Question: The elementary reversible liquid-phase reaction A takes place in a CSTR with a heat exchanger. Pure A enters the reactor. (a) Derive an expression
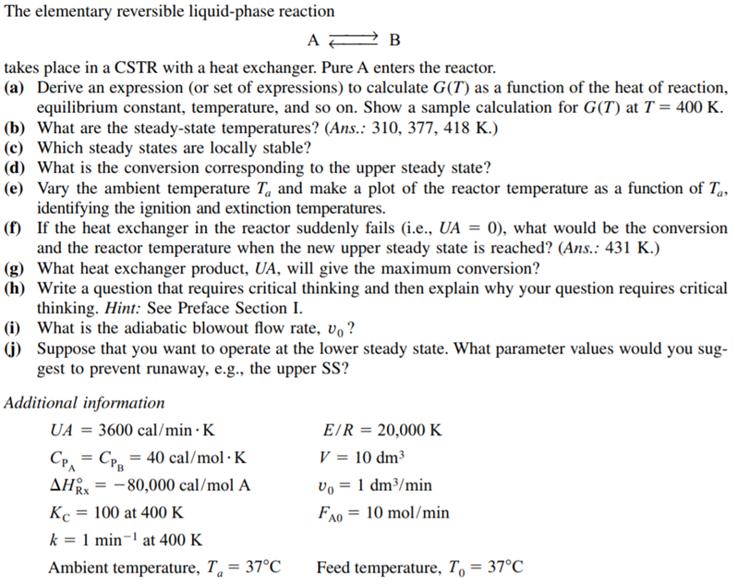
The elementary reversible liquid-phase reaction A takes place in a CSTR with a heat exchanger. Pure A enters the reactor. (a) Derive an expression (or set of expressions) to calculate G(T) as a function of the heat of reaction, equilibrium constant, temperature, and so on. Show a sample calculation for G(T) at T = 400 K. (b) What are the steady-state temperatures? (Ans.: 310, 377, 418 K.) (c) Which steady states are locally stable? (d) What is the conversion corresponding to the upper steady state? (e) Vary the ambient temperature T, and make a plot of the reactor temperature as a function of T., identifying the ignition and extinction temperatures. (f) If the heat exchanger in the reactor suddenly fails (i.e., UA = 0), what would be the conversion and the reactor temperature when the new upper steady state is reached? (Ans.: 431 K.) (g) What heat exchanger product, UA, will give the maximum conversion? (h) Write a question that requires critical thinking and then explain why your question requires critical thinking. Hint: See Preface Section I. (i) What is the adiabatic blowout flow rate, v, ? (j) Suppose that you want to operate at the lower steady state. What parameter values would you sug- gest to prevent runaway, e.g., the upper SS? Additional information UA = 3600 cal/min K EIR = 20,000 K C = Cr = 40 cal/mol K AH = -80,000 cal/mol A Kc = 100 at 400 K V = 10 dm3 vo = 1 dm/min Rx FA0 = 10 mol/min k = 1 min- at 400 K Ambient temperature, T = 37C Feed temperature, T, = 37C
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To address this question we will go through each part step by step Heres a breakdown for each a Derive an expression for GT The function GT typically ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


