Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The iodination of acetone is catalyzed by the proton and monochloroacetic acid (general acid catalysis), the reaction in water being negligible. For monochloroacetic acid CH2ClCOOH
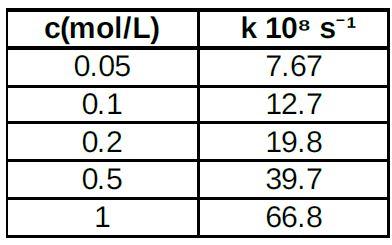
The iodination of acetone is catalyzed by the proton and monochloroacetic acid (general acid catalysis), the reaction in water being negligible. For monochloroacetic acid CH2ClCOOH the acid dissociation constant is 1.5510 mol dm . The data of rate constants were obtained as a function of the concentration of monochloroacetic acid from the table. Determine the catalytic constants ( k=k H [H ]+k AH[CH2ClCOOH] ).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


