Question
The classified balance sheet, although generally required internationally, contains certain variations in format when reporting under IFRS. Key Points Following are the key similarities and
The classified balance sheet, although generally required internationally, contains certain variations in format when reporting under IFRS.
Key Points
Following are the key similarities and differences between GAAP and IFRS related to the closing process and the financial statements.
Similarities
- The procedures of the closing process are applicable to all companies, whether they are using IFRS or GAAP.
- IFRS generally requires a classified statement of financial position similar to the classified balance sheet under GAAP.
- IFRS follows the same guidelines as this textbook for distinguishing between current and noncurrent assets and liabilities.
Differences
- IFRS recommends but does not require the use of the title statement of financial position rather than balance sheet.
- The format of statement of financial position information is often presented differently under IFRS. Although no specific format is required, many companies that follow IFRS present statement of financial position information in this order:
- Non-current assets
- Current assets
- Equity
- Non-current liabilities
- Current liabilities
- Under IFRS, current assets are usually listed in the reverse order of liquidity. For example, under GAAP cash is listed first, but under IFRS it is listed last.
- IFRS has many differences in terminology from what are shown in your textbook. For example, in the following sample statement of financial position, notice in the investment category that stock is called shares.
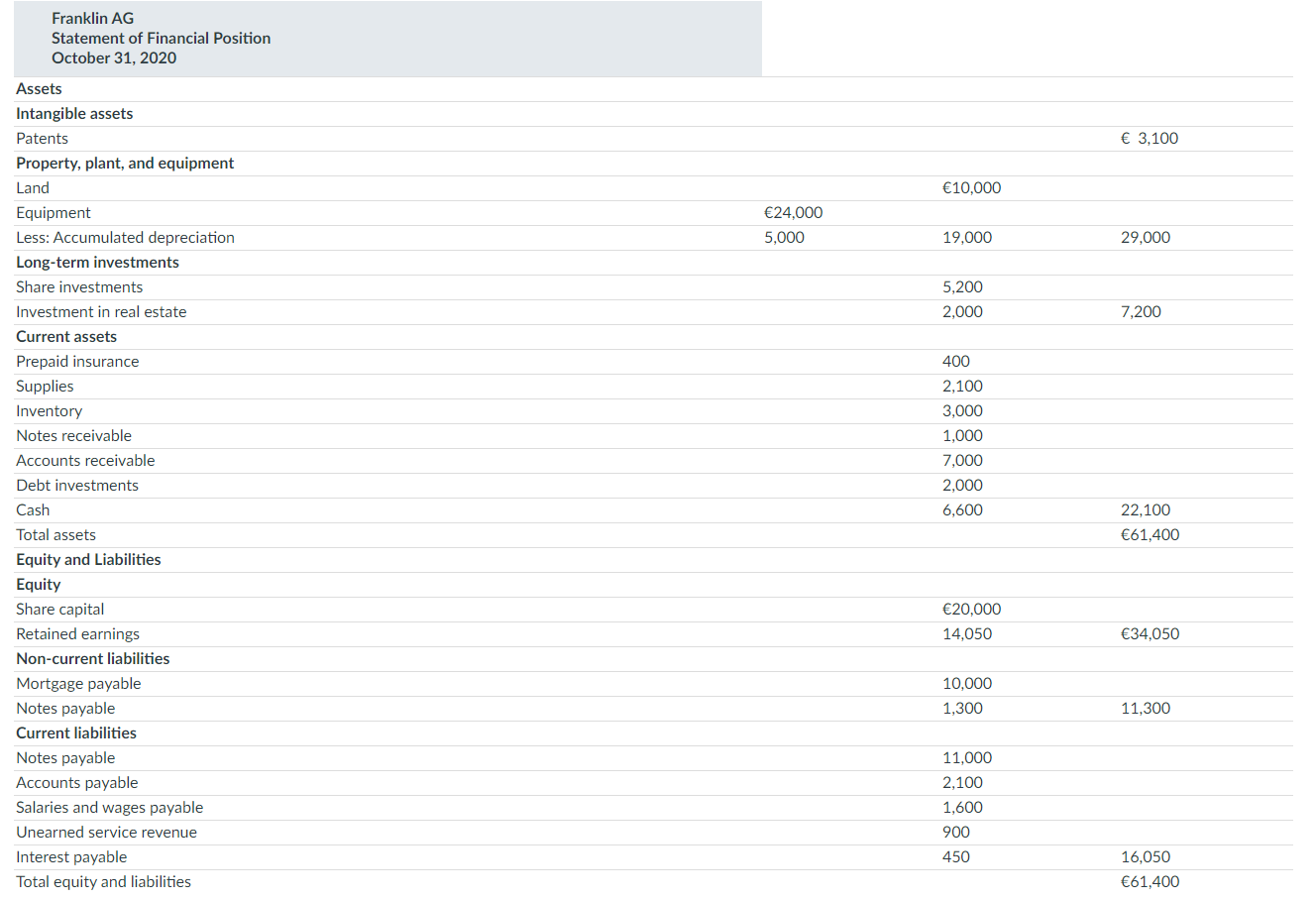
- Both GAAP and IFRS are increasing the use of fair value to report assets. However, at this point IFRS has adopted it more broadly. As examples, under IFRS companies can apply fair value to property, plant, and equipment, and in some cases intangible assets.
-
Looking to the Future
The IASB and the FASB are working on a project to converge their standards related to financial statement presentation. A key feature of the proposed framework is that each of the statements will be organized in the same format, to separate an entity's financing activities from its operating and investing activities and, further, to separate financing activities into transactions with owners and creditors. Thus, the same classifications used in the statement of financial position would also be used in the income statement and the statement of cash flows. The project has three phases. You can follow the joint financial presentation project at the FASB website.
IFRS Exercises
IFRS4.1
In what ways does the format of a statement of financial of position under IFRS often differ from a balance sheet presented under GAAP?
IFRS4.2
What term is commonly used under IFRS in reference to the balance sheet?
IFRS4.3
The statement of financial position for Sundell Company includes the following accounts (in British pounds): Accounts Receivable 12,500, Prepaid Insurance 3,600, Cash 15,400, Supplies 5,200, and Debt Investments (short-term) 6,700. Prepare the current assets section of the statement of financial position, listing the accounts in proper sequence.
IFRS4.4
The following information is available for Lessila Bowling Alley at December 31, 2020.
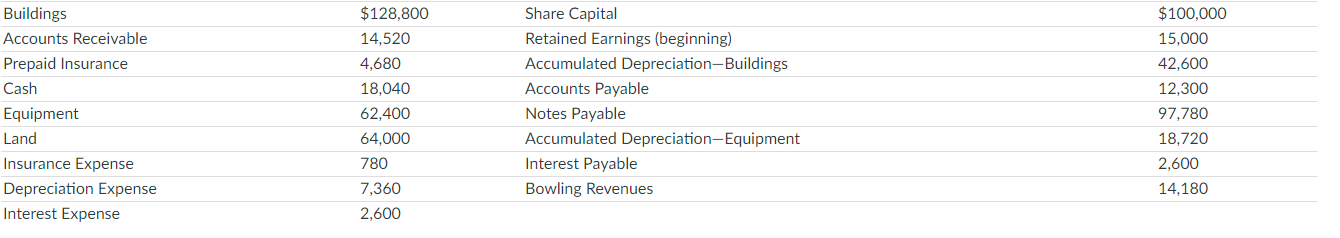 Prepare a classified statement of financial position. Assume that $13,900 of the notes payable will be paid in 2021.
Prepare a classified statement of financial position. Assume that $13,900 of the notes payable will be paid in 2021.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


