Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The condenser of a large steam power plant is a heat exchanger in which steam is condensed to liquid water. Assume the condenser to
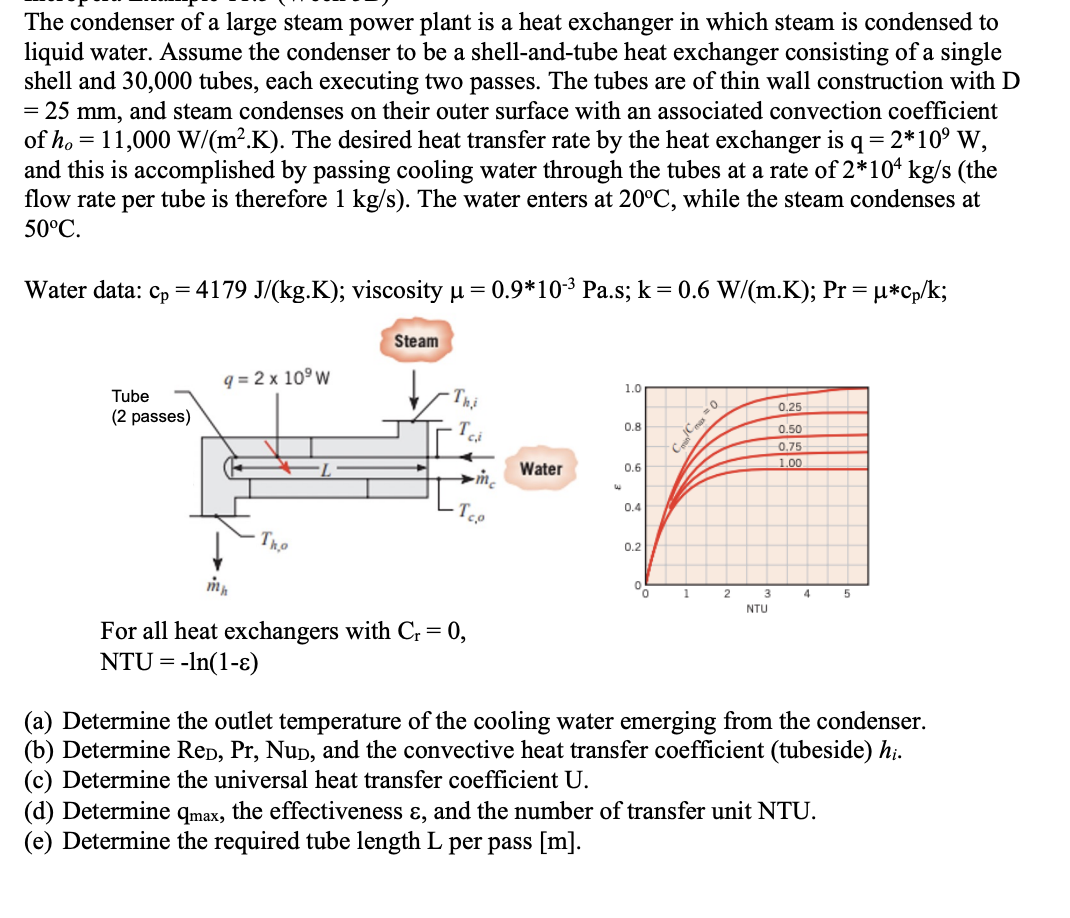
The condenser of a large steam power plant is a heat exchanger in which steam is condensed to liquid water. Assume the condenser to be a shell-and-tube heat exchanger consisting of a single shell and 30,000 tubes, each executing two passes. The tubes are of thin wall construction with D = 25 mm, and steam condenses on their outer surface with an associated convection coefficient of ho=11,000 W/(m2.K). The desired heat transfer rate by the heat exchanger is q = 2*10 W, and this is accomplished by passing cooling water through the tubes at a rate of 2*104 kg/s (the flow rate per tube is therefore 1 kg/s). The water enters at 20C, while the steam condenses at 50C. Water data: cp=4179 J/(kg.K); viscosity = 0.9*10- Pa.s; k = 0.6 W/(m.K); Pr = *cp/k; Steam q=2x 10W Tube (2 passes) Thi 1.0 0.8 Water 0.6 mc w 0.4 -Tco mh Tho For all heat exchangers with Cr = 0, NTU = -ln(1-) 0.2 Carl Cox = 0 0.25 0.50 0,75 1.00 1 3 4 5 NTU (a) Determine the outlet temperature of the cooling water emerging from the condenser. (b) Determine Red, Pr, NuD, and the convective heat transfer coefficient (tubeside) hi. (c) Determine the universal heat transfer coefficient U. (d) Determine qmax, the effectiveness &, and the number of transfer unit NTU. (e) Determine the required tube length L per pass [m].
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


