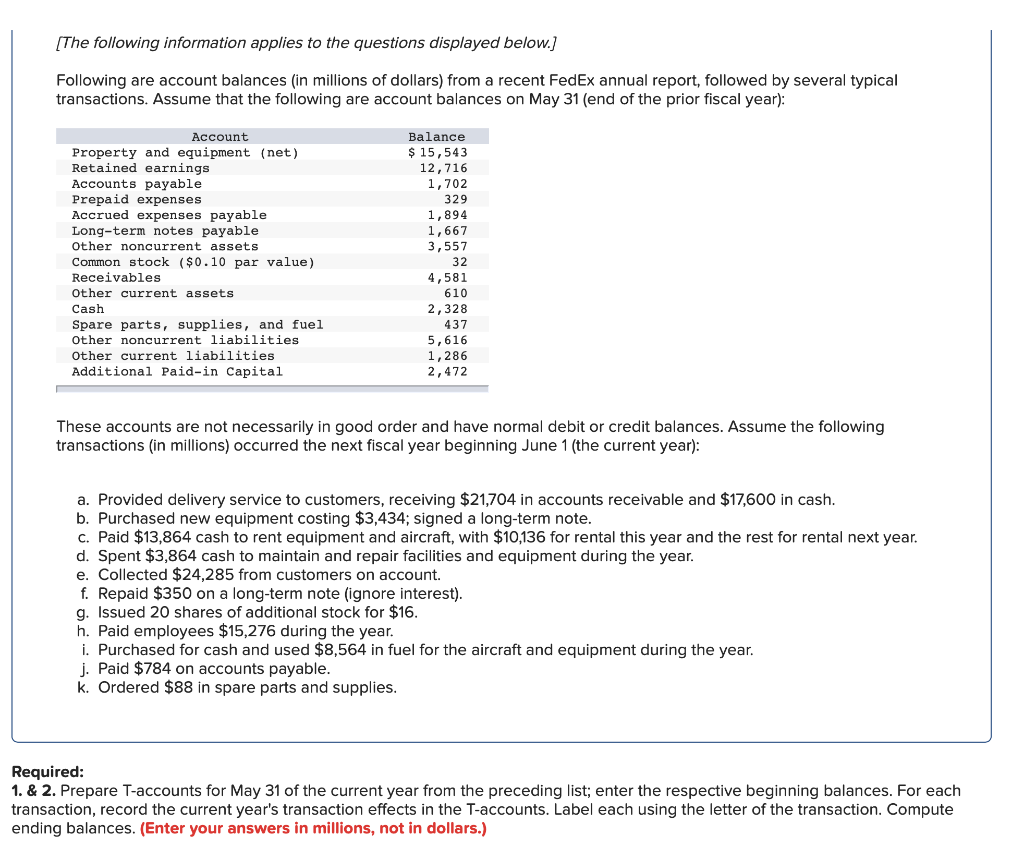
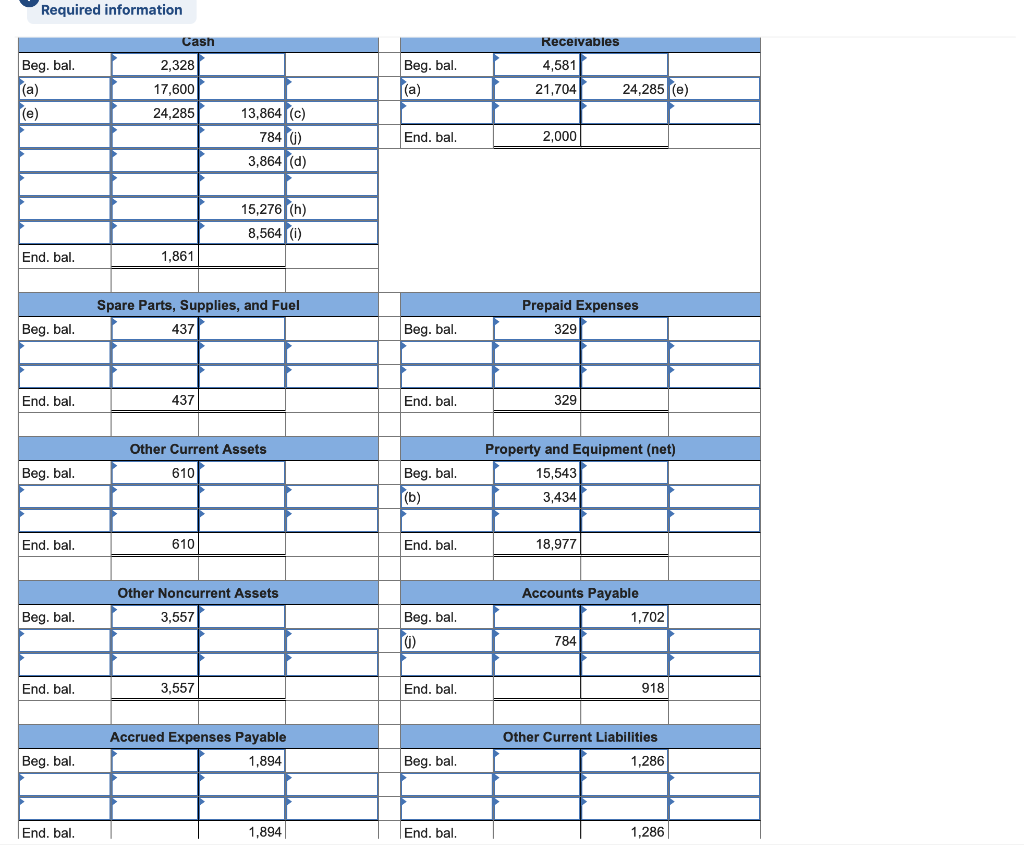
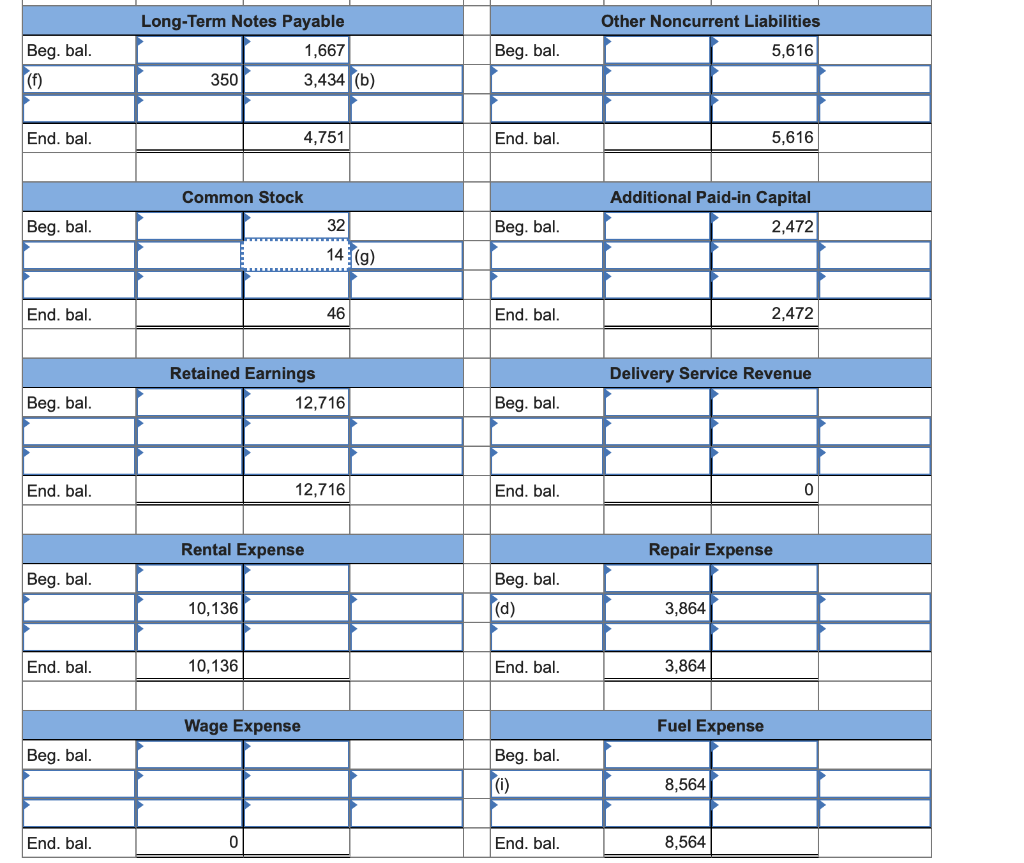
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.) Following are account balances (in millions of dollars) from a recent FedEx annual report, followed by several typical transactions. Assume that the following are account balances on May 31 (end of the prior fiscal year): Balance $ 15,543 12,716 1,702 . . Account Property and equipment (net) Retained earnings Accounts payable Prepaid expenses Accrued expenses payable Long-term notes payable Other noncurrent assets Common stock ($0.10 par value) Receivables Other current assets Cash Spare parts, supplies, and fuel Other noncurrent liabilities Other current liabilities Additional Paid-in Capital wou un acow O NA 5,616 1,286 2,472 These accounts are not necessarily in good order and have normal debit or credit balances. Assume the following transactions (in millions) occurred the next fiscal year beginning June 1 (the current year): a. Provided delivery service to customers, receiving $21,704 in accounts