Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The Expected Return on Union Pacific Corporation's Common Stock Suppose that in early 2009 you had been asked to estimate the company cost of capital
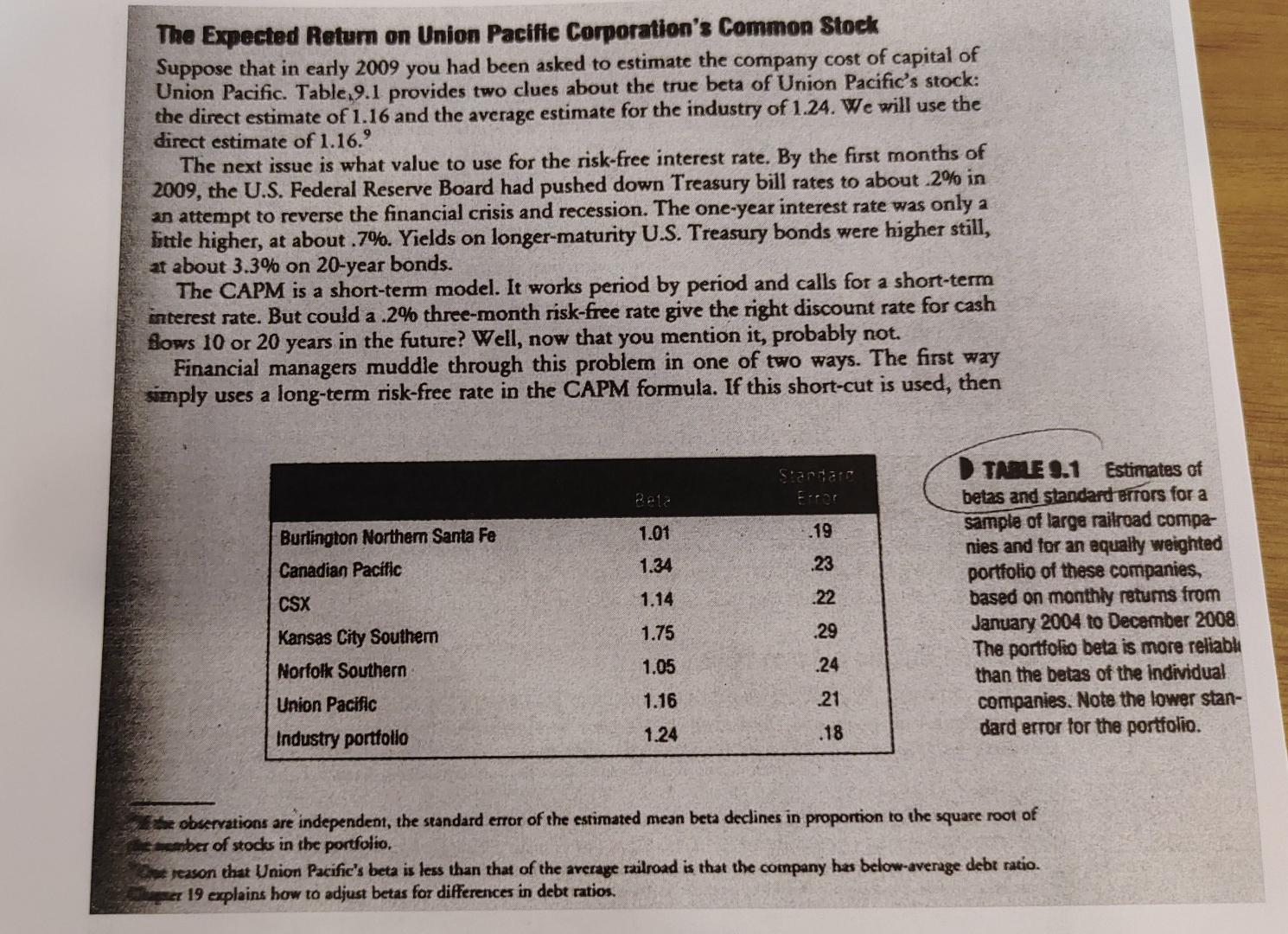

The Expected Return on Union Pacific Corporation's Common Stock Suppose that in early 2009 you had been asked to estimate the company cost of capital of Union Pacific. Table 9.1 provides two clues about the true beta of Union Pacific's stock: the direct estimate of 1.16 and the average estimate for the industry of 1.24. We will use the direct estimate of 1.16.9 The next issue is what value to use for the risk-free interest rate. By the first months of 2009, the U.S. Federal Reserve Board had pushed down Treasury bill rates to about 2% in an attempt to reverse the financial crisis and recession. The one-year interest rate was only a little higher, at about .7%. Yields on longer-maturity U.S. Treasury bonds were higher still, at about 3.3% on 20-year bonds. The CAPM is a short-term model. It works period by period and calls for a short-term interest rate. But could a .2% three-month risk-free rate give the right discount rate for cash flows 10 or 20 years in the future? Well, now that you mention it, probably not. Financial managers muddle through this problem in one of two ways. The first way simply uses a long-term risk-free rate in the CAPM formula. If this short-cut is used, then Starta 1.01 -19 Burlington Northern Santa Fe Canadian Pacific 1.34 .23 CSX 1.14 .22 TALE 9.1 Estimates of betas and standard Brrors for a sample of large railroad compe- nies and for an equally weighted portfolio of these companies, based on monthly retums from January 2004 to December 2008 The portfolio beta is more reliabh than the betas of the Individual companies. Note the lower stan- dard error for the portfolio. Kansas City Southern 1.75 .29 Norfolk Southern 1.05 .24 Union Pacific 1.16 .21 Industry portfolio 1.24 .18 de observations are independent, the standard error of the estimated mean beta declines in proportion to the square root of arber of stocks in the portfolio reason that Union Pacific's beta is less than that of the average railroad is that the company has below-average debt ratio. er 19 explains how to adjust betas for differences in debt ratios. TURN INTERMEDIATE 17. Listed below are some common terms of sale. Can you explain that each means? 2 2/30, pet 60. b. 275, EOM, net 30. C COD. 18 Some of the items in Problem 17 involve a cash discount. Por each of these, calculate the rate of interest paid by customers who pay on the due date instead of taking the cash discount 19. Phoenix Lambert currently sells its goods cash-on-delivery. Howeter, the financial manager believes that by offering credit terms of 2/10 net 30 the company can increase sales by 49, without significant additional costs. If the interest rate is 6% and the profit margin is 5%, pould you recommend offering credit? Assume first that all customers take the cash discount. Then assume that they all pay on day 30. 