Question
The Morpheus company has an industrial activity. It manufactures in its workshops two types of finished products (red pills and blue pills) from two raw
The Morpheus company has an industrial activity. It manufactures in its workshops two types of finished products (red pills and blue pills) from two raw materials (Zion powder and gelatin).The red pill frees those who consume it from the enslaving control of the Matrix, and the blue pill allows it to remain in the fabricated reality of the Matrix.
In September of year Y, Director Morpheus hires you as a management controller and asks you to build the budget for year Y + 1. It provides you with the following forecast information.
- Sales
As, usually, consumers mostly choose blue pills, the sales goals (in quantities) for years Y, Y+1 and Y+2 are the following:
| Y | Y+1 | Y+2 | |
| Red pills | 125 | 150 | 160 |
| Blue pills | 600 | 700 | 720 |
Unit sales prices, identical to those of year Y, are estimated at:
| Y+1 | |
| Red pills | ? 350 |
| Blue pills | ? 210 |
Based on previous years, it can be assumed that at the end of year Y + 1, 10% of sales will not be collected given the payment period granted to customers. It should also be noted that in order to be able to deliver its customers quickly, the company always keeps a stock of finished products corresponding to 10% of the expected sales of the following year, for both red and blue pills of the period considered (here the year). The inventory valuation method used is the FIFO method.
- Production
- Direct production costs
The production department estimated that for Y + 1 the quantities of raw materials necessary to produce pills would be:
Y+1 | ||
Red pills | Blue pills | |
Zion powder | 20 gram | 0 gram |
Gelatin | 30 gram | 20 gram |
Since the blue pill has no effect, no Zion powder is required to make it. Forecasts for the unit purchase cost of raw materials are as follows:
Y+1 | |
Zion powder | ? 3,000 per kg |
Gelatin | ? 1,500 per kg |
For the Y + 1 budget, concerning the Zion Powder bought from the supplier Oracle, it is estimated that 3 months (on average) of purchase, that is 25% of the amount of raw material purchases, will not yet be paid to the suppliers at the end of December, due to the payment terms granted by this supplier. For Gelatin, however, the supplier The Merovingian does not grant us any payment term. In addition, there are no stocks of raw materials (neither for Zion powder nor for gelatin), the Oracle and the Merovingian are on site and immediately deliver the necessary raw materials to us.
Production labour is considered a direct variable cost of production. Indeed, the Morpheus company uses temporary workers (the inhabitants of Zion) to adjust the need for labour to fluctuations in production. According to the operating schedule, reviewed by the production manager, No, the manufacturing duration for each of the two products are as follows:
Y+1 | ||
Red pills | Blue pills | |
Direct labour | 6 hours | 1.5 hours |
According to the director, the average hourly cost of production labour should be in year Y + 1 of ? 17 (including social charges). Salaries are paid within the month; therefore, there are no payment delays on salaries.
- Manufacturing overhead costs
The cost of machines used in production is considered an overhead (indirect) charge as the machines are used to produce the two finished products. In addition, this cost is considered fixed and corresponds to the depreciation expenses of the machines. The machines started to be operated on January 1 of year Y and their value is reported in the balance sheet. The depreciation of these machines is done on a straight-line basis over 8 years, with no residual value at the end of the depreciation period. The annual salary cost of the production manager, Mr. No, is also considered as an overhead fixed production charge and is estimated at ? 42,000 for the year Y + 1. These overhead fixed charges are used 80% for the production of blue pills and 20% for the production of red pills. Disbursable charges are paid within the month.
There are also variable overhead production costs. They are generated by the use of machines. For Y + 1, the estimated time related to the use of machines per finished product are as follows:
Y+1 | ||
Red pills | Blue pills | |
Machine time / finished product units produced | 30 minutes | 15 minutes |
These overhead variable production costs correspond to various maintenance products, lubrication and the energy required to operate the machines. In total, they are estimated at ?10 per machine hour for year Y + 1. They are all paid during the month in which they are consumed.
