Question
The number of entrees purchased in a single order at a Noodles & Company restaurant has had a historical average of 1.2 entrees per order.
The number of entrees purchased in a single order at a Noodles & Company restaurant has had a historical average of 1.2 entrees per order. On a particular Saturday afternoon, a random sample of 38 Noodles orders had a mean number of entrees equal to 1.3 with a standard deviation equal to 0.74. At the 1 percent level of significance, does this sample show that the average number of entrees per order was greater than expected?
Hypotheses: H0:? ?1.2 vs.H1:? >1.2
Tcalc: 0.83
- Find the p-value?
A ski company in Vail owns two ski shops, one on the west side and one on the east side of Vail. Ski hat sales data (in dollars) for a random sample of 5 Saturdays during the 2004 season showed the following results. Is there a significant difference in sales dollars of hats between the west side and east side stores at the 10 percent level of significance?
Saturday Sales Data ($) for Ski Hats | ||
|---|---|---|
Saturday | East Side Shop | West Side Shop |
1 | 579 | 523 |
2 | 458 | 756 |
3 | 624 | 643 |
4 | 515 | 586 |
5 | 464 | 566 |
- Choose the appropriate hypotheses. Assume?dis the difference in average sales between the east side and west side stores.
- H0:?d= 0 versusH1:?d? 0.
- H0:?d? 0 versusH1:?d= 0.
- Find the test statistic tcalc.
GreenBeam Limited claims that its compact fluorescent bulbs average no more than 3.66 mg of mercury. A sample of 35 bulbs shows a mean of 3.74 mg of mercury. (a) State the hypotheses for a right-tailed test, using GreenBeam's claim as the null hypothesis about the mean.
- H0: ? ? 3.66 mg vs. H1: ?
- H0: ? ? 3.66 mg vs. H1: ? > 3.66 mg
- H0: ? = 3.66 mg vs. H1: ? ? 3.66 mg
(d) Find the p-value. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.)
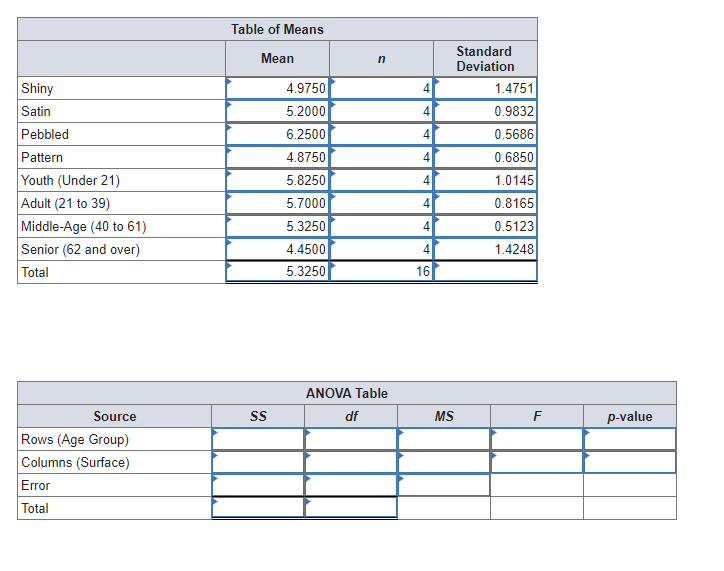
In a market research study, members of a consumer test panel are asked to rate the visual appeal (on a 1 to 10 scale) of the texture of dashboard plastic trim in a mockup of a new fuel cell car. The manufacturer is testing four finish textures. Panelists are assigned randomly to evaluate each texture. The test results are shown below. Each cell shows the average rating by panelists who evaluated each texture. Research question: Is mean rating affected by age group and/or by surface type?
| Mean Ratings of Dashboard Surface Texture | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Age Group | Shiny | Satin | Pebbled | Pattern |
| Youth (under 21) | 6.8 | 6.4 | 5.6 | 4.5 |
| Adult (21 to 39) | 5.1 | 5.3 | 6.9 | 5.5 |
| Middle-Age (40 to 61) | 4.8 | 5.1 | 6.0 | 5.4 |
| Senior (62 and over) | 3.2 | 4.0 | 6.5 | 4.1 |
(a-2) Choose the correct row-effect hypotheses.
a. H0:A1=A2=A3= 0 ?? Age group means are the same
H1: Not all theAjare equal to zero ?? Age group means are the same
b. H0:A1?A2?A3? 0 ?? Age group means are the same
H1: All theAjare equal to zero ?? Age group means differ
(a-3) Choose the correct column-effect hypotheses.
