Question
/* The Card class implements the Comparable interface. Interfaces are an important and useful topic but no longer part of the APCSA curriculum. */ public

/* The Card class implements the Comparable interface. Interfaces are an important and useful topic but no longer part of the APCSA curriculum. */
public class Card implements Comparable
public Card( String suit, String name, int rank ) { this.suit = suit.toLowerCase(); this.name = name.toLowerCase(); this.rank = rank; } public String getSuit() { return suit; } public int getRank() { return rank; } public String getName() { // new for this program return name; } public String toString() { String symbol = ""; if (suit.equals("spades")) //symbol = "\u2660"; unicode does not render correctly in codeboard //symbol = "spades "; symbol = "♠"; // this is an HTML entity, it works because codeboard renders the program output as HTML else if (suit.equals("hearts")) //symbol = "\u2665"; //symbol = "hearts "; symbol = "♥"; // this is an HTML entity, it works because codeboard renders the program output as HTML else if (suit.equals("diamonds")) //symbol = "\u2666"; //symbol = "diamonds"; symbol = "♦"; // this is an HTML entity, it works because codeboard renders the program output as HTML else //symbol = "\u2663"; //symbol = "clubs "; symbol = "♣"; // this is an HTML entity, it works because codeboard renders the program output as HTML // the following is done so that returned string always has a length of 11 if ( rank >= 2 && rank king > queen > jack ... return diffRanks; // if the ranks are the same if ( this.suit.equals( other.suit ) ) return 0; // otherwise spades > hearts > diamonds > clubs if ( this.suit.equals( "spades" ) ) return 1; if ( other.suit.equals( "spades" ) ) return -1; // neither one is spades if ( this.suit.equals( "hearts" ) ) return 1; if ( other.suit.equals( "hearts" ) ) return -1; // neither one is hearts, but the suits are different // therefore one is diamonds and the other is clubs if ( this.suit.equals( "diamonds" ) ) return 1; else return -1; } // The equals method code involves a number of concepts // that we have not covered yet // You are not responsible for its content public boolean equals( Object x ) { if ( !(x instanceof Card) ) return false; Card other = (Card)x; return this.suit.equals( other.suit ) && this.rank == other.rank; } }
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Random;
public class Deck { private ArrayList
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner( System.in ); System.out.print("Seed: "); int seed = sc.nextInt(); Deck deck = new Deck( seed ); System.out.println(); // Create a 3 by 3 array of Card objects // Add cards to the array by calling the Deck's get method
// Display the 2D array
// call the check method and print the returned value
} public static String check( Card [][] cards ) { /* Call the hasFlush and hasThreeSame methods. If there is both a flush and 3 of kind, return "GRAND PRIZE WINNER". If there is only 3 of a kind, return "THREE OF A KIND". If there is only a flush, return "FLUSH". If there is neither a flush nor 3 of a kind, return "YOU LOST" */
