Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The feasible set of a linear programming problem and a mixed-integer problem is given in Figure 1. The feasible region depicts the area within
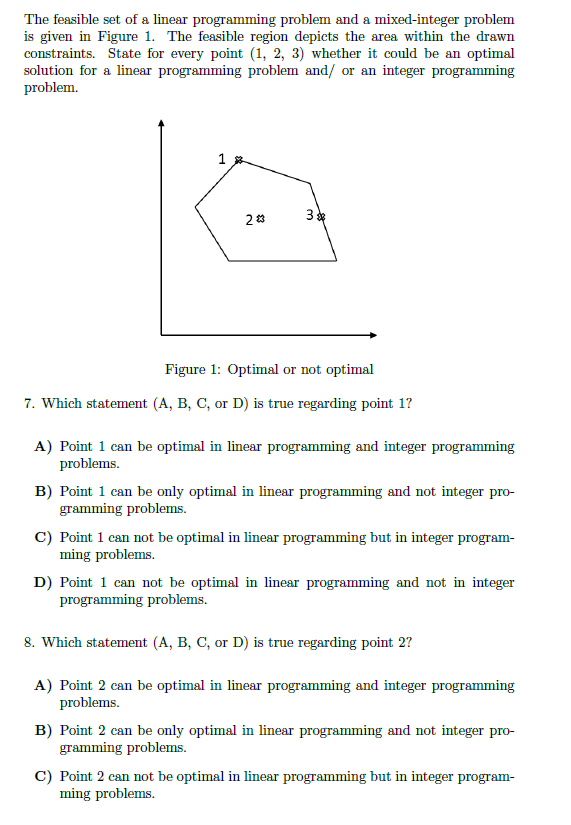

The feasible set of a linear programming problem and a mixed-integer problem is given in Figure 1. The feasible region depicts the area within the drawn constraints. State for every point (1, 2, 3) whether it could be an optimal solution for a linear programming problem and/ or an integer programming problem. 23 3* m Figure 1: Optimal or not optimal 7. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 1? A) Point 1 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 1 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 1 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 1 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems. 8. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 2? A) Point 2 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 2 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 2 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 2 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems. 9. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 37 A) Point 3 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 3 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 3 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 3 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems. The feasible set of a linear programming problem and a mixed-integer problem is given in Figure 1. The feasible region depicts the area within the drawn constraints. State for every point (1, 2, 3) whether it could be an optimal solution for a linear programming problem and/ or an integer programming problem. 23 3* m Figure 1: Optimal or not optimal 7. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 1? A) Point 1 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 1 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 1 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 1 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems. 8. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 2? A) Point 2 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 2 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 2 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 2 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems. 9. Which statement (A, B, C, or D) is true regarding point 37 A) Point 3 can be optimal in linear programming and integer programming problems. B) Point 3 can be only optimal in linear programming and not integer pro- gramming problems. C) Point 3 can not be optimal in linear programming but in integer program- ming problems. D) Point 3 can not be optimal in linear programming and not in integer programming problems.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.41 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
The skin friction coefficient Cf for a laminar boundary ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


