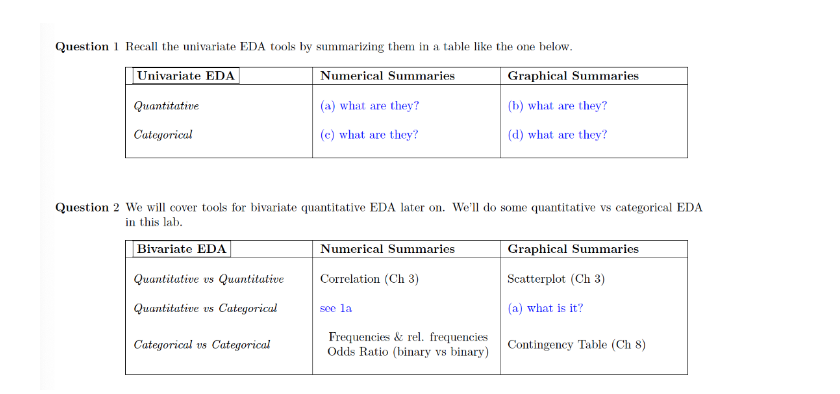
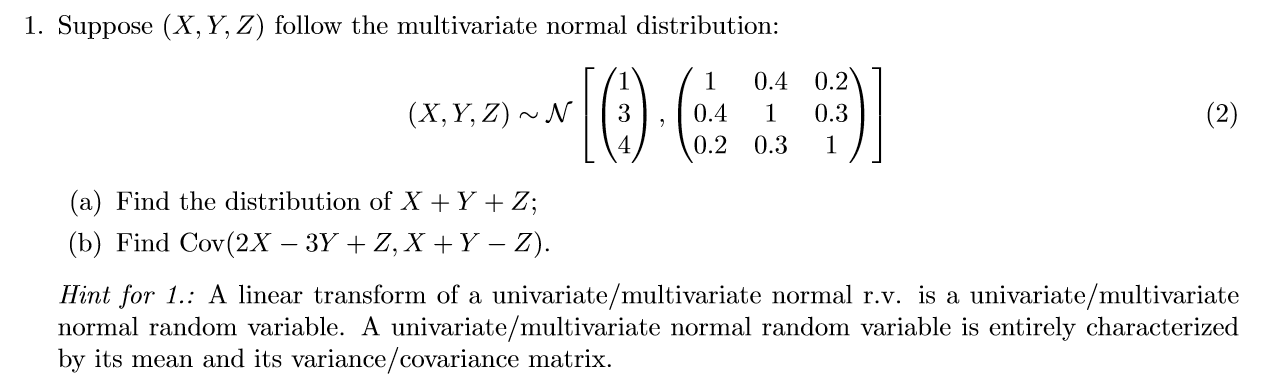
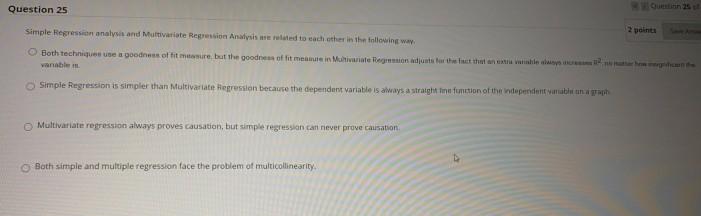
Question
The log-normal distribution is the probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm follows a normal distribution.Unfortunately, we are witnessing a practical application of it
The log-normal distribution is the probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm follows a normal distribution.Unfortunately, we are witnessing a practical application of it in the log-normal distribution of new cases of COVID-19 per day. From the video lectures of this course, we also know that infinance, the log-normal distribution is often used to model the price of a stock and forms the foundation of many asset pricing models. Which of the following is one of the reasons that thelog-normal distribution is used to model stock prices rather than the normal distribution?
A.
The normal distribution has positive skewness.
B.
The normal distribution overestimates the probability of tail risks.
C.
The normal distribution is leptokurtic.
D.
The normal distribution describes multiplicative situations like compounding stock prices.
E.
The normal distribution allows for negative stock prices.

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


