Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
the photos are from a example of the same problem just with diffrent numbers i provided the charts with the values i need to be









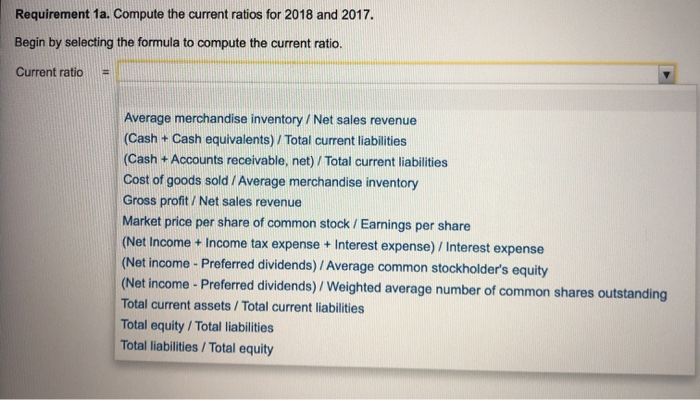
the photos are from a example of the same problem just with diffrent numbers
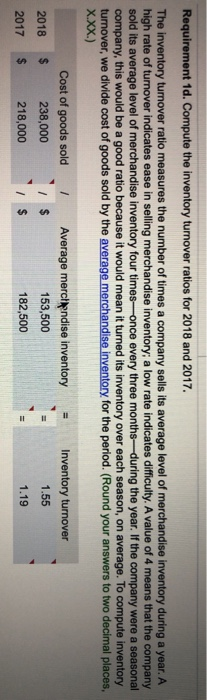
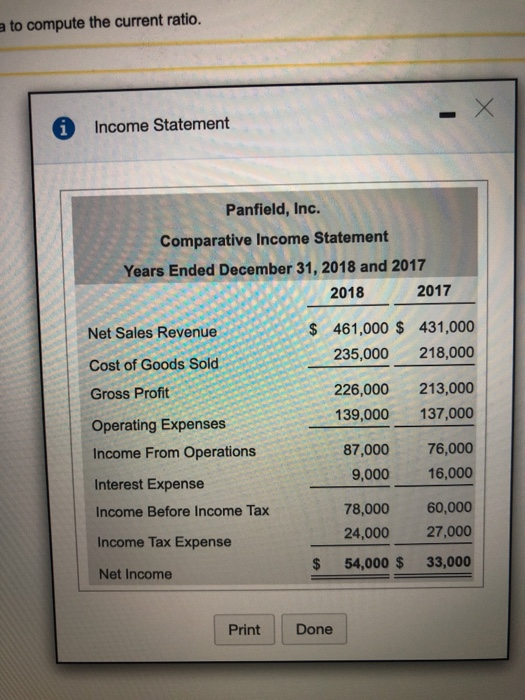
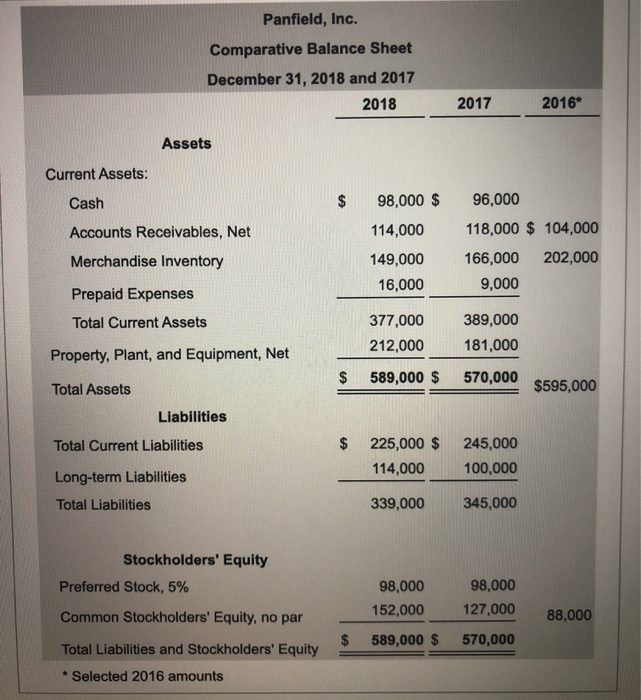
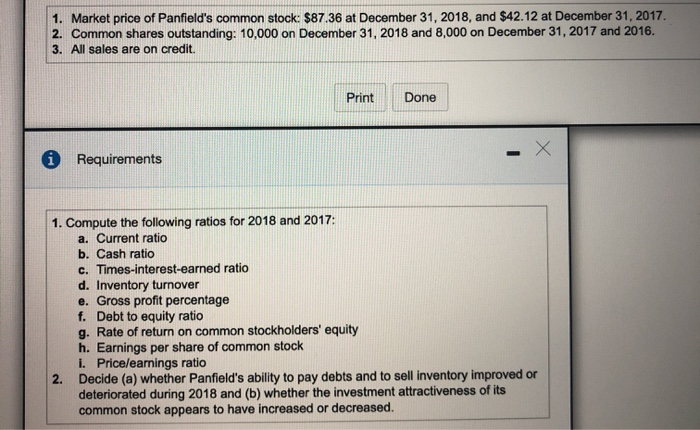
Requirement 1a. Compute the current ratios for 2018 and 2017. The most widely used ratio is the current ratio, which is calculated as the total current assets divided by total current liabilities. The current ratio measures a company's ability to pay its current liabilities with its current assets. Refer to the information provided and calculate the current ratios for 2018 and 2017. (Round your answers to two decimal places, X.XX.) Total current assets / Total current liabilities Current ratio 2018 $ 363,000 / $ 224,000 1.62 2017 379,000 $ 246,000 1.54 Requirement 1b. Compute the cash ratios for 2018 and 2017. Cash is an important part of every business. Without an adequate supply of available cash, businesses cannot continue to operate. Businesses, therefore, monitor cash very carefully. One measure that can be used to calculate a company's liquidity is the cash ratio. The cash ratio helps to determine a company's ability to meet its short-term obligations and is calculated as cash plus cash equivalents divided by total current liabilities. Notice that the cash ratio includes cash and cash equivalents. As a reminder, cash equivalents are highly liquid investments that can be converted into cash in three months or less. Refer to the information provided and calculate the cash ratio for Canfield. (Complete all input boxes. Enter a "0" for items with a zero value. Round your answers to two decimal places, X.XX.) Cash equivalents 0 Cash ( $ 93,000 ( $ 92,000 2018 )/ Total current liabilities )/ $ 224,000 )/ $ 246,000 Cash ratio 0.42 2017 0 0.37 Requirement 1c. Compute the times-interest-earned ratios for 2018 and 2017. Analysts and investors use the times-interest-earned ratio to evaluate a business's ability to pay interest expense. This ratio measures the number of times earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) can cover (pay) interest expense. This ratio is also called the interest-coverage ratio. A high times-interest-earned ratio indicates a business's ease in paying interest expense; a low ratio suggests difficulty. The times-interest-earned ratio is calculated as EBIT (Net income + Income tax expense + Interest expense) divided by interest expense. In this problem, the income from operations is also equal to the EBIT. Thus, we will simply divide the income from operations by the interest expense to compute the times-interest-earned ratio. (Round your answers to two decimal places, X.XX.) Income from operations 1 Interest expense Times-interest-earned 2018 $ 82,000 $ 10,000 8.2 2017 $ 73,000 11,000 6.64 = $ Requirement 1d. Compute the inventory turnover ratios for 2018 and 2017. The inventory turnover ratio measures the number of times a company sells its average level of merchandise inventory during a year. A high rate of turnover indicates ease in selling merchandise inventory; a low rate indicates difficulty. A value of 4 means that the company sold its average level of merchandise inventory four times-once every three months-during the year. If the company were a seasonal company, this would be a good ratio because it would mean it turned its inventory over each season, on average. To compute inventory