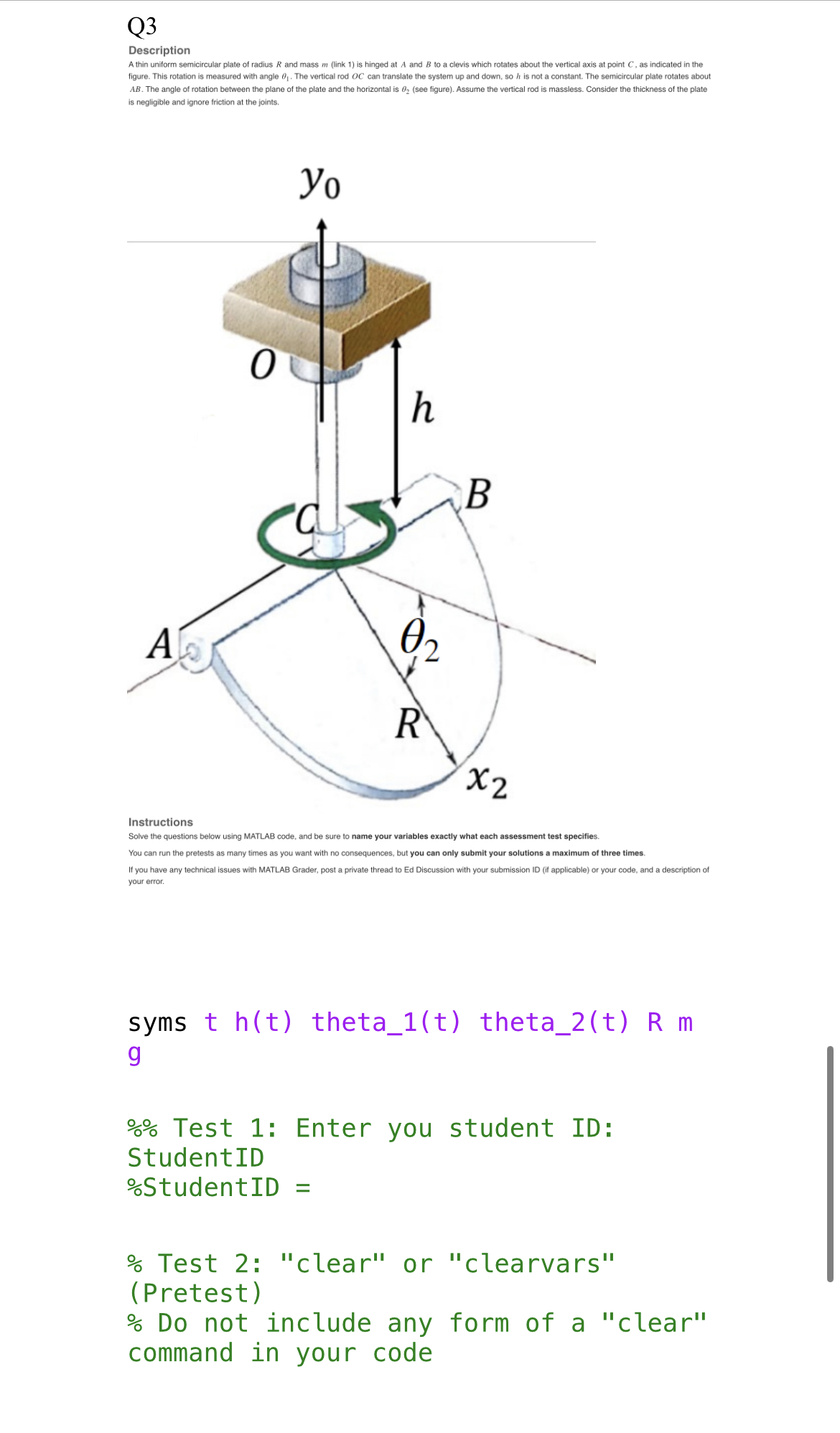
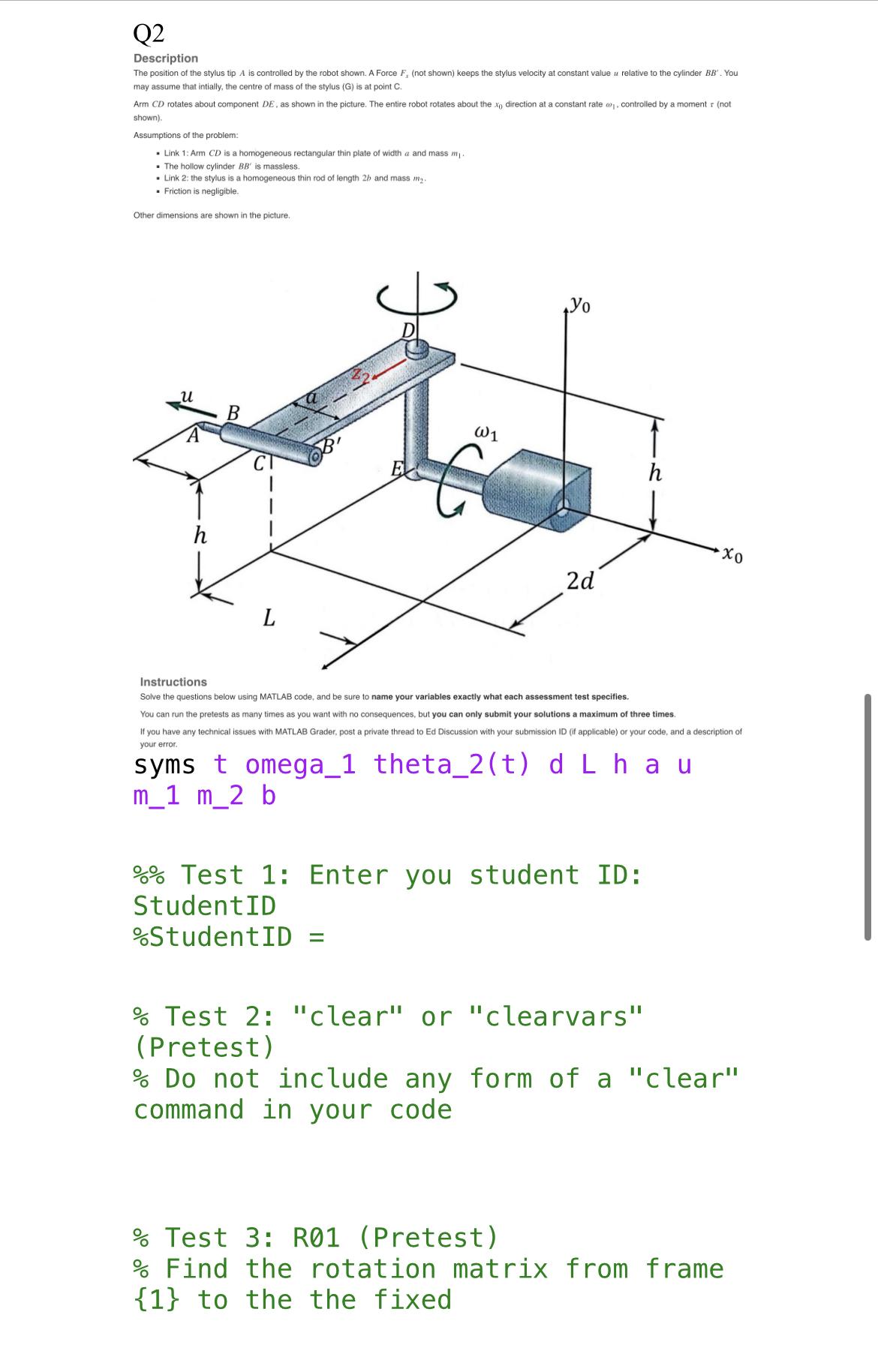
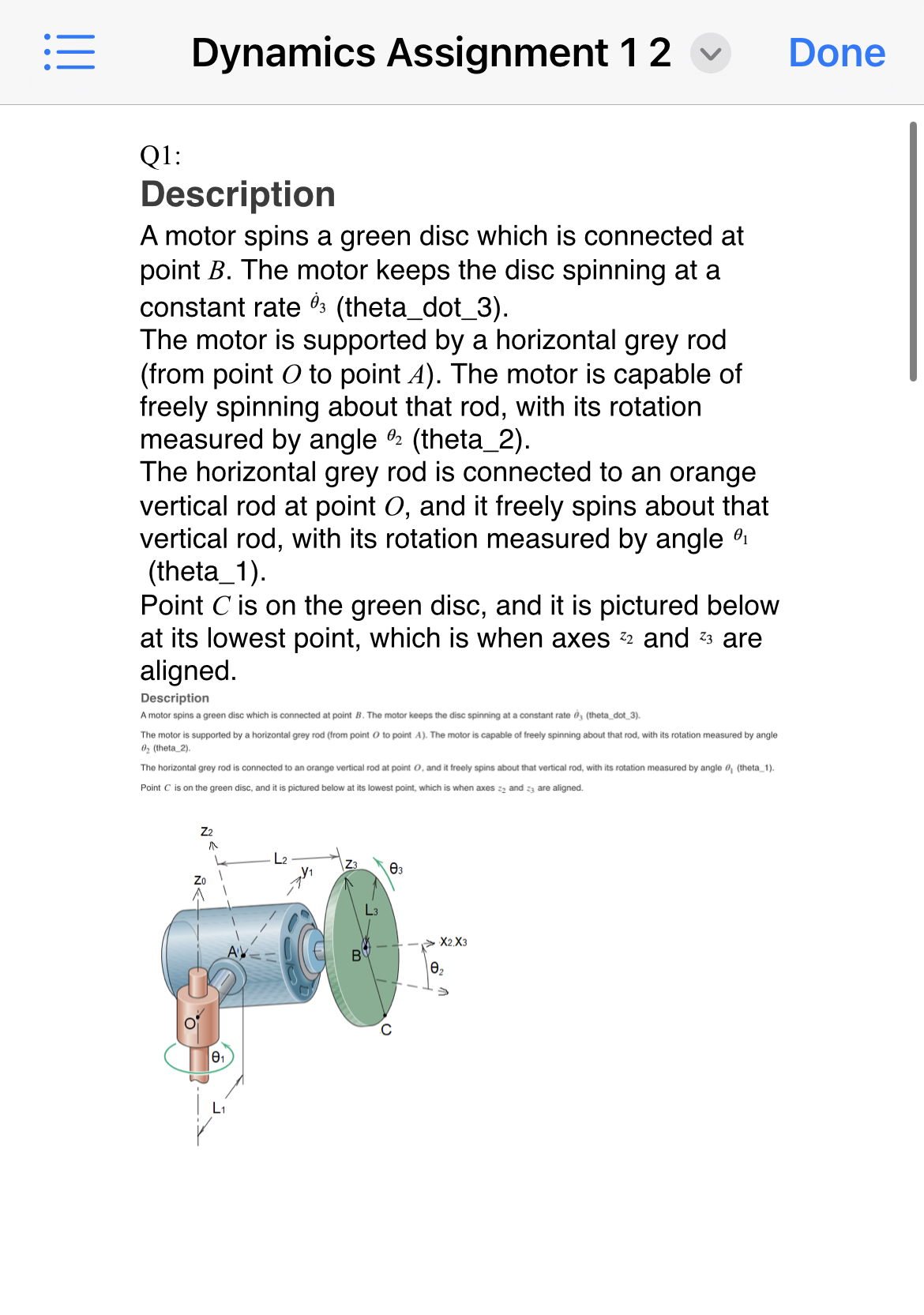

% Test 4: R21 % Find the rotation matrix from frame {1} to the frame moving with the rectangular plate. % Test 5: cyl_to_sty_2 (Pretest) % Find the position vector from the centre of cylinder BB' to the centre of mass of the stylus in frame {2} Test 6: pos_E_to_sty_2 Find the position vector from point E to the centre of mass of the stylus in frame {2} Test 7: ang_vel_plate_DE_2 (Pretest) % Find the angular velocity of the rectangular plate relative to component DE in frame {2} % Test 8: ang_vel_sty_2 % Find the absolute angular velocity of the stylus in frame {2} % Test 9: lin_vel_sty_1 (Pretest) % Find the absolute linear velocity of the centre of mass of the stylus in frame {1} % Test 10: lin_acc_sty_D_2 % Find the linear acceleration of the centre of mass of the stylus relative to point D in frame {2} % Test 11: lin_acc_sty_2 % Find the absolute linear acceleration of the centre of mass of the stylus in frame {2} % Test 13: w32_3 % Find the angular velocity of the link that frame {3} is attached to, relative to the link that frame {2} is attached to, and express that vector in frame {3} % Test 14: w3_3 Find the absolute angular velocity of the link that frame {3} is attached to, and express that vector in frame {3} % Test 15: rOC_dot_2 (Pretest) % Find the absolute linear velocity of point C in frame {2} % Test 16: rOC_ddot_2 % Find the absolute linear acceleration of point C in frame {2} % Test 17: w3_dot_2 % Find the absolute angular acceleration of the link that frame {3} is attached to, and express that vector in frame {2} % Test 3: R10 (Pretest) % Find the rotation matrix between the fixed frame and frame {1} % R10 = % Test 4: R21 % Find the rotation matrix between the frames {1} and {2} % R21 = % Test 5: C_to_centre_mass_2 (Pretest) % Find the position vector between the fixed point C and the centre of mass of the semicircular plate in frame {2} %C_to_centre_mass_2 = % Test 6: ang_vel_plate_2 Find the absolute angular velocity of the plate in frame {2} % ang_vel_plate_2 = Test 6: lin_acc_plate_2 % Find the absolute linear acceleration of the plate in frame {2} % lin_acc_plate_2 = % Test 6: R30 % Find the rotation matrix that brings a vector from frame {0} into frame {3} % Test 7: OA_2 (Pretest) % Find the position vector from point O to point A in frame {2} Test 8: rAB_2 (Pretest) % Find the position vector from point A to point B in frame {2} % Test 9: rBC_3 % Find the position vector from point B to point C in frame {3} % Test 10: rOC_2 % Find the position vector from point 0 to point C in frame {2} % Test 11: w1_1 (Pretest) Find the absolute angular velocity of the link that frame {1} is attached to, and express that vector in frame {1} % Test 12: w21_2 (Pretest) % Find the angular velocity of the link that frame {2} is attached to, relative to the link that frame {1} is attached to, and express that vector in frame {2} Q3 Description A thin uniform semicircular plate of radius R and mass m (link 1) is hinged at A and B to a clevis which rotates about the vertical axis at point C, as indicated in the figure. This rotation measured with angle . The vertical rod OC can translate the system up and down, so I is not a constant. The semicircular plate rotates about AB. The angle of rotation between the plane of the plate and the horizontal is 0, (see figure). Assume the vertical rod is massless. Consider the thickness of the plate is negligible and ignore friction at the joints. A Yo 0 h B 02 R x2 Instructions Solve the questions below using MATLAB code, and be sure to name your variables exactly what each assessment test specifies. You can run the pretests as many times as you want with no consequences, but you can only submit your solutions a maximum of three times. If you have any technical issues with MATLAB Grader, post a private thread to Ed Discussion with your submission ID (if applicable) or your code, and a description of your