The following list summarizes the transactions that took place during a start ups second year of operations. Using the information below (and assuming FIFO for inventory), create a Balance Sheet and Income Statement.

The information for year one is the following:
The startup uses straight line when depreciating long-term assets and a perpetual inventory system. It has an estimated tax rate of 35%.
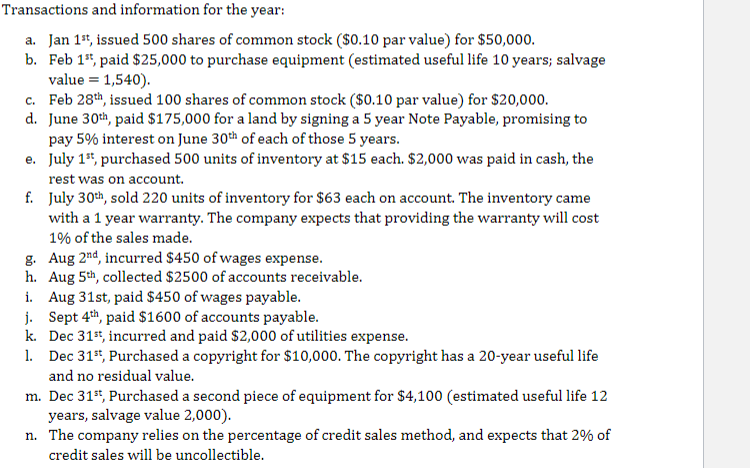
Transactions and information for the year: a. Jan 1st Spent $3,500 to improve the first piece of equipment purchased in Year 1. Revised useful life is 5 more years while the new salvage value is $2,000. b. Jan 2nd, ordered and received 200 units of inventory purchased on account for $13 each c. Jan 15th, paid $100 to settle a warranty claim from a customer. d. Feb 3rd, ordered and received 150 units of inventory purchased on account for $12 each 0. Feb 22nd, sold 250 units of inventory at $65 each. $10,000 was on account. The inventory came with a 1 year warranty. The company expects that providing the warranty will cost 1% of the sales made. e. March 1st, incurred and paid $900 of wages expense f. Mar 30th, collected $5000 of accounts receivable g. April 1st, paid $50 to settle a warranty claim from a customer. h. May 2nd, Paid $4000 of accounts payable. i. June 1st, Paid $409 of taxes payable j. June 30th, made first interest payment on Note Payable. k. Aug 12th, wrote-off a $250 account receivable for a customer who filed for bankruptcy. p. Oct 12th, sold 100 units of inventory at $56 each. The inventory came with a 1 year warranty. The company expects that providing the warranty will cost 1% of the sales made. 1. Dec 31st, spent $1,500 at end of year to repair equipment. m. Estimated that 2% of Year 2 sales on account would not be collected. n. Estimated tax rate is 35% Transactions and information for the year: a. Jan 1st, issued 500 shares of common stock ($0.10 par value) for $50,000. b. Feb 1st, paid $25,000 to purchase equipment (estimated useful life 10 years; salvage value = 1,540) C. Feb 28th, issued 100 shares of common stock ($0.10 par value) for $20,000. d. June 30th, paid $175,000 for a land by signing a 5 year Note Payable, promising to pay 5% interest on June 30th of each of those 5 years. e. July 15, purchased 500 units of inventory at $15 each. $2,000 was paid in cash, the rest was on account. f. July 30th, sold 220 units of inventory for $63 each on account. The inventory came with a 1 year warranty. The company expects that providing the warranty will cost 1% of the sales made. g. Aug 2nd, incurred $450 of wages expense. h. Aug 5th, collected $2500 of accounts receivable. i. Aug 31st, paid $450 of wages payable. j. Sept 4th, paid $1600 of accounts payable. k. Dec 31st, incurred and paid $2,000 of utilities expense. 1. Dec 31st, Purchased a copyright for $10,000. The copyright has a 20-year useful life and no residual value. m. Dec 31st, Purchased a second piece of equipment for $4,100 (estimated useful life 12 years, salvage value 2,000). n. The company relies on the percentage of credit sales method, and expects that 2% of credit sales will be uncollectible. Transactions and information for the year: a. Jan 1st Spent $3,500 to improve the first piece of equipment purchased in Year 1. Revised useful life is 5 more years while the new salvage value is $2,000. b. Jan 2nd, ordered and received 200 units of inventory purchased on account for $13 each c. Jan 15th, paid $100 to settle a warranty claim from a customer. d. Feb 3rd, ordered and received 150 units of inventory purchased on account for $12 each 0. Feb 22nd, sold 250 units of inventory at $65 each. $10,000 was on account. The inventory came with a 1 year warranty. The company expects that providing the warranty will cost 1% of the sales made. e. March 1st, incurred and paid $900 of wages expense f. Mar 30th, collected $5000 of accounts receivable g. April 1st, paid $50 to settle a warranty claim from a customer. h. May 2nd, Paid $4000 of accounts payable. i. June 1st, Paid $409 of taxes payable j. June 30th, made first interest payment on Note Payable. k. Aug 12th, wrote-off a $250 account receivable for a customer who filed for bankruptcy. p. Oct 12th, sold 100 units of inventory at $56 each. The inventory came with a 1 year warranty. The company expects that providing the warranty will cost 1% of the sales made. 1. Dec 31st, spent $1,500 at end of year to repair equipment. m. Estimated that 2% of Year 2 sales on account would not be collected. n. Estimated tax rate is 35% Transactions and information for the year: a. Jan 1st, issued 500 shares of common stock ($0.10 par value) for $50,000. b. Feb 1st, paid $25,000 to purchase equipment (estimated useful life 10 years; salvage value = 1,540) C. Feb 28th, issued 100 shares of common stock ($0.10 par value) for $20,000. d. June 30th, paid $175,000 for a land by signing a 5 year Note Payable, promising to pay 5% interest on June 30th of each of those 5 years. e. July 15, purchased 500 units of inventory at $15 each. $2,000 was paid in cash, the rest was on account. f. July 30th, sold 220 units of inventory for $63 each on account. The inventory came with a 1 year warranty. The company expects that providing the warranty will cost 1% of the sales made. g. Aug 2nd, incurred $450 of wages expense. h. Aug 5th, collected $2500 of accounts receivable. i. Aug 31st, paid $450 of wages payable. j. Sept 4th, paid $1600 of accounts payable. k. Dec 31st, incurred and paid $2,000 of utilities expense. 1. Dec 31st, Purchased a copyright for $10,000. The copyright has a 20-year useful life and no residual value. m. Dec 31st, Purchased a second piece of equipment for $4,100 (estimated useful life 12 years, salvage value 2,000). n. The company relies on the percentage of credit sales method, and expects that 2% of credit sales will be uncollectible