turnover, we divide cost of goods sold by the average merchandise inventory for the period. (Round your answers to two decimal places, X.XX.) Cost of goods sold Average merchandise inventory Inventory turnover 2018 238,000 / $ 153,500 1.55 2017 $ 218,000 182,500 1.19 = 1 Requirement 1e. Compute the gross profit percentage for 2018 and 2017. Gross profit (sometimes called gross margin) is net sales minus the cost of goods sold. Merchandisers strive to increase the gross profit percentage (also called the gross margin percentage). This ratio measures the profitability of each net sales dollar above the cost of goods sold and is computed as gross profit divided by net sales revenue. The gross profit percentage is one of the most carefully watched measures of profitability. It reflects a business's ability to earn a profit on the merchandise inventory. The gross profit earned on merchandise inventory must be high enough to cover the remaining operating expenses and to earn net income. A small increase in the gross profit percentage from last year to this year may signal an important rise in income. Conversely, a small decrease from last year to this year may signal trouble. (Round your answers to one tenth of a percent, X.X%.) Gross profit Net sales revenue Gross profit percentage 2018 221,000 459,000 2017 $ 210,000 $ 428,000 $ 48.1 % 49.1 % Requirement ll. Compule uld UOL U Lyuity TUUS IUI 20 IU DNIU 2011. The debt to equity ratio shows the relationship between total liabilities and total equity, it shows the proportion of total liabilities relative to total equity. Thus, this ratio measures financial leverage. If the debt to equity ratio is greater than 1, then the company is financing more assets with debt than with equity. If the ratio is less than 1, then the company is financing more assets with equity than with debt. The higher the debt to equity ratio, the greater the company's financial risk. Go ahead and compute Canfield's debt to equity ratio for 2018 and 2017. You will also need to compute the total stockholders' equity, which is the sum of the preferred stock and common stockholders' equity. (Round your answers to two decimal places, X.XX.) Total liabilities Toral equity Debt to equity ratio 2018 $ 338,000 243,000 1.39 2017 $ 345,000 $ 214,000 1.61 Requirement 1g. Compute the rate of return on common stockholders' equity for 2018 and 2017. A popular measure of profitability is rate of return on common stockholders' equity, often shortened to return on equity. This ratio shows the relationship between net income available to common stockholders and their average common equity invested in the company. The rate of return on common stockholders' equity shows how much income is earned for each $1 invested by the common shareholders. To compute this ratio, we first subtract preferred dividends from net income to get net income available to the common stockholders. Then we divide net income available to common stockholders by average common stockholders' equity during the year. (Round your answers to one tenth of a percent, X.X%.) Preferred Average common Rate of return on common (Net income dividends ) stockholders' equity stockholders' equity 2018 $ 49,000 $ 3,060 ) $ 126,500 2017 $ 37,000 $ 3,060 $ 103,000 36.3 % 33 % Requirement 1h. Compute the earnings per share of common stock for 2018 and 2017. Earnings per share (EPS) is perhaps the most widely quoted of all financial statistics, EPS is the only ratio that must appear on the financial statements. Earnings per share reports the amount of net income (loss) for each share of the company's outstanding common stock. Earnings per