Question
The goal of this exercise is to compile all cash flows associated with each form of occupancy, and then calculate the rate of return that
The goal of this exercise is to compile all cash flows associated with each form of occupancy, and then calculate the rate of return that will be earned on the funds used to make an equity investment (down payment) if the property is purchased. Alternatively, it is this rate of return that an investor would have to earn on the down payment saved if renting is chosen, to make renting the financial equivalent of owning.
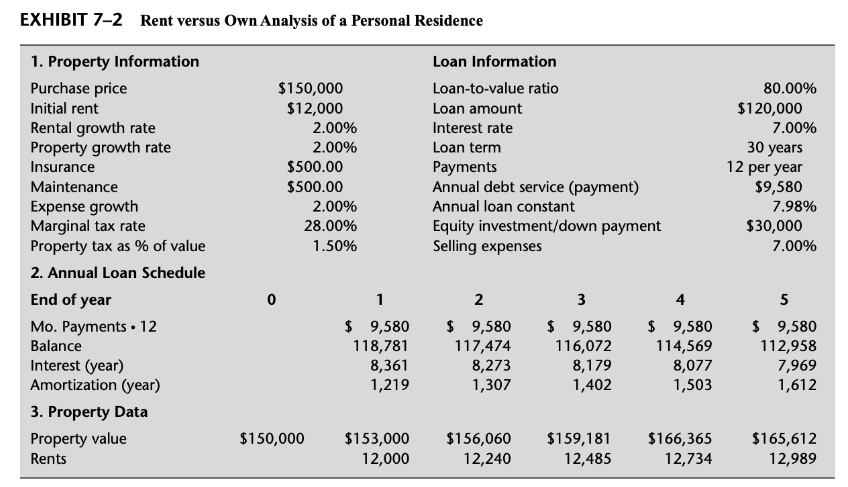
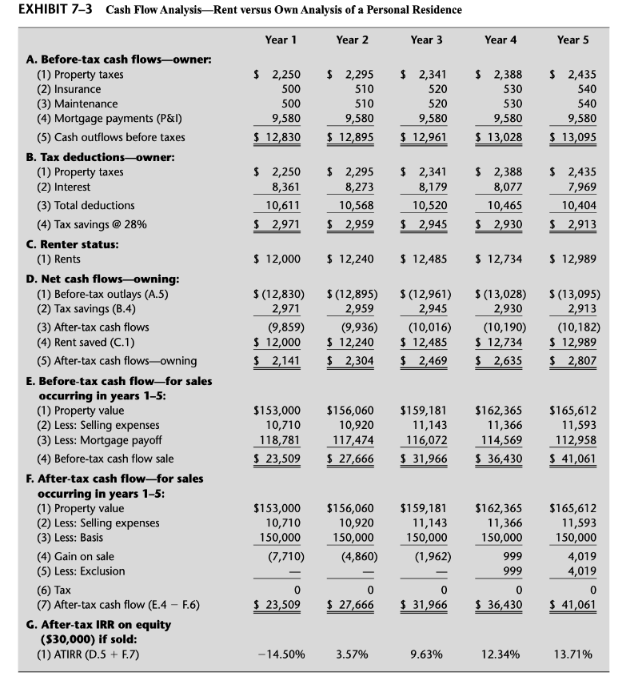
The framework for making a comparison between renting and owning is presented in the example summarized in Exhibit 72. In this example, we have a property that could be rented for $12,000 per year ($1,000 per month) or purchased for $150,000 with $30,000 down and financed with a fully amortizing mortgage loan of $120,000 at 7 percent interest for 30 years. Other costs associated with owning include maintenance, insurance, and property taxes. In our example, these expenses would not have to be paid if renting is chosen. All other expenses would have to be paid regardless of whether the property is owned or rented, such as utilities, and so on. Because they offset, they do not have to be included in our analysis. Other assumptions include (1) a federal income tax rate of 28 percent, (2) escalation in expenses, rents, and property value at 2 percent per year, and (3) a five-year period of analysis, at the end of which, the property would be sold (if owned). Selling expenses of 7 percent would have to be paid at that time. Cash flows associated with our analysis are summarized annually for convenience and presented in Exhibit 73.
Case Study: Now, you are required to analyze new case of Renting versus Owning.All other informations are same as in Exhibit 7-2 besides property price, initial rent, LTV(loan to value) ratio and interest rate. Suppose the purchase price of property is $250,000, the initial rent is $24,000(yr), LTV(Loan to Value) ratio is 65% and interest rate is 4%. 1) Discuss whether you support the purchasing a property or renting a property based on your computation as in Exhibit 7-3. 2) Attach a spreadsheet that can support your conclusion.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