return "not done yet"; // placeholder } public static boolean hasFlush( Card [][] cards ) { /* Return true if three cards in a row or column have the same suit. Otherwise it returns false */
return false; // placeholder } public static boolean hasThreeSame( Card [][] cards ) { /* Return true if three cards in a row or column have the same rank. Otherwise it returns false */
return false; // placeholder } }
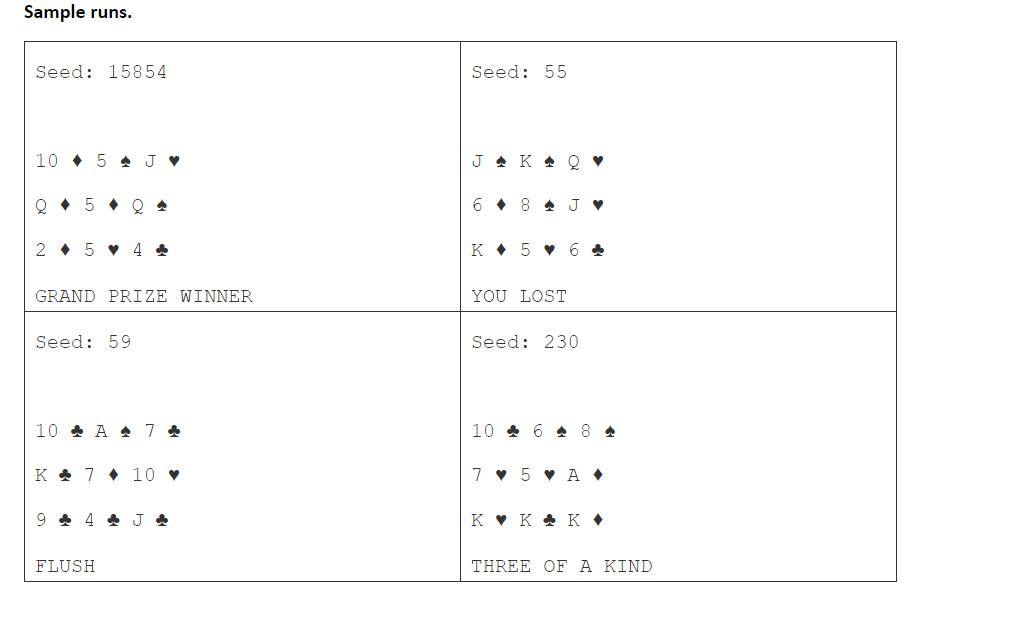
Nine Cards. This is a simple game. The user enters an integer that is used as the seed to the Random object. Then 9 cards are dealt in a 3-by-3 arrangement. If a row or column contains all the same suit, it prints FLUSH If a row or column contains all the same rank (e.g all queens), it prints THREE OF A KIND If a row or column contains all the same suit, it prints FLUSH . If a row or columns has a flush and another row or column has matching ranks, it prints GRAND PRIZE WINNER If there are no flushes or matches, it prints YOU LOST. L. Complete the portion of the main method that completes the 2D array of Cards and displays the cards. 2. Write the hasFlush method. Test this by temporarily calling it from the main method and seeing what it returns. 3. Write the hasThreeSame method. Test this by temporarily calling it from the main method and seeing what it returns. 1. Write the check method, call it from the main method, and print the returned string. Remeber to comment your program. Sample runs. Seed: 15854 Seed: 55 10 5 J JKO Q5 Q4 6 8 J 2 54 K 5 6 GRAND PRIZE WINNER YOU LOST Seed: 59 Seed: 230 10 A7 10 6 8 4 K 7 10 7 5 A 9 4 4 4J KKK FLUSH THREE OF A KIND Nine Cards. This is a simple game. The user enters an integer that is used as the seed to the Random object. Then 9 cards are dealt in a 3-by-3 arrangement. If a row or column contains all the same suit, it prints FLUSH If a row or column contains all the same rank (e.g all queens), it prints THREE OF A KIND If a row or column contains all the same suit, it prints FLUSH . If a row or columns has a flush and another row or column has matching ranks, it prints GRAND PRIZE WINNER If there are no flushes or matches, it prints YOU LOST. L. Complete the portion of the main method that completes the 2D array of Cards and displays the cards. 2. Write the hasFlush method. Test this by temporarily calling it from the main method and seeing what it returns. 3. Write the hasThreeSame method. Test this by temporarily calling it from the main method and seeing what it returns. 1. Write the check method, call it from the main method, and print the returned string. Remeber to comment your program. Sample runs. Seed: 15854 Seed: 55 10 5 J JKO Q5 Q4 6 8 J 2 54 K 5 6 GRAND PRIZE WINNER YOU LOST Seed: 59 Seed: 230 10 A7 10 6 8 4 K 7 10 7 5 A 9 4 4 4J KKK FLUSH THREE OF A KIND
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


