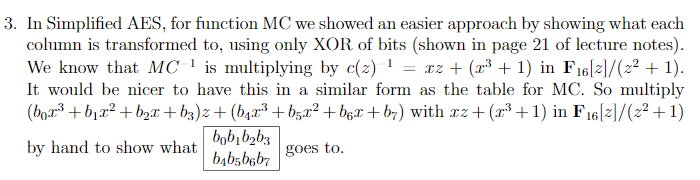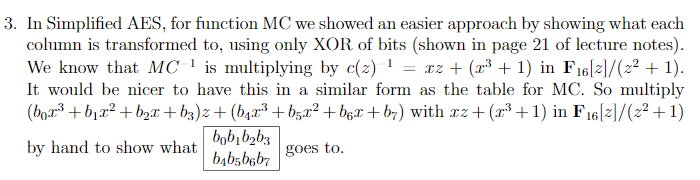
The Function SR: The abbreviation SR stands for shift row. The function SR takes the state No N2 to N. NA to the state N. 13 N3 N The Function MC: The abbreviation MC stands for mic column. A column (Ni, N; of the state is considered to be the element Niz + N; of F16[2]/(22 +1). As an example, if the column consists of Ni, Nil where Ni = 1010 and N; = 1001 then that would be (23 + 2)2 + (2 + 1). Like before, F16[2] denotes polynomials in z with coefficients in F16- So F16[2)/(22 + 1) means that polynomials are considered modulo 22 + 1; thus 22 = 1. So representatives consist of the 162 polynomials of degree less than 2 in 2. The function MC multiplies each column by the polynomial c(z) = x^2 +1. This polynomial is always the same for Simplified AES. As an example, [((2+2)2 + (z.? + 1))](2+z+1) = (2,5 + 2?)+ (x3 +1 +2 + x)2 + (z.? +1) = (2 + x3 + x + 2)2 + (2 + x3 + x3 + 1) = (-+++2 +2)2+(2++1) = (??)2 + (+1+1), which goes to the column (Nk, N) where Nx = 1000 and N = 0111. Note that 22 +1 = (z + 1)2 is reducible over F16 so F162)/(22 +1) is not a field and not all of its non-zero elements are invertible; the polynomial c(2), however, is. The simplest way to explain MC is to note that MC sends a column bobb2b3.bo be bi b4b7b2b4b5b3b5 b4b5b6b7b2b4 bob3 b5 bo ebbe bb The Rounds: The composition of functions AKOMCO SRONS is considered to be the i-th round. So this simplified algorithm has two rounds. There is an extra Ak before the first round and the last round does not have an MC. 3. In Simplified AES, for function MC we showed an easier approach by showing what each column is transformed to, using only XOR of bits (shown in page 21 of lecture notes). We know that MC is multiplying by c(2)! = rz + + 1) in F16/21/(22 + 1). It would be nicer to have this in a similar form as the table for MC. So multiply (bor +212 +62.2 +63)z + (64.? +b5.r +61 +b7) with rz+(2+1) in F16[2/(22 +1) by hand to show what - bobb2b3 6465bgb7 goes to. The Function SR: The abbreviation SR stands for shift row. The function SR takes the state No N2 to N. NA to the state N. 13 N3 N The Function MC: The abbreviation MC stands for mic column. A column (Ni, N; of the state is considered to be the element Niz + N; of F16[2]/(22 +1). As an example, if the column consists of Ni, Nil where Ni = 1010 and N; = 1001 then that would be (23 + 2)2 + (2 + 1). Like before, F16[2] denotes polynomials in z with coefficients in F16- So F16[2)/(22 + 1) means that polynomials are considered modulo 22 + 1; thus 22 = 1. So representatives consist of the 162 polynomials of degree less than 2 in 2. The function MC multiplies each column by the polynomial c(z) = x^2 +1. This polynomial is always the same for Simplified AES. As an example, [((2+2)2 + (z.? + 1))](2+z+1) = (2,5 + 2?)+ (x3 +1 +2 + x)2 + (z.? +1) = (2 + x3 + x + 2)2 + (2 + x3 + x3 + 1) = (-+++2 +2)2+(2++1) = (??)2 + (+1+1), which goes to the column (Nk, N) where Nx = 1000 and N = 0111. Note that 22 +1 = (z + 1)2 is reducible over F16 so F162)/(22 +1) is not a field and not all of its non-zero elements are invertible; the polynomial c(2), however, is. The simplest way to explain MC is to note that MC sends a column bobb2b3.bo be bi b4b7b2b4b5b3b5 b4b5b6b7b2b4 bob3 b5 bo ebbe bb The Rounds: The composition of functions AKOMCO SRONS is considered to be the i-th round. So this simplified algorithm has two rounds. There is an extra Ak before the first round and the last round does not have an MC. 3. In Simplified AES, for function MC we showed an easier approach by showing what each column is transformed to, using only XOR of bits (shown in page 21 of lecture notes). We know that MC is multiplying by c(2)! = rz + + 1) in F16/21/(22 + 1). It would be nicer to have this in a similar form as the table for MC. So multiply (bor +212 +62.2 +63)z + (64.? +b5.r +61 +b7) with rz+(2+1) in F16[2/(22 +1) by hand to show what - bobb2b3 6465bgb7 goes to