The income statement indicates sales increased 30 percent from year 1 to year 2 and 35 percent from year 2 to year 3. Net income increased 14 percent from year 1 to year 2, and 18 percent from year 2 to year 3. One member on the committee, Vivian Bentley, would like to offer the CEO a multiyear extension with a significant bump in salary and thousands of shares of stock options. When questioned why, Vivian pointed to the positive results reflected on the income statement.
Another committee member, Carter Posey, agrees with Vivian that income statement trends look great, but she would like to review other measures of performance as well. Carter has asked you to come up with two measures of performance that go beyond simply looking at the income statement.
Required:
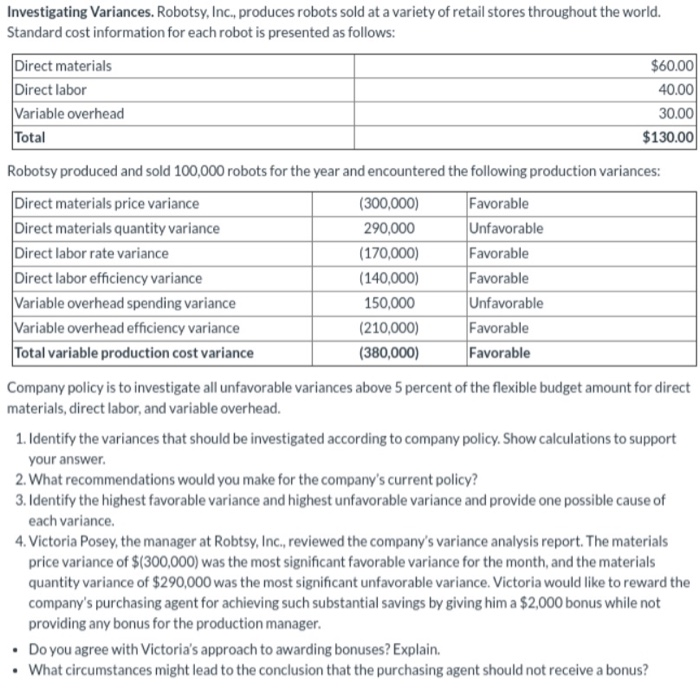
Calculate return on investment for each of the three years. Note that balance sheet amounts presented for each year are already average balances (i.e., no need to calculate average balances). Assume land held for sale is not an operating asset.
Calculate residual income for each of the three years assuming the companys cost of capital rate is 12 percent.
-
Summarize and explain your findings in parts 1 and 2 to the committee.
please use attached template
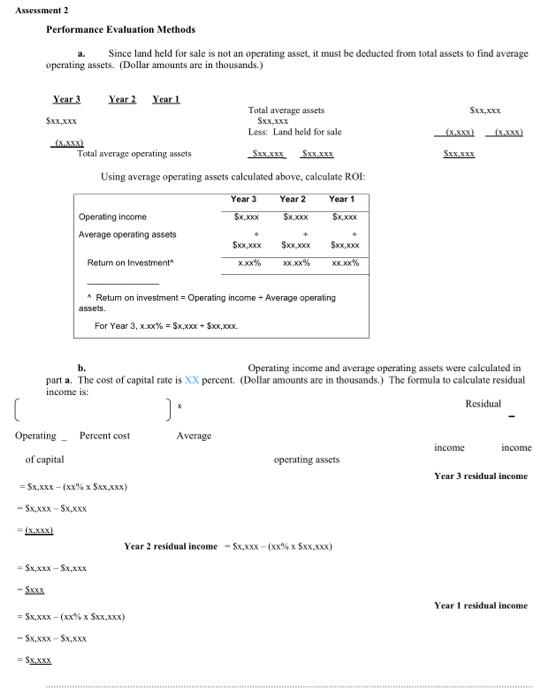
1) Identify the variances that should be investigated according to company policy. Show calculations to support your answer.
2) What recommendations would you make for the companys current policy?
3) Identify the highest favorable variance and highest unfavorable variance and provide one possible cause of each variance.
4) Victoria Posey, the manager at Robtsy, Inc., reviewed the companys variance analysis report. The materials price variance of $(300,000) was the most significant favorable variance for the month, and the materials quantity variance of $290,000 was the most significant unfavorable variance. Victoria would like to reward the companys purchasing agent for achieving such substantial savings by giving him a $2,000 bonus while not providing any bonus for the production manager.
