Question: The answers are required to be programmed in OCAML language Statistics play an important part in computer science. As such, it is important to encode

The answers are required to be programmed in OCAML language
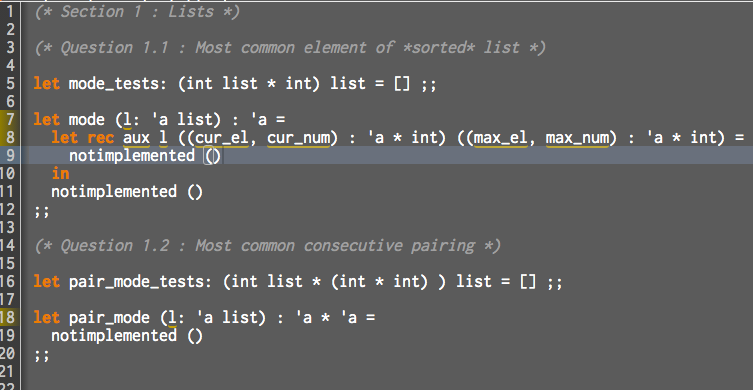
Statistics play an important part in computer science. As such, it is important to encode even the simplest statistical functions. For example, Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field that uses a lot of statistics. It is often needed in NLP to evaluate the most common elements of language, as it helps with sentence generation. In particular, n-grams, an n-long subsequence of elements of language, are studied and used in depth. For this question, you must write tests for and implement two functions: mode and pair_mode. 1. mode : 'a list -> 'a is a function that takes a list containing any-type (a) elements and returns the most common one (aka the mode of the distribution represented by the list). The tests should be placed in the list named mode_tests; however, while these tests assume that mode is used on integers, your function should remain generic. In case of tie-breakers (two elements are presently the same, highest number of times in the list), return the first one encountered. Hint 1: You are allowed to use the function call List.sort compare (your list here). This sorts your list with the default comparison function. This also means that in the case of tie-breakers, the "lower" value should be returned. Hint 2: A tail-recursive helper might be required! 2. pair_mode : 'a list -> 'a * 'a takes any list and returns the most common pair of consecutive elements (or bi-gram) in the list. Hint 1: You should be using mode within this function! Hint 2: A lot of List. module functions may be useful here - make sure to consult them. 6 II 1 (* Section 1 : Lists *) 2 3 (* Question 1.1 : Most common element of *sorted* list *) 4 5 let mode_tests: (int list * int) list = [] ;; 7 let mode (1: 'a list) : 'a = 8 let rec aux 1 ((cur_el, cur_num) : 'a * int) ((max_el, max_num) : 'a * int) 9 notimplemented 10 in 11 notimplemented () 13 14 (* Question 1.2 : Most common consecutive pairing *) 15 16 let pair_mode_tests: (int list * (int * int) ) list = [] ;; 17 18 let pair_mode (1: 'a list) : 'a * 'a = 19 notimplemented () 12 ;; 20 ;; 21 Statistics play an important part in computer science. As such, it is important to encode even the simplest statistical functions. For example, Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a field that uses a lot of statistics. It is often needed in NLP to evaluate the most common elements of language, as it helps with sentence generation. In particular, n-grams, an n-long subsequence of elements of language, are studied and used in depth. For this question, you must write tests for and implement two functions: mode and pair_mode. 1. mode : 'a list -> 'a is a function that takes a list containing any-type (a) elements and returns the most common one (aka the mode of the distribution represented by the list). The tests should be placed in the list named mode_tests; however, while these tests assume that mode is used on integers, your function should remain generic. In case of tie-breakers (two elements are presently the same, highest number of times in the list), return the first one encountered. Hint 1: You are allowed to use the function call List.sort compare (your list here). This sorts your list with the default comparison function. This also means that in the case of tie-breakers, the "lower" value should be returned. Hint 2: A tail-recursive helper might be required! 2. pair_mode : 'a list -> 'a * 'a takes any list and returns the most common pair of consecutive elements (or bi-gram) in the list. Hint 1: You should be using mode within this function! Hint 2: A lot of List. module functions may be useful here - make sure to consult them. 6 II 1 (* Section 1 : Lists *) 2 3 (* Question 1.1 : Most common element of *sorted* list *) 4 5 let mode_tests: (int list * int) list = [] ;; 7 let mode (1: 'a list) : 'a = 8 let rec aux 1 ((cur_el, cur_num) : 'a * int) ((max_el, max_num) : 'a * int) 9 notimplemented 10 in 11 notimplemented () 13 14 (* Question 1.2 : Most common consecutive pairing *) 15 16 let pair_mode_tests: (int list * (int * int) ) list = [] ;; 17 18 let pair_mode (1: 'a list) : 'a * 'a = 19 notimplemented () 12 ;; 20 ;; 21
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


