the 1. graph is correct while the 2A graph is incorrect (I think),
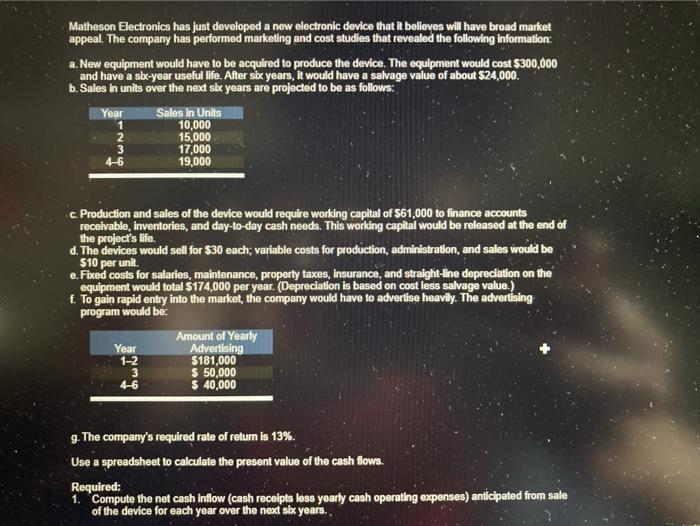
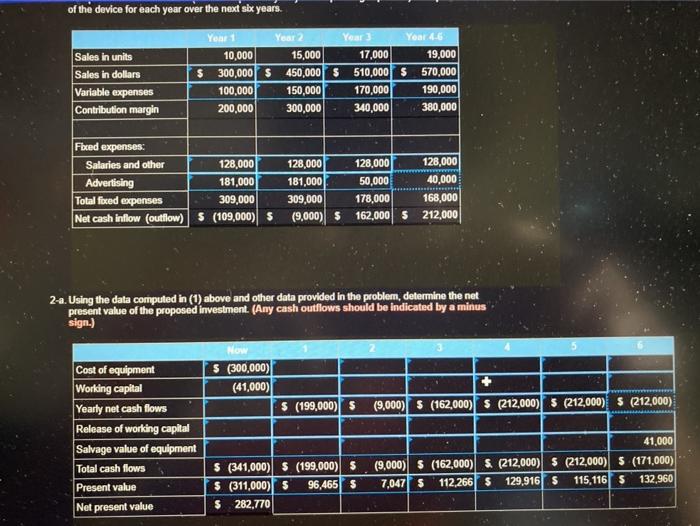
Matheson Electronics has just developed a new electronic device that it believes will have broad market appeal. The company has performed marketing and cost studies that revealed the following information: a. New equipment would have to be acquired to produce the device. The equipment would cost $300,000 and have a six-year useful life. After six years, it would have a salvage value of about $24,000. b. Sales in units over the next sbe years are projected to be as follows: Year . 2 3 4-6 Sales in Units 10,000 15,000 17,000 19,000 c Production and sales of the device would require working capital of 561,000 to finance accounts receivable, inventories, and day-to-day cash needs. This working capital would be released at the end of the project's life. d. The devices would sell for $30 each: variable costs for production, administration, and sales would be $10 per unit. e. Fixed costs for salaries, maintenance, property taxes, insurance, and straight-line depreciation on the equipment would total $174,000 per year. (Depreciation is based on cost less salvage value. f. To gain rapid entry into the market, the company would have to advertise heavily. The advertising program would be: Amount of Yearly Year Advertising 1-2 S181,000 3 S 50,000 4-6 $ 40,000 g. The company's required rate of return is 13%. Use a spreadsheet to calculate the present value of the cash flows. Required: 1. Compute the net cash inflow (cash receipts less yearly cash operating expenses) anticipated from sale of the device for each year over the next six years.. of the device for each year over the next six years. Sales In units Sales in dollars Variable expenses Contribution margin Yen 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4-6 10,000 15,000 17,000 19,000 $ 300,000 $ 450,000 $ 510,000 $570,000 100,000 150,000 170,000 190,000 200,000 300,000 340,000 380,000 Fbeed expenses Salaries and other 128,000 Advertising 181,000 Total fized expenses 309,000 Net cash inflow (outflow) S (109,000) $ 128,000 181,000 309,000 (9,000) $ 128,000 128,000 50,000 40,000 178,000 168,000 162,000 5 212,000 2-a. Using the data computed in (1) above and other data provided in the problem, determine the net present value of the proposed investment. (Any cash outflows should be indicated by a minus sign.) 3 Now $ (300,000) (41,000) $ (199,000) $ (9,000) $ (162,000) S (212,000) 5 (212,000) S (212,000) Cost of equipment Working capital Yearly net cash flows Release of working capital Salvage value of equipment Total cash flows Present value Net present value $ (341,000) S (199,000) S $ (311,000) $ 96,465 $ $ 282,770 41,000 (9,000) $ (162,000) S (212,000) $ (212,000) S (171,000) 7,047 s 112.266 $ 129,916 S 115,116 S 132.960