20 As treasures of the Universal Bed Corporation, Aristotle Procrustes is worried about his bed debt ratio, which is currently running at 6%. He believes that imposing a more stringent credit policy might reduce sales by 5% and reduce the bad debt ratio to 4%. I the cost of goods sold is 80% of the selling price, should Mr. Procrustes adopt the more stringent policy? 21. Jim Khana, the credit manager of Velcro Saddles, is reappraising the company's credit policy. Velcro sells on terms of net 30. Cost of goods sold is 85% of sales, and feed costs are a further 54 of sales. Velcro classifies customers on a scale of 1 to 4. Daring the past five the collection experience was as follows: Rierage Caterina Sazis 35 Pereira Classic 103 Perces e Sales ligadefaulting Access 0 2.0 2. 10.0 8 $ R 3 20.0 4 The crerage interest rate was 15%. What condusions (if any) can you draw about Velcro's credit policy? What other fac- tons should be taken into account before changing this policy? z Look again at Problem 21. Suppose (a) that it costs $95 to classify each new credit applicant and (b) that an almost equal proportion of new applicants fills into each of the four catego ries. In what circumstances should Mr. Khana pot bother to undertake a credit check? 23 Until recently, Augean Cleaning Products sold its products on terms of net 60, with a average collection period of 75 days. In an attempt to induce customers to pay more promptly, it has changed its terms to 2/10, EOM, net 60. The initial effect of the changed terms is as follows: A.erage Colection Peness Us Cash Discount Net Percent of Sales with Cash Discount 30 80 60 Some stones dobut the cash discount even though they pay after the specified dela. Calculate the effect of the changed terms. Assume Sales volume is unchanged. The interest rate is 12%. The Expected Return on Union Pacific Corporation's Common Stock Suppose that in early 2009 you had been asked to estimate the company cost of capital of Union Pacific. Table 9.1 provides two clues about the true beta of Union Pacific's stock: the direct estimate of 1.16 and the average estimate for the industry of 1.24. We will use the direct estimate of 1.16.9 The next issue is what value to use for the risk-free interest rate. By the first months of 2009, the U.S. Federal Reserve Board had pushed down Treasury bill rates to about 2% in an attempt to reverse the financial crisis and recession. The one-year interest rate was only a little higher, at about .7%. Yields on longer-maturity U.S. Treasury bonds were higher still, at about 3.3% on 20-year bonds. The CAPM is a short-term model. It works period by period and calls for a short-term interest rate. But could a .2% three-month risk-free rate give the right discount rate for cash flows 10 or 20 years in the future? Well, now that you mention it, probably not. Financial managers muddle through this problem in one of two ways. The first way simply uses a long-term risk-free rate in the CAPM formula. If this short-cut is used, then Starta 1.01 -19 Burlington Northern Santa Fe Canadian Pacific 1.34 .23 CSX 1.14 .22 TALE 9.1 Estimates of betas and standard Brrors for a sample of large railroad compe- nies and for an equally weighted portfolio of these companies, based on monthly retums from January 2004 to December 2008 The portfolio