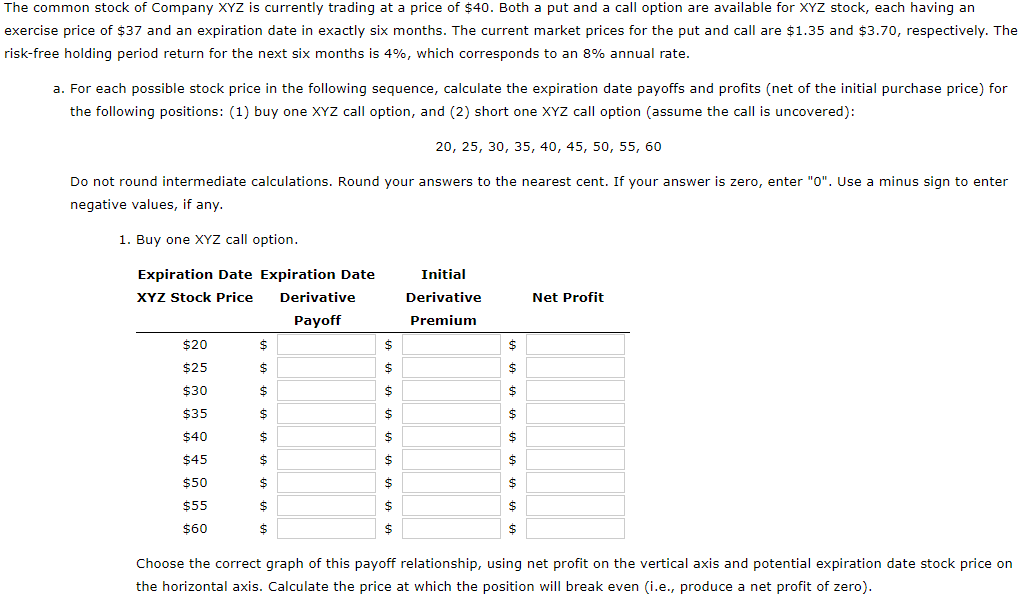
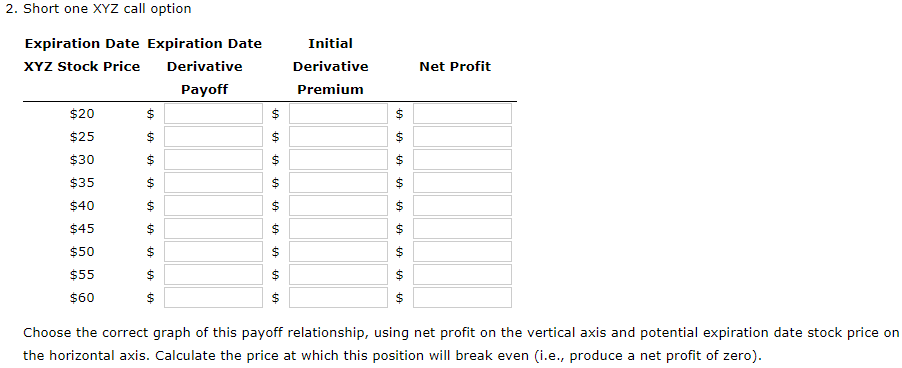
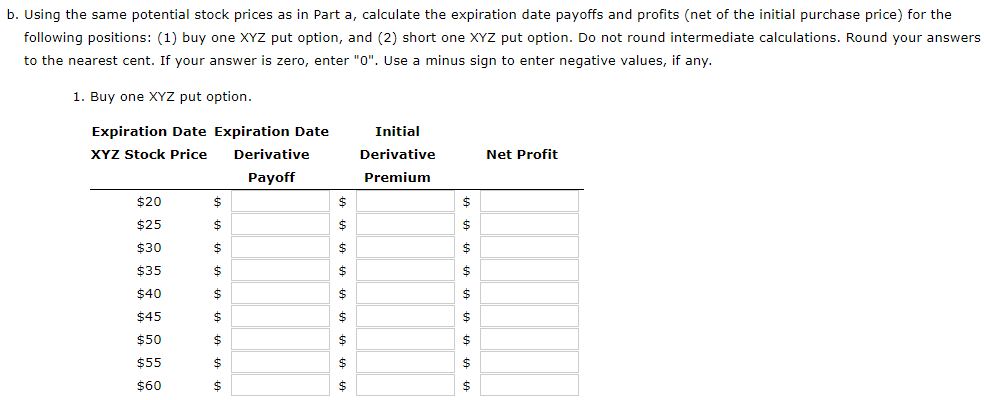
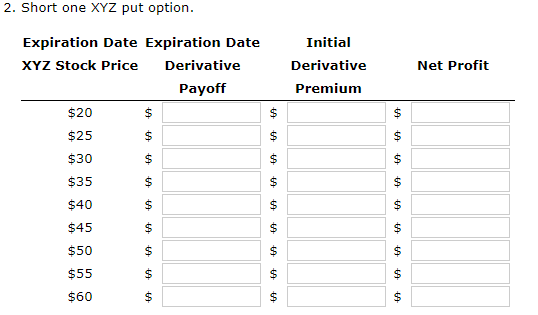

The common stock of Company XYZ is currently trading at a price of $40. Both a put and a call option are available for XYZ stock, each having an exercise price of $37 and an expiration date in exactly six months. The current market prices for the put and call are $1.35 and $3.70, respectively. The risk-free holding period return for the next six months is 4%, which corresponds to an 8% annual rate. a. For each possible stock price in the following sequence, calculate the expiration date payoffs and profits (net of the initial purchase price) for the following positions: (1) buy one XYZ call option, and (2) short one XYZ call option (assume the call is uncovered): 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60 Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. If your answer is zero, enter "0". Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any. 1. Buy one XYZ call option. Initial Derivative Premium Net Profit $ Expiration Date Expiration Date XYZ Stock Price Derivative Payoff $20 $ $ $25 $ $ $30 $ $ $35 $ $ $40 $ $ $45 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $50 $55 $60 $ $ $ $ $ $ Choose the correct graph of this payoff relationship, using net profit on the vertical axis and potential expiration date stock price on the horizontal axis. Calculate the price at which the position will break even (i.e., produce a net profit of zero). 2. Short one XYZ call option Expiration Date Expiration Date XYZ Stock Price Derivative Payoff $20 $ Initial Derivative Premium Net Profit $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $25 $ $30 $ } $35 $ $ $ $ $40 $ $ $45 $ $ $50 $ $ $55 $ 01 $60 $ $ $ Choose the correct graph of this payoff relationship, using net profit on the vertical axis and potential expiration date stock price on the horizontal axis. Calculate the price at which this position will break even i.e., produce a net profit of zero). b. Using the same potential stock prices as in Part a, calculate the expiration date payoffs and profits (net of the initial purchase price) for the following positions: (1) buy one XYZ put option, and (2) short one XYZ put option. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. If your answer is zero, enter "0". Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any. 1. Buy one XYZ put option. Initial Derivative Premium Net Profit $ $ Expiration Date Expiration Date XYZ Stock Price Derivative Payoff $20 $ $ $25 $ $ $30 $ $ $35 $ $ $40 $ $ $45 $ $ $50 $ $ $55 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $60 $ $ $ 2. Short one XYZ put option. Initial Derivative Premium Net Profit Expiration Date Expiration Date XYZ Stock Price Derivative Payoff $20 $ $ $25 $ $ $30 $ $ $35 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 01 $40 $ $45 $ $ $ $ $50 $55 $60 $ $ c. Determine whether the $2.35 difference in the market prices between the call and put options is consistent with the put-call parity relationship for European-style contracts. