Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The linearized equations of perturbed longitudinal motion for a given flight condition are given (in SI units) by: u=200.00 +0.035a-9.810-0.18u q=-0.65q-0.25-a-1.28 =q-0.25u-0.6a-0.0356 1) Determine
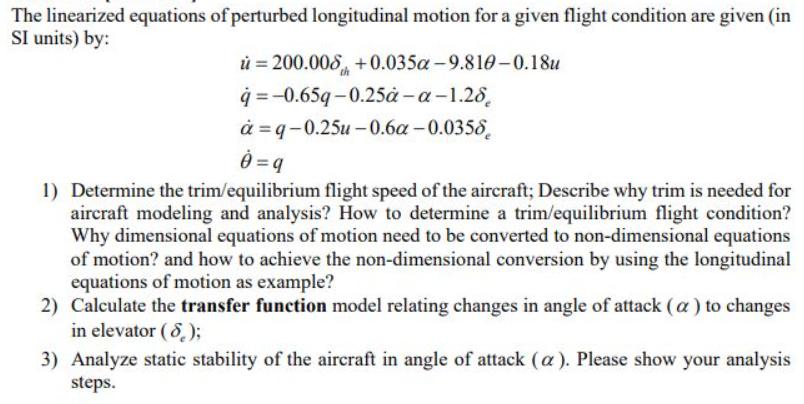
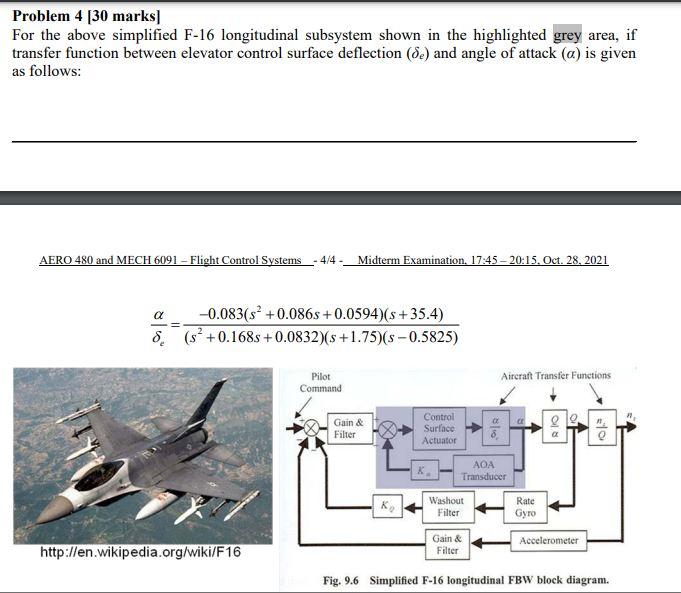
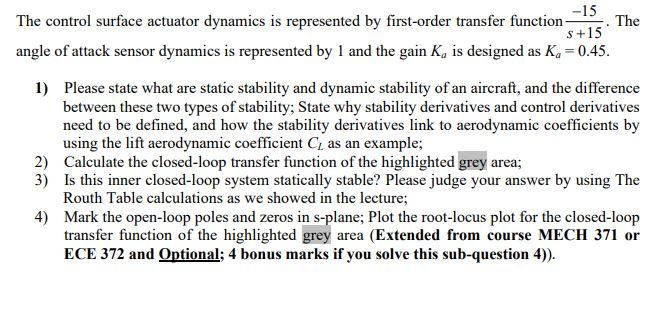
The linearized equations of perturbed longitudinal motion for a given flight condition are given (in SI units) by: u=200.00 +0.035a-9.810-0.18u q=-0.65q-0.25-a-1.28 =q-0.25u-0.6a-0.0356 1) Determine the trim/equilibrium flight speed of the aircraft; Describe why trim is needed for aircraft modeling and analysis? How to determine a trim/equilibrium flight condition? Why dimensional equations of motion need to be converted to non-dimensional equations of motion? and how to achieve the non-dimensional conversion by using the longitudinal equations of motion as example? 2) Calculate the transfer function model relating changes in angle of attack (a) to changes in elevator (8.); 3) Analyze static stability of the aircraft in angle of attack (a). Please show your analysis steps. Problem 4 [30 marks] For the above simplified F-16 longitudinal subsystem shown in the highlighted grey area, if transfer function between elevator control surface deflection (de) and angle of attack (a) is given as follows: AERO 480 and MECH 6091 - Flight Control Systems 4/4- Midterm Examination. 17:45-20:15. Oct. 28, 2021 -0.083(s+0.086s+0.0594)(s+35.4) 8 (s+0.168s+0.0832)(s+1.75)(s-0.5825). Pilot Command Aircraft Transfer Functions Control Gain & Filter Surface Actuator 8/10 22 AOA Transducer K Washout Filter Rate Gyro Accelerometer http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/F16 Gain & Filter Fig. 9.6 Simplified F-16 longitudinal FBW block diagram. -15 S+15 The control surface actuator dynamics is represented by first-order transfer function- angle of attack sensor dynamics is represented by 1 and the gain K, is designed as Ka = 0.45. The 1) Please state what are static stability and dynamic stability of an aircraft, and the difference between these two types of stability; State why stability derivatives and control derivatives need to be defined, and how the stability derivatives link to aerodynamic coefficients by using the lift aerodynamic coefficient CL as an example; 2) Calculate the closed-loop transfer function of the highlighted grey area; 3) Is this inner closed-loop system statically stable? Please judge your answer by using The Routh Table calculations as we showed in the lecture; 4) Mark the open-loop poles and zeros in s-plane; Plot the root-locus plot for the closed-loop transfer function of the highlighted grey area (Extended from course MECH 371 or ECE 372 and Optional; 4 bonus marks if you solve this sub-question 4)).
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.45 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 The trim or equilibrium flight speed of an aircraft is the speed at which the forces and moments acting on the aircraft are balanced resulting in steady level flight Trim is needed for aircraft mode...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