beta is more reliabh than the betas of the Individual companies. Note the lower stan- dard error for the portfolio. Kansas City Southern 1.75 .29 Norfolk Southern 1.05 .24 Union Pacific 1.16 .21 Industry portfolio 1.24 .18 de observations are independent, the standard error of the estimated mean beta declines in proportion to the square root of arber of stocks in the portfolio reason that Union Pacific's beta is less than that of the average railroad is that the company has below-average debt ratio. er 19 explains how to adjust betas for differences in debt ratios. TURN INTERMEDIATE 17. Listed below are some common terms of sale. Can you explain that each means? 2 2/30, pet 60. b. 275, EOM, net 30. C COD. 18 Some of the items in Problem 17 involve a cash discount. Por each of these, calculate the rate of interest paid by customers who pay on the due date instead of taking the cash discount 19. Phoenix Lambert currently sells its goods cash-on-delivery. Howeter, the financial manager believes that by offering credit terms of 2/10 net 30 the company can increase sales by 49, without significant additional costs. If the interest rate is 6% and the profit margin is 5%, pould you recommend offering credit? Assume first that all customers take the cash discount. Then assume that they all pay on day 30. 20 As treasures of the Universal Bed Corporation, Aristotle Procrustes is worried about his bed debt ratio, which is currently running at 6%. He believes that imposing a more stringent credit policy might reduce sales by 5% and reduce the bad debt ratio to 4%. I the cost of goods sold is 80% of the selling price, should Mr. Procrustes adopt the more stringent policy? 21. Jim Khana, the credit manager of Velcro Saddles, is reappraising the company's credit policy. Velcro sells on terms of net 30. Cost of goods sold is 85% of sales, and feed costs are a further 54 of sales. Velcro classifies customers on a scale of 1 to 4. Daring the past five the collection experience was as follows: Rierage Caterina Sazis 35 Pereira Classic 103 Perces e Sales ligadefaulting Access 0 2.0 2. 10.0 8 $ R 3 20.0 4 The crerage interest rate was 15%. What condusions (if any) can you draw about Velcro's credit policy? What other fac- tons should be taken into account before changing this policy? z Look again at Problem 21. Suppose (a) that it costs $95 to classify each new credit applicant and (b) that an almost equal proportion of new applicants fills into each of the four catego ries. In what circumstances should Mr. Khana pot bother to undertake a credit check? 23 Until recently, Augean Cleaning Products sold its products on terms of net 60, with a average collection period of 75 days. In an attempt to induce customers to pay more promptly, it has changed its terms to 2/10, EOM, net 60. The initial effect of the changed terms is as follows: A.erage Colection Peness Us Cash Discount Net Percent of Sales with Cash Discount 30 80 60 Some stones dobut the cash discount even though they pay after the specified dela. Calculate the effect of the changed terms. Assume Sales volume is unchanged. The interest rate is 12%
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