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest cent. Difference between the call and put prices according to the put-call parity: $ Put-call parity -Select- for this European-style contract. The common stock of Company XYZ is currently trading at a price of $40. Both a put and a call option are available for XYZ stock, each having an exercise price of $37 and an expiration date in exactly six months. The current market prices for the put and call are $1.35 and $3.70, respectively. The risk-free holding period return for the next six months is 4%, which corresponds to an 8% annual rate. a. For each possible stock price in the following sequence, calculate the expiration date payoffs and profits (net of the initial purchase price) for the following positions: (1) buy one XYZ call option, and (2) short one XYZ call option (assume the call is uncovered): 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60 Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. If your answer is zero, enter "0". Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any. 1. Buy one XYZ call option. Initial Derivative Premium Net Profit $ Expiration Date Expiration Date XYZ Stock Price Derivative Payoff $20 $ $ $25 $ $ $30 $ $ $35 $ $ $40 $ $ $45 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $50 $55 $60 $ $ $ $ $ $ Choose the correct graph of this payoff relationship, using net profit on the vertical axis and potential expiration date stock price on the horizontal axis. Calculate the price at which the position will break even (i.e., produce a net profit of zero). 2. Short one XYZ call option Expiration Date Expiration Date XYZ Stock Price Derivative Payoff $20 $ Initial Derivative Premium Net Profit $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $25 $ $30 $ } $35 $ $ $ $ $40 $ $ $45 $ $ $50 $ $ $55 $ 01 $60 $ $ $ Choose the correct graph of this payoff relationship, using net profit on the vertical axis and potential expiration date stock price on the horizontal axis. Calculate the price at which this position will break even i.e., produce a net profit of zero). b. Using the same potential stock prices as in Part a, calculate the expiration date payoffs and profits (net of the initial purchase price) for the following positions: (1) buy one XYZ put option, and (2) short one XYZ put option. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent. If your answer is zero, enter "0". Use a minus sign to enter negative values, if any. 1. Buy one XYZ put option. Initial Derivative Premium Net Profit $ $ Expiration Date Expiration Date XYZ Stock Price Derivative Payoff $20 $ $ $25 $ $ $30 $ $ $35 $ $ $40 $ $ $45 $ $ $50 $ $ $55 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $60 $ $ $ 2. Short one XYZ put option. Initial Derivative Premium Net Profit Expiration Date Expiration Date XYZ Stock Price Derivative Payoff $20 $ $ $25 $ $ $30 $ $ $35 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 01 $40 $ $45 $ $ $ $ $50 $55 $60 $ $ c. Determine whether the $2.35 difference in the market prices between the call and put options is consistent with the put-call parity relationship for European-style contracts. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest cent. Difference between the call and put prices according to the put-call parity: $ Put-call parity -Select- for this European-style contract