receivable and $17,600 in cash. b. Purchased new equipment costing $3,434; signed a long-term note. C. Paid $13,864 cash to rent equipment and aircraft, with $10,136 for rental this year and the rest for rental next year. d. Spent $3,864 cash to maintain and repair facilities and equipment during the year. e. Collected $24,285 from customers on account. f. Repaid $350 on a long-term note (ignore interest). g. Issued 20 shares of additional stock for $16. h. Paid employees $15,276 during the year. i. Purchased for cash and used $8,564 in fuel for the aircraft and equipment during the year. j. Paid $784 on accounts payable. k. Ordered $88 in spare parts and supplies. Required: 1. & 2. Prepare T-accounts for May 31 of the current year from the preceding list; enter the respective beginning balances. For each transaction, record the current year's transaction effects in the T-accounts. Label each using the letter of the transaction. Compute ending balances. (Enter your answers in millions, not in dollars.) Required information Cash Beg. bal. (a) (e) 2,328 17,600] 24,285 Beg. bal. (a) Receivables 4,581 21,704 24,285(e) 13,864 (c) 7840) 3,864 (d) End. bal. 2,000 15,276 (n) 8,564 (1) End. bal. 1,861 Spare Parts, Supplies, and Fuel 437| Prepaid Expenses 329 Beg. bal. Beg. bal. End. bal. 437 End. bal. 329 Other Current Assets Beg. bal. Beg. bal. Property and Equipment (net) 15,543 3,434| End. bal. 610 End. bal. 18,977 Other Noncurrent Assets 3,557 Beg. bal. Beg. bal. 0 Accounts Payable 1,702 784 End. bal. 3,557 End. bal. 918 Accrued Expenses Payable 1,894 Other Current Liabilities 1,286 Beg. bal. Beg. bal. End. bal. 1,894 End. bal. 1,286 Long-Term Notes Payable 1,667 350 3,434 (b) Other Noncurrent Liabilities 5,616 Beg. bal. Beg. bal. End. bal. 4,751 End. bal. 5,616 Common Stock Additional Paid-in Capital 2,472 Beg. bal. 32 Beg. bal. 14 (9) End. bal. 46 End. bal. 2,472 Delivery Service Revenue Retained Earnings 12,716 Beg. bal. Beg. bal. End. bal. 12,716 End. bal. 10 Rental Expense Repair Expense Beg. bal. Beg. bal. (d) 10,136 3,864 End. bal. 10,136 End. bal. 3,864 Wage Expense Fuel Expense Beg. bal. Beg. bal. 100) 8,564 End. bal. 0 End. bal. 8,564









