The answers are vice versa. Which is the correct solution?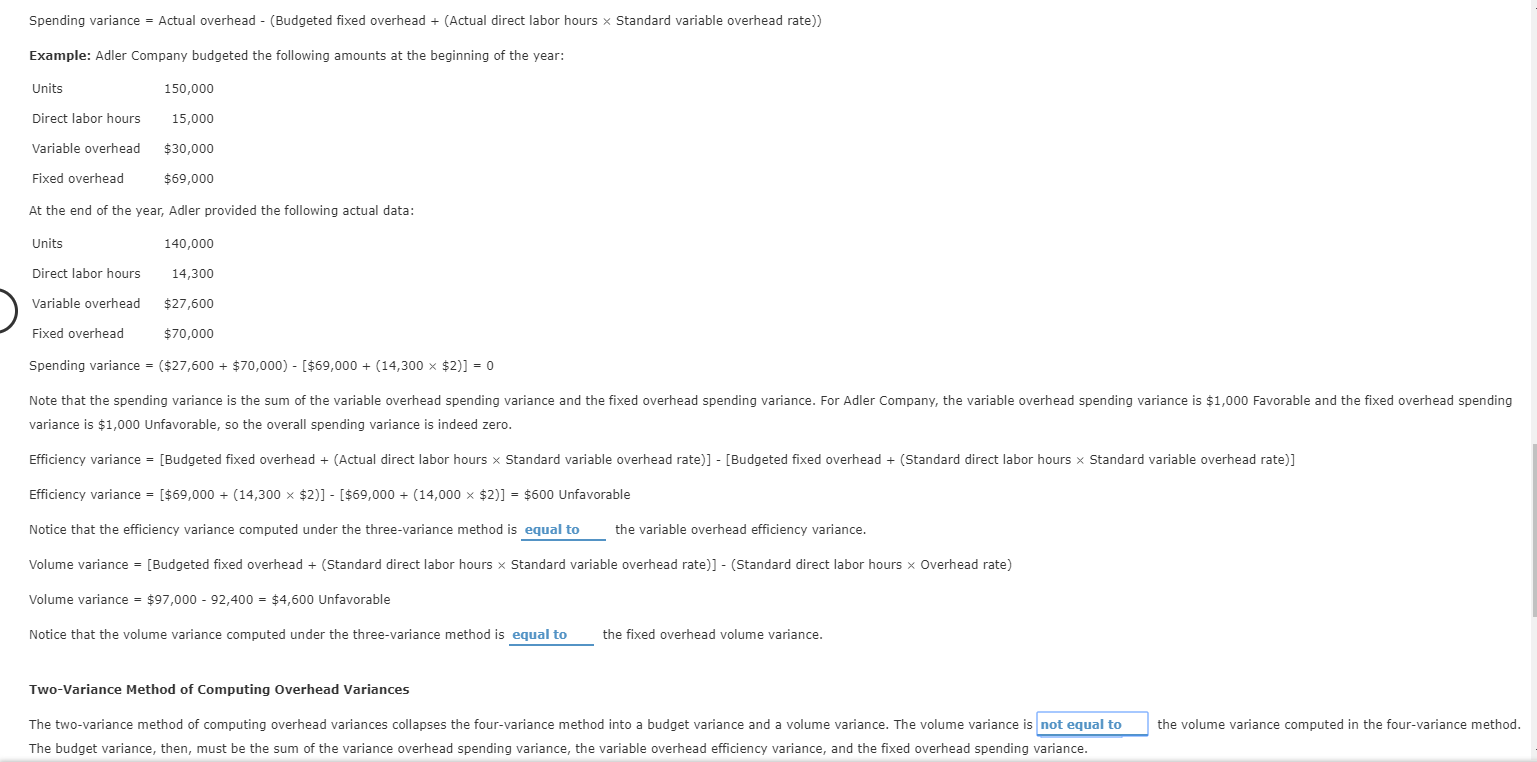
Spending variance = Actual overhead - (Budgeted fixed overhead + (Actual direct labor hours x Standard variable overhead rate) Example: Adler Company budgeted the following amounts at the beginning of the year: Units 150,000 Direct labor hours 15,000 Variable overhead $30,000 Fixed overhead $69,000 At the end of the year, Adler provided the following actual data: Units 140,000 Direct labor hours Variable overhead Fixed overhead 14,300 $27,600 $70,000 Spending variance - ($27,600 + $70,000) - ($69,000 + (14,300 x $2)] = 0 Note that the spending variance is the sum of the variable overhead spending variance and the fixed overhead spending variance. For Adler Company, the variable overhead spending variance is $1,000 Favorable and the fixed overhead spending variance is $1,000 Unfavorable, so the overall spending variance is indeed zero. Efficiency variance = (Budgeted fixed overhead + (Actual direct labor hours x Standard variable overhead rate)] - [Budgeted fixed overhead + (Standard direct labor hours x Standard variable overhead rate)] Efficiency variance = ($69,000 + (14,300 x $2)] - [$69,000 + (14,000 $2)] = $600 Unfavorable Notice that the efficiency variance computed under the three-variance method is equal to the variable overhead efficiency variance. Volume variance = (Budgeted fixed overhead + (Standard direct labor hours x Standard variable overhead rate)] - (Standard direct labor hours x Overhead rate) Volume variance = $97,000 - 92,400 = $4,600 Unfavorable Notice that the volume variance computed under the three-variance method is equal to the fixed overhead volume variance. Two-Variance Method of Computing Overhead Variances the volume variance computed in the four-variance method. The two-variance method of computing overhead variances collapses the four-variance method into a budget variance and a volume variance. The volume variance is not equal to The budget variance, then, must be the sum of the variance overhead spending variance, the variable overhead efficiency variance, and the fixed overhead spending variance. Spending variance = Actual overhead - (Budgeted fixed overhead + (Actual direct labor hours x Standard variable overhead rate) Example: Adler Company budgeted the following amounts at the beginning of the year: Units 150,000 Direct labor hours 15,000 Variable overhead $30,000 Fixed overhead $69,000 At the end of the year, Adler provided the following actual data: Units 140,000 Direct labor hours Variable overhead Fixed overhead 14,300 $27,600 $70,000 Spending variance - ($27,600 + $70,000) - ($69,000 + (14,300 x $2)] = 0 Note that the spending variance is the sum of the variable overhead spending variance and the fixed overhead spending variance. For Adler Company, the variable overhead spending variance is $1,000 Favorable and the fixed overhead spending variance is $1,000 Unfavorable, so the overall spending variance is indeed zero. Efficiency variance = (Budgeted fixed overhead + (Actual direct labor hours x Standard variable overhead rate)] - [Budgeted fixed overhead + (Standard direct labor hours x Standard variable overhead rate)] Efficiency variance = ($69,000 + (14,300 x $2)] - [$69,000 + (14,000 $2)] = $600 Unfavorable Notice that the efficiency variance computed under the three-variance method is equal to the variable overhead efficiency variance. Volume variance = (Budgeted fixed overhead + (Standard direct labor hours x Standard variable overhead rate)] - (Standard direct labor hours x Overhead rate) Volume variance = $97,000 - 92,400 = $4,600 Unfavorable Notice that the volume variance computed under the three-variance method is equal to the fixed overhead volume variance. Two-Variance Method of Computing Overhead Variances the volume variance computed in the four-variance method. The two-variance method of computing overhead variances collapses the four-variance method into a budget variance and a volume variance. The volume variance is not equal to The budget variance, then, must be the sum of the variance overhead spending variance, the variable overhead efficiency variance, and the fixed overhead spending variance