error. syms th(t) theta_1(t) theta_2(t) Rm g %% Test 1: Enter you student ID: Student ID %Student ID = % Test 2: "clear" or "clearvars" (Pretest) % Do not include any form of a "clear" command in your code Q2 Description The position of the stylus tip A is controlled by the robot shown. A Force F, (not shown) keeps the stylus velocity at constant value relative to the cylinder BB'. You may assume that intially, the centre of mass of the stylus (G) is at point C. Arm CD rotates about component DE, as shown in the picture. The entire robot rotates about the x direction at a constant rate w, controlled by a moment + (not shown). Assumptions of the problem: Link 1: Arm CD is a homogeneous rectangular thin plate of width a and mass m. The hollow cylinder BB' is massless. Link 2: the stylus is a homogeneous thin rod of length 2b and mass m. Friction is negligible. Other dimensions are shown in the picture. h L W1 30 2d h xo Instructions Solve the questions below using MATLAB code, and be sure to name your variables exactly what each assessment test specifies. You can run the pretests as many times as you want with no consequences, but you can only submit your solutions a maximum of three times. If you have any technical issues with MATLAB Grader, post a private thread to Ed Discussion with your submission ID (if applicable) or your code, and a description of your error. syms t omega_1 theta_2(t) d Lha u m_1 m 2 b %% Test 1: Enter you student ID: Student ID %Student ID = % Test 2: "clear" or "clearvars" (Pretest) % Do not include any form of a "clear" command in your code % Test 3: R01 (Pretest) % Find the rotation matrix from frame {1} to the the fixed := Dynamics Assignment 12 Q1: Description A motor spins a green disc which is connected at point B. The motor keeps the disc spinning at a constant rate 03 (theta_dot_3). The motor is supported by a horizontal grey rod (from point O to point A). The motor is capable of freely spinning about that rod, with its rotation measured by angle 2 (theta_2). 