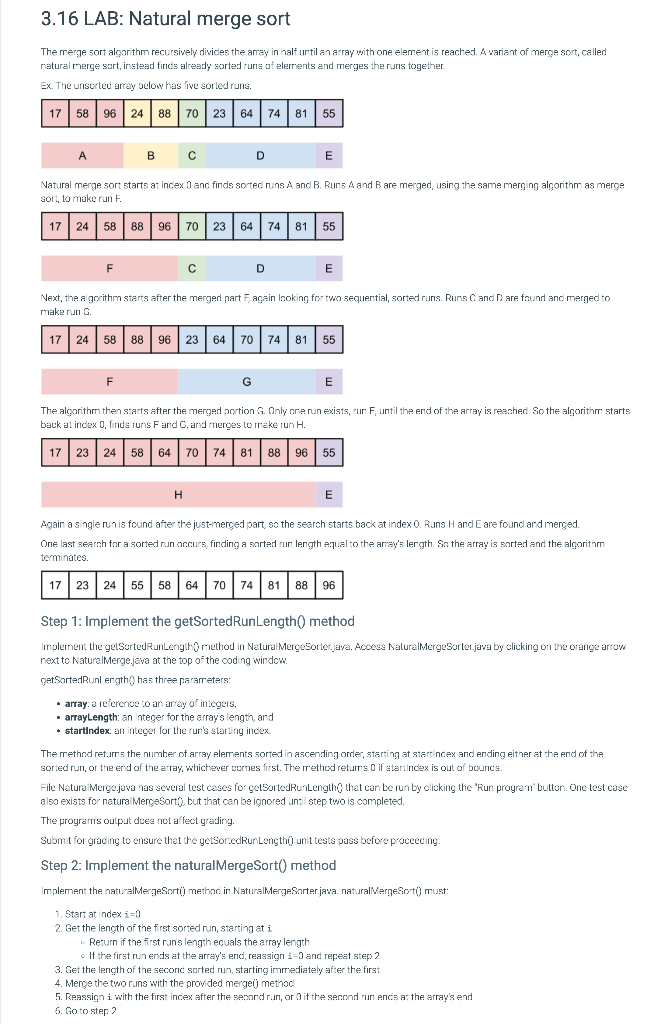



The merge sort algarithm recursively divides the aray in half until an array with one element is reached, A variant of merge sort, called natural rerge sart, instead finds already sorted runs af elerrents and merges the runs together. Ex. The unserted array oelow has five sonted runs. Natural merge sort starts at incex 0 and finds sorted runs A and B. Runs A and B are merged, using the same merging algorithm as merge sort, to make run F. FCDE Next, the a groithm starts after the merged nart F, again Inoking for two sequential, sorted runs. Runs C and D are faund and merged to make run G. The aloorithm then starts after the merged sortion G. Only nne run exists, rur F, until the end of the array is reanhed. So the algorithrn starts back at index 0 , finds runs F and G, and meroes to make run H. Again a s igle run is found after the just-merced part, so the search starts back at index 0 . Runs H and E are found and merced. One last searah far a sorted run orcurs, finding a sarted run length equal to the aray's lergth. Sn the array is sartad and the algoritam terminates. Step 1: Implement the getSortedRunLength 0 method implement the getSortedRunLengthO method in Nctural MergeSorter.java. Aooess NaturalMergeSarter.java by clicking on the orange arrow rext to Naturalmerge.java at the top 2 the coding window. getSartedRunl ength 0 has three parameters: - array. a referenoe to an aray of integers. - arrayLength: an integer for the array's length, and - startindex: an integer for the run's starling index. The methnd ret.urss the number of array elements sorted in ascending order, starting at start incex and ending either at the end of the sorted run, or the end of the array, whichever comes first. The rrethod returrs 0 if startindex is out of bouncs. File Natura Nerge.java nas several test cases fo' get SartedRunLengthg that can be nun by clicking the "Run program' buttan. One test case a so exists for natura Mercesort0, but that can be ignored until step two is completed. The programs output doea not affect greding. Submt for grading to ensure that the getSortedRunLengthif unit tests pass before proceeding. Step 2: Implement the naturalMergeSort() method Implernent the naturalmergeSnrtij methoc in NaturalkergeSorter java. naturalkergeSor0 must: 1. Start at index i=0 2. Get the length of the first sorted run, starting at i - Return if the first run's length ecuals the array length - If the first run ends at the array's end, reassign i=0 and repeat step 2 3. Get the length of the seconc sarted run, starting immediately after the first 4. Merge the two runs with the provided mergeij methoo 5. Reassign i with the first incex after the senard run, or 0 if the serond run ends at the array's end 6. Goto step? marked as read only Current file: NaturalMerge.java - port java.io.PrintWriter; port java.util.Arrays; blic class NaturalMerge \{ public static void main(String[] args) \{ // Test case array: A completely sorted array int [ arr1 ={15,23,23,23,31,64,77,87,88,91}; int arr1Length = arr1. length; 1/ Test case array: Sorted run of 3 followed by sorted run of 6 int [ arr2 ={64,88,91,12,21,34,43,56,65}; int arr2Length =arr2. length; 1/ Test case array: 5 elements in descending order, so 5 runs of length 1 int [ arr3 ={10,20,30,40,50}; int arr3 Length =arr3. length; I/ Test case array: 8 equal elements, so 1 run of 8 int [ arr4 ={99,99,99,99,99,99,99,99}; int arr4Length = arr4. length; I/ Test cases: RunLengthTestCase[] testCases ={ 1/ First test case uses an out-of-bounds starting index. Remaining test I/ cases do not. new RunLengthTestCase(arr1, arr1Length, arr1Length, 0 ), new RunLengthTestCase(arr1, arr1Length, 0 , arr1Length), new RunLengthTestCase(arr1, arr1Length, 3, arr1Length - 3), new RunLengthTestCase(arr2, arr2Length, 0,3 ), new RunLengthTestCase(arr2, arr2Length, 2, 1), new RunLengthTestCase(arr2, arr2Length, 3, 6), new RunLengthTestCase(arr3, arr3Length, 0,1), new RunLengthTestCase (arr3, arr3Length, 3, 1), new RunLengthTestCase(arr4, arr4Length, 0 , arr4Length), new RunLengthTestCase(arr4, arr4Length, 4, arr4Length - 4), new RunLengthTestCase(arr4, arr4Length, 5, arr4length - 5) \}; // Execute each test case PrintWriter testFeedback = new PrintWriter(System.out); int testCasesLength = testCases, length; for (int i=0;i