- Non-manufacturing overhead costs
A sales representative, Trinity, was hired by the company. His annual salary for Y + 1 is estimated at ? 70,000.
In addition, two new ships, the Logos and the Hammer, will be purchased to defend Sion against the Sentinels for a total estimated amount of 200,000 euros. The purchase will be made and paid for on year Y+1, July 1. The machines will be amortized on a straight-line basis over 10 years.
Your predecessor had already prepared an estimate of the balance sheet at year Y, December 31 (in Euros). There were also some elements on his way of building it.
Variance analyses
In fact, fewer and fewer people want to see reality in the face, and free themselves from the grip of the Matrix. A year later, the Matrix company therefore recorded the following achievements for N + 1:
| Red pills | Blue pills | |
| Actual quantity produced (units)* | 100 | 720 |
* Please note that, to calculate the cost variances, it will therefore be necessary to consider the quantities (of finished products) to be produced from the production budget calculated in the Budget section , as well as the other budgetary data pertaining to raw materials and direct labour.
In addition, the costs of raw materials and direct labour were in reality:
| Actual unit cost of Zion Powder (per kg) | 3,000 | The cost is in line with what was expected |
| Actual unit cost of gelatin (per kg) | 1,700 | A Sentinel attack during the year made the extraction of gelatin more difficult |
| Actual cost per hour of direct production labour | 19 | A social movement of the inhabitants of Zion pushed Morpheus to agreed with a salary increase |
In addition, the quantities actually consumed of raw material and direct labor in the production of the pills were:
| Actual total quantities consumed | Red pills | Blue pills |
| Total Zion powder raw material (kg) | 3,1 | 0 |
| Total gelatin raw material (kg) | 4.2 | 13.5 |
| Total direct production labour (hours) | 800 | 1000 |
In addition, the sales data actually realized for Y + 1 are as follows:
| Actual unit sales price | Actual quantities sold (units) | |
| Red pills | ? 350 | 100 |
| Blue pills | ? 230 | 720 |
These are to be compared to the sales budgetary data, as given in the first part of this test. Finally, the market size that had been anticipated was 1,000 units. In reality, the market size was for Y + 1 of 1,050 units.
Questions
All questions relate to year Y + 1.
Part 1: Estimating budgets
Q1. What amount of sales will be collected?
Q2. What is the quantity to produce for the red pills and for the blue pills?
Q3. What is the total cost of raw materials consumed for red pills and blue pills?
Q4. What is the cost of finished product stocks for red pills?
Q5.What is the total amount of disbursement of non-manufacturing costs?
Part 2: Variance Analysis
Q6. For red pills, calculate the level 2 of cost variances (variances on flexible budget and on sales volume). Interpret the results obtained.
Q7. For red pills, calculate the level 3 of cost variances (price and efficiency variance). Interpret the results obtained.
Q8. For blue pills, calculate the level 3 cost variances (price and efficiency variances). Interpret the results obtained.
Q9. For the blue and red pills, calculate the level 2 revenue variances (price and quantity variances). Interpret the results obtained.
Q10. Calculate the level 4 of revenue variance (variance on market share and market size). Interpret the results obtained.