02 The horizontal grey rod is connected to an orange vertical rod at point O, and it freely spins about that vertical rod, with its rotation measured by angle (theta_1). Point C is on the green disc, and it is pictured below at its lowest point, which is when axes 22 and 23 are aligned. Description A motor spins a green disc which is connected at point B. The motor keeps the disc spinning at a constant rate 03 (theta_dot_3). The motor is supported by a horizontal grey rod (from point O to point A). The motor is capable of freely spinning about that rod, with s rotation measured by angle 02 (theta 2). The horizontal grey rod is connected to an orange vertical rod at point 0, and it freely spins about that vertical rod, with its rotation measured by angle 0, (theta_1). Point C is on the green disc, and it is pictured below at its lowest point, which is when axes z and 23 are aligned. Z A Zo 01 AV Z3 63 X2.X3 02 Done Instructions Solve the questions below using MATLAB code, and be sure to name your variables exactly what each assessment test specifies. You can run the pretests as many times as you want with no consequences, but you can only submit your solutions a maximum of three times. If you have any technical issues with MATLAB Grader, post a private thread to Ed Discussion with your submission ID (if applicable) or your code, and a description of your error. References: Image source: Meriam, Kraige - Engineering Mechanics Dynamics. syms t theta_1(t) theta_2(t) theta_dot_3 L_1 L_2 L_3 rho % Test 1: Enter you student ID: Student ID %Student ID = % Test 2: "clear" or "clearvars" (Pretest) % Do not include any form of a "clear" command in your code % Test 3: R10 (Pretest) % Find the rotation matrix that brings a vector from frame {0} into frame {1} % Test 4: R21 (Pretest) % Find the rotation matrix that brings a vector from frame {1} into frame {2} % Test 5: R32 % Find the rotation matrix that brings a vector from frame {2} into frame {3}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