Investigating Variances. Robotsy, Inc., produces robots sold at a variety of retail stores throughout the world. Standard cost information for each robot is presented as follows: Direct materials $60.00 Direct labor 40.00 Variable overhead 30.00 Total $130.00 Robotsy produced and sold 100,000 robots for the year and encountered the following production variances: Direct materials price variance (300,000) Favorable Direct materials quantity variance 290,000 Unfavorable Direct labor rate variance (170,000) Favorable Direct labor efficiency variance (140,000) Favorable Variable overhead spending variance 150,000 Unfavorable Variable overhead efficiency variance (210,000) Favorable Total variable production cost variance (380,000) Favorable Company policy is to investigate all unfavorable variances above 5 percent of the flexible budget amount for direct materials, direct labor, and variable overhead. 1. Identify the variances that should be investigated according to company policy. Show calculations to support your answer. 2. What recommendations would you make for the company's current policy? 3. Identify the highest favorable variance and highest unfavorable variance and provide one possible cause of each variance. 4. Victoria Posey, the manager at Robtsy, Inc., reviewed the company's variance analysis report. The materials price variance of $(300,000) was the most significant favorable variance for the month, and the materials quantity variance of $290,000 was the most significant unfavorable variance. Victoria would like to reward the company's purchasing agent for achieving such substantial savings by giving him a $2,000 bonus while not providing any bonus for the production manager. Do you agree with Victoria's approach to awarding bonuses? Explain. What circumstances might lead to the conclusion that the purchasing agent should not receive a bonus? Assessment 2 Performance Evaluation Methods Since land held for sale is not an operating asset, it must be deducted from total assets to find average operating assets. (Dollar amounts are in thousands.) Sxx, XXX Sxx XXX Year 3 Year Year 1 Total average assets Sxx.xxx Sxx.xxx Less: Land held for sale (xxxx) Total average operating assets Sxxxxx $XXXXX Using average operating assets calculated above, calculate ROI: Year 3 Year 2 Year 1 Operating income $x xxx Sx.xxx Sx.xxx Average operating assets $xx xxx Sxx.xxx Sxx.xx Return on Investment x.xx% xxxx% XXXX% assets. Retum on investment = Operating income + Average operating For Year 3, x.xx% = $x,XXX + $xx,XXX. b. Operating income and average operating assets were calculated in part a. The cost of capital rate is XX percent. (Dollar amounts are in thousands.) The formula to calculate residual income is: Residual * Operating - Percent cost Average income income of capital operating assets Year 3 residual income = $x,XXX - (xx% x $XX.XXX) - Sx.xxx - Sx.xxx =(x.xxx) Year 2 residual income - SxxXx - (xx% x $XXXXX) = $x.xxx - Sx.xxx Year 1 residual income = $x,xxx-(xx% x Sxx,xxx) -SX.XXX-Sx.xxx = Sx XXX Investigating Variances. Robotsy, Inc., produces robots sold at a variety of retail stores throughout the world. Standard cost information for each robot is presented as follows: Direct materials $60.00 Direct labor 40.00 Variable overhead 30.00 Total $130.00 Robotsy produced and sold 100,000 robots for the year and encountered the following production variances: Direct materials price variance (300,000) Favorable Direct materials quantity variance 290,000 Unfavorable Direct labor rate variance (170,000) Favorable Direct labor efficiency variance (140,000) Favorable Variable overhead spending variance 150,000 Unfavorable Variable overhead efficiency variance (210,000) Favorable Total variable production cost variance (380,000) Favorable Company policy is to investigate all unfavorable variances above 5 percent of the flexible budget amount for direct materials, direct labor, and variable overhead. 1. Identify the variances that should be investigated according to company policy. Show calculations to support your answer. 2. What recommendations would you make for the company's current policy? 3. Identify the highest favorable variance and highest unfavorable variance and provide one possible cause of each variance. 4. Victoria Posey, the manager at Robtsy, Inc., reviewed the company's variance analysis report. The materials price variance of $(300,000) was the most significant favorable variance for the month, and the materials quantity variance of $290,000 was the most significant unfavorable variance. Victoria would like to reward the company's purchasing agent for achieving such substantial savings by giving him a $2,000 bonus while not providing any bonus for the production manager. Do you agree with Victoria's approach to awarding bonuses? Explain. What circumstances might lead to the conclusion that the purchasing agent should not receive a bonus? Assessment 2 Performance Evaluation Methods Since land held for sale is not an operating asset, it must be deducted from total assets to find average operating assets. (Dollar amounts are in thousands.) Sxx, XXX Sxx XXX Year 3 Year Year 1 Total average assets Sxx.xxx Sxx.xxx Less: Land held for sale (xxxx) Total average operating assets Sxxxxx $XXXXX Using average operating assets calculated above, calculate ROI: Year 3 Year 2 Year 1 Operating income $x xxx Sx.xxx Sx.xxx Average operating assets $xx xxx Sxx.xxx Sxx.xx Return on Investment x.xx% xxxx% XXXX% assets. Retum on investment = Operating income + Average operating For Year 3, x.xx% = $x,XXX + $xx,XXX. b. Operating income and average operating assets were calculated in part a. The cost of capital rate is XX percent. (Dollar amounts are in thousands.) The formula to calculate residual income is: Residual * Operating - Percent cost Average income income of capital operating assets Year 3 residual income = $x,XXX - (xx% x $XX.XXX) - Sx.xxx - Sx.xxx =(x.xxx) Year 2 residual income - SxxXx - (xx% x $XXXXX) = $x.xxx - Sx.xxx Year 1 residual income = $x,xxx-(xx% x Sxx,xxx) -SX.XXX-Sx.xxx = Sx XXX








