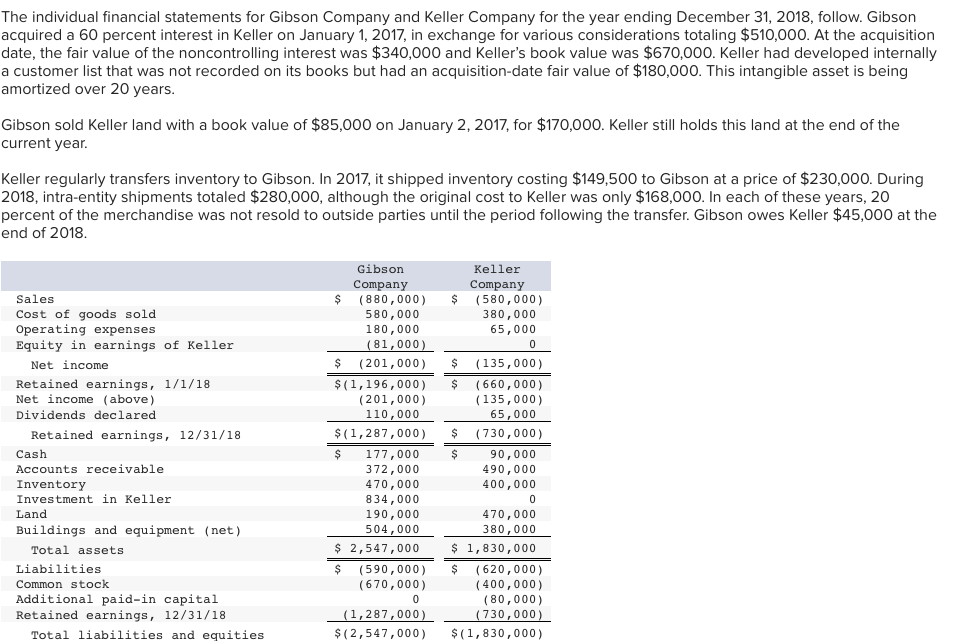
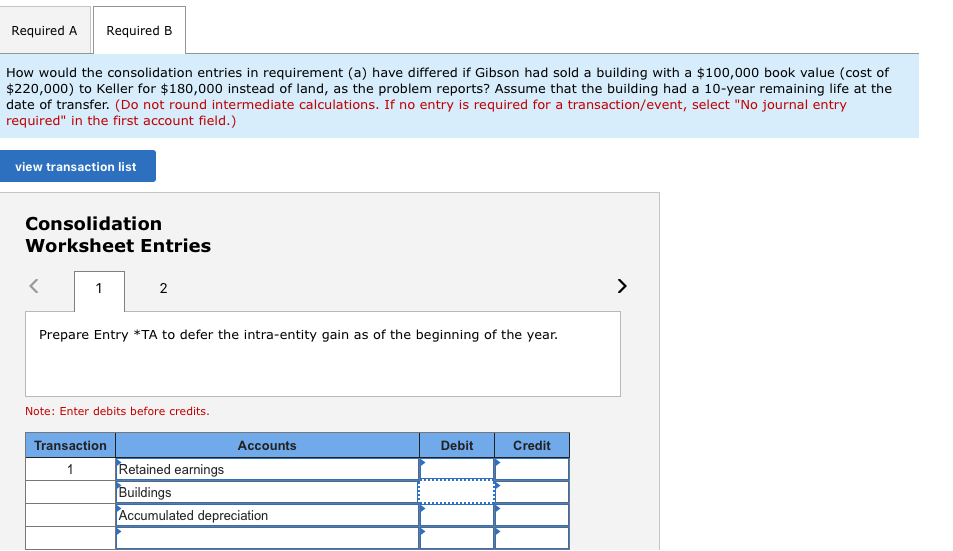
The individual financial statements for Gibson Company and Keller Company for the year ending December 31, 2018, follow. Gibson acquired a 60 percent interest in Keller on January 1, 2017, in exchange for various considerations totaling $510,000. At the acquisition date, the fair value of the noncontrolling interest was $340,000 and Keller's book value was $670,000. Keller had developed internally a customer list that was not recorded on its books but had an acquisition-date fair value of $180,000. This intangible asset is being amortized over 20 years. Gibson sold Keller land with a book value of $85,000 on January 2, 2017, for $170,000. Keller still holds this land at the end of the current year. Keller regularly transfers inventory to Gibson. In 2017, it shipped inventory costing $149,500 to Gibson at a price of $230,000. During 2018, intra-entity shipments totaled $280,000, although the original cost to Keller was only $168,000. In each of these years, 20 percent of the merchandise was not resold to outside parties until the period following the transfer. Gibson owes Keller $45,000 at the end of 2018 Gibson Keller Company (880,000) 580,000 180,000 (81,000) Company (580,000) 380,000 65,000 Sales Cost of goods sold Operating expenses Equity in earnings of Keller 0 (201,000) $ (135,000) Net income $(1,196,000) (201,000) 110,000 Retained earnings, 1/1/18 Net income (above) (660,000) (135,000) Dividends declared 65,000 (730,000) $(1,287,000) Retained earnings, 12/31/18 90,000 Cash 177,000 372,000 470,000 834,000 190,000 Accounts receivable 490,000 400,000 Inventory Investment in Keller C Land 470,000 Buildings and equipment (net) 504,000 380,000 $ 2,547,000 1,830,000 Total assets Liabilities S (590,000) (670,000) (620,000) (400,000) Common stock Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings, 12/31/18 0 (80,000) (1,287,000) (730,000) $ (2,547,000) $ (1,830,000) Total liabilities and equities Required A Required B How would the consolidation entries in requirement (a) have differed if Gibson had sold a building with a $100,000 book value (cost of $220,000) to Keller for $180,000 instead of land, date of transfer. (Do not round intermediate calculations. If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select "No journal entry required" in the first account field.) as the problem reports? Assume that the building had a 10-year remaining life at the view transaction list Consolidation Worksheet Entries 1 2 Prepare Entry *TA to defer the intra-entity gain as of the beginning of the year. Note: Enter debits before credits. Transaction Credit Accounts Debit Retained earnings 1 Buildings Accumulated depreciation