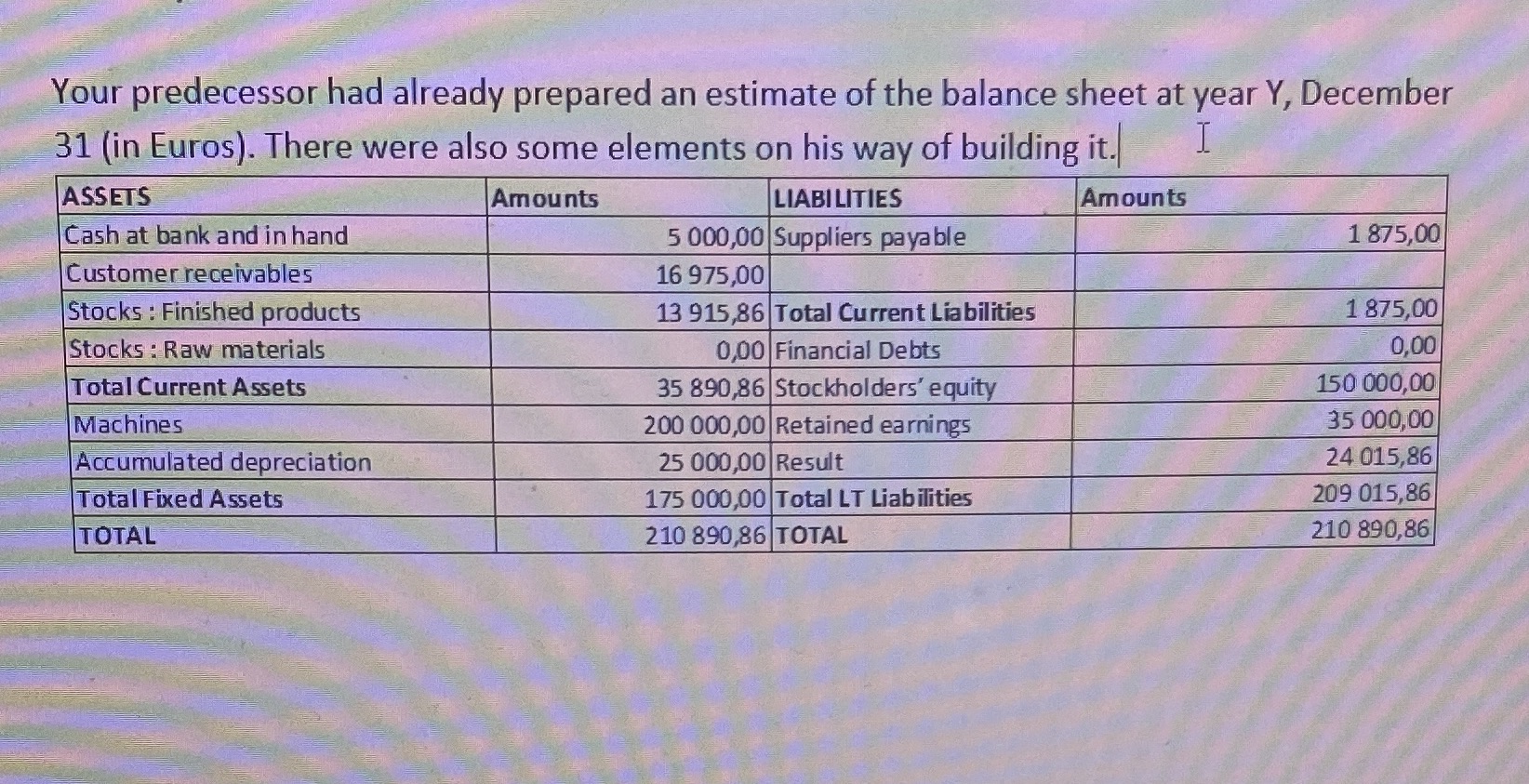
Your predecessor had already prepared an estimate of the balance sheet at year Y, December 31 (in Euros). There were also some elements on his way of building it. ASSETS Cash at bank and in hand Customer receivables Stocks: Finished products Stocks: Raw materials Total Current Assets Machines Accumulated depreciation Total Fixed Assets TOTAL Amounts LIABILITIES 5 000,00 Suppliers payable 16 975,00 13 915,86 Total Current Liabilities 0,00 Financial Debts 35 890,86 Stockholders' equity 200 000,00 Retained earnings 25 000,00 Result 175 000,00 Total LT Liabilities 210 890,86 TOTAL Amounts I 1875,00 1875,00 0,00 150 000,00 35 000,00 24 015,86 209 015,86 210 890,86
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


