Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The evalexp function take in 2 arguments, a expression (p1) and a binding for that expression. E.G given an expression and a binding as follow:
The evalexp function take in 2 arguments, a expression (p1) and a binding for that expression. E.G
given an expression and a binding as follow: (and x (or x (and y (not z)))) Bindings: {x false, z true}
it should bind x and z into the expression and evaluate that expression. The function should therefore evaluate (and false (or false (and y (not true)))), returning False.
If the result might be a symbol like (and x y) bindings: {y: true}, return x.
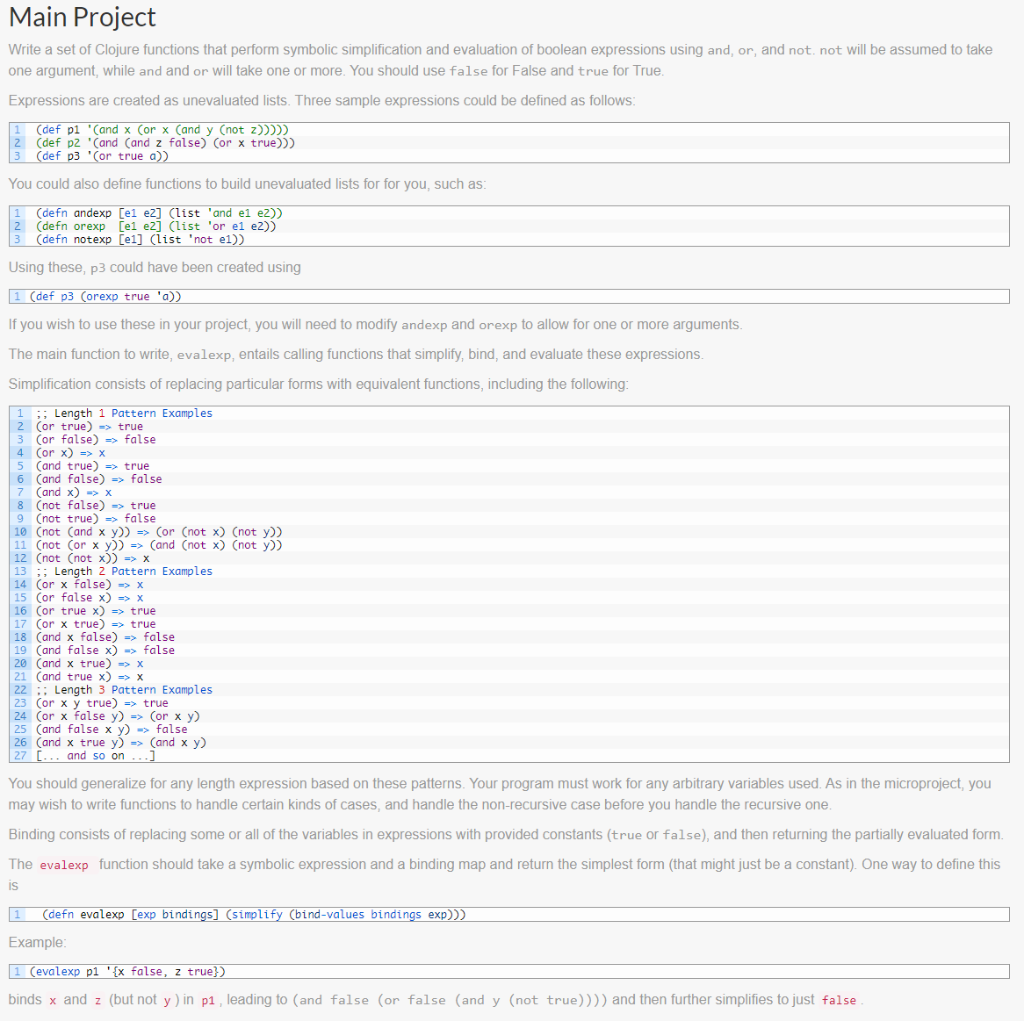
Main Project Write a set of Clojure functions that perform symbolic simplification and evaluation of boolean expressions using and, or, and not. not will be assumed to take one argument, while and and or will take one or more. You should use false for False and true for True. Expressions are created as unevaluated lists. Three sample expressions could be defined as follows: (def pi '(and x Cor x Cand y (not z))))) (def pz Cand Cand z false) Cor x true)) (def p3 (or true a)) You could also define functions to build unevaluated lists for for you, such as: (defn andexp (el e2] (list and el ez)) 2 (defn orexp [ei e2] (list 'or el e2) 3 (defn notexp [ei] (list 'not e1) Using these, p3 could have been created using 1 (def P3 Corexp true 'a)) If you wish to use these in your project, you will need to modify andexp and orexp to allow for one or more arguments. The main function to write, evalexp, entails calling functions that simplify, bind, and evaluate these expressions. Simplification consists of replacing particular forms with equivalent functions, including the following: ; Length 1 Pattern Examples 2 (or true) -> true 3 (or false) => false 4 Cor x) => X Cand true) => true 6 Cand false) => false 7 Cand x) -> X 8 (not false) -> true 9 (not true) => false 10 (not (and x y)) => (or (not x) (not y)) 11 (not (or xy)) => (and (not x) (not y)) 12 (not (not x)) => X 13 ;; Length 2 Pattern Examples 14 (or x false) => X 15 (or false x) => X 16 (or true x) => true 17 (or x true) => true 18 Cand x false) => false 19 (and false x) => false 20 (and x true) -> X 21 (and true x) => X 22 :: Length 3 Pattern Examples 23 (or x y true) => true 24 (or x false y) => (or x y) 25 (and false x y) => false 26 (and x true y) => (and x y) 27 [.., and so on ...] You should generalize for any length expression based on these patterns. Your program must work for any arbitrary variables used. As in the microproject, you may wish to write functions to handle certain kinds of cases, and handle the non-recursive case before you handle the recursive one. Binding consists of replacing some or all of the variables in expressions with provided constants (true or false), and then returning the partially evaluated form. The evalexp function should take a symbolic expression and a binding map and return the simplest form (that might just be a constant). One way to define this IS 1 (defn evalexp [exp bindings] (simplify (bind-values bindings exp))) Example: 1 (evalexp p1 '{x false, z true}) binds x and z (but not y) in p1, leading to (and false (or false (and y (not true)))) and then further simplifies to just false
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