a. H0:B1=B2=B3= 0 ?? Surface type means are the same
H1: Not all theBkare equal to zero ?? Surface type means differ
b. H0:B1?B2?B3? 0 ?? Surface type means are the same
H1:Not all theBkare equal to zero ?? Surface type means differ
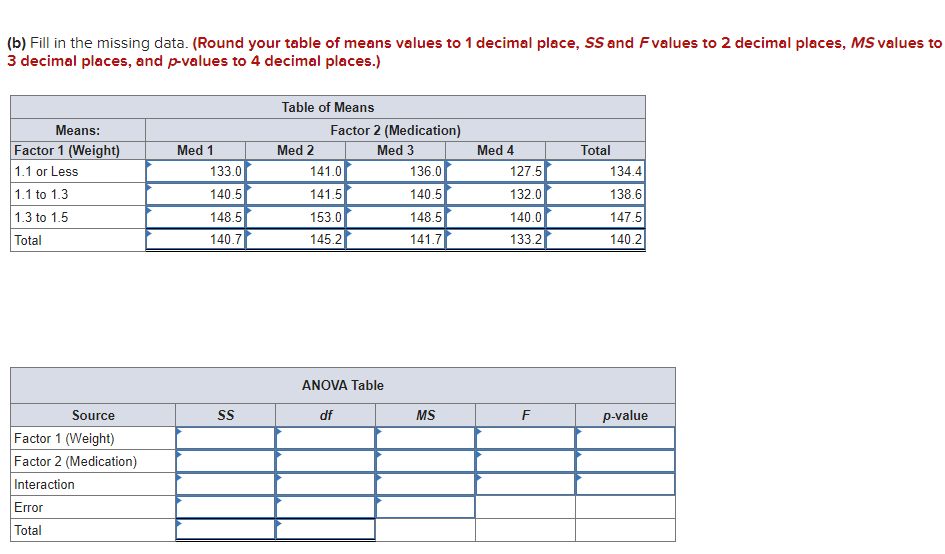
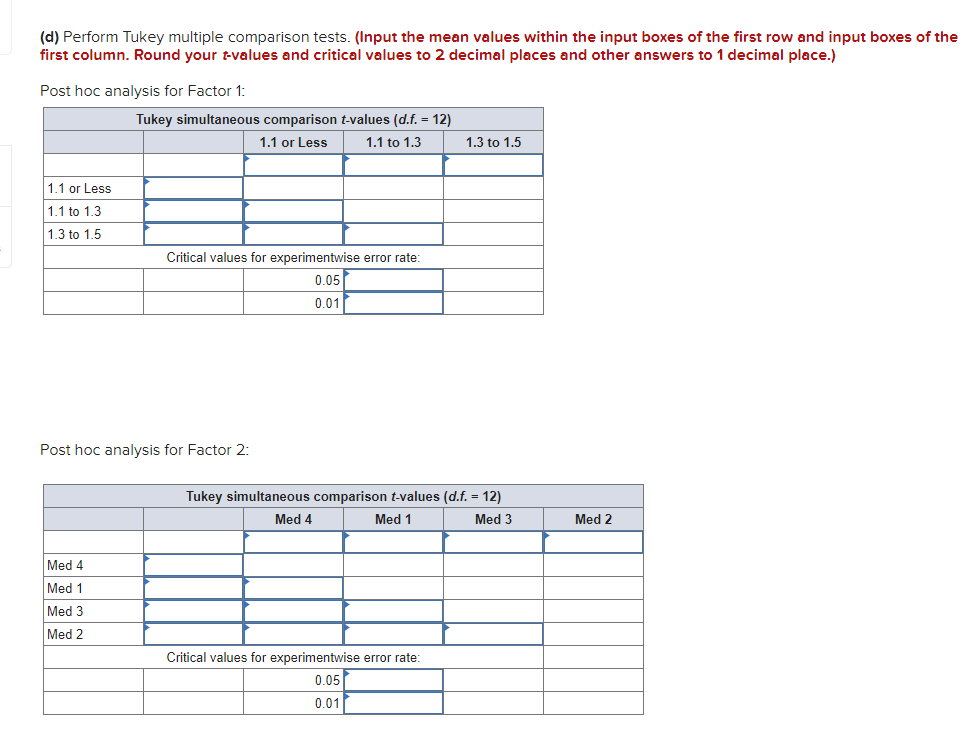
(b) Fill in the missing data. (Round your SS valuesto 3 decimal places, F values to 2 decimal places, and other answers to 4 decimal places.)

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