share is calculated as net income minus preferred dividends divided by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Preferred dividends are subtracted from net income because the preferred stockholders have the first claim to dividends. The computation for the weighted average number of common shares outstanding is covered in advanced accounting courses. For simplicity, we will determine earnings per share on the average number of shares outstanding, calculated as the beginning balance plus ending balance divided by two. The preferred dividends amount you have computed above has been entered in the table for you. (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) I Weighted average number of (Net income Preferred dividends / common shares outstanding Earnings per share 2018 ( $ 49,000 $ 3,060 >/ 10,500 $ 4.38 2017 ( $ 37,000 3,060 ) / 10,000 $ 3.39 The price/earnings ratio is the ratio of the market price of a share of common stock to the company's earnings per share. The price/earnings ratio shows the market price of $1 of earnings. This ratio measures the value that the stock market places on a company's earnings. The earnings per share amounts you computed in the preceding step have been entered in the table for you. (Round your answers to two decimal places, X.XX.) Market price per share of common stock Earnings per share Price/earnings ratio 2018 61.32 "Is 4.38 14.00 2017 44.07 / $ 3.39 13.00 Requirement 2. Decide (a) whether Canfield's ability to pay debts and to sell inventory improved or deteriorated during 2018 and (b) whether the investment attractiveness of its common stock appears to have increased or decreased. (a) Carefully compare the following ratios for each year. Did Canfield's ability to pay its debts and to sell inventory improve or deteriorate during 2018? 2018 2017 Current ratio 1.62 1.54 Cash ratio 0.42 0.37 Times interest earned 8.2 6.64 Inventory turnover 1.55 1.19 Gross profit percentage 48.1% 49.1% (b) Carefully compare the following ratios for each year. Did the investment attractiveness of Canfield's common stock appear to have increased or decreased? Debt to equity ratio Return on common stockholders' equity Earnings per share Price eamings ratio 2018 1.39 36.3% $4.38 14 2017 1.61 33% $3.39 13 a to compute the current ratio. Income Statement Panfield, Inc. Comparative Income Statement Years Ended December 31, 2018 and 2017 2018 2017 Net Sales Revenue $ 461,000 $ 431,000 235,000 218,000 Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit 226,000 139,000 213,000 137,000 Operating Expenses Income From Operations 87,000 9,000 76,000 16,000 Interest Expense Income Before Income Tax 78,000 24,000 60,000 27,000 Income Tax Expense 54,000 $ 33,000 Net Income Print Done Panfield, Inc. Comparative Balance Sheet December 31, 2018 and 2017 2018 2017 2016* Assets Current Assets: Cash $ 98,000 $ 96,000 Accounts Receivables, Net Merchandise Inventory 114,000 149,000 16,000 118,000 $ 104,000 166,000 202,000 9,000 Prepaid Expenses Total Current Assets 377,000 212,000 389,000 181,000 Property, Plant, and Equipment, Net $ 589,000 $ 570,000 Total Assets $595,000 Liabilities Total Current Liabilities $ 225,000 $ 114,000 245,000 100,000 Long-term Liabilities Total Liabilities 339,000 345,000 Stockholders' Equity Preferred Stock, 5% 98,000 152,000 98,000 127,000 Common Stockholders' Equity, no par 88,000 $ 589,000 $ 570,000 Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity * Selected 2016 amounts 1. Market price of Panfield's common stock: $87.36 at December 31, 2018, and $42.12 at December 31, 2017 2. Common shares outstanding: 10,000 on December 31, 2018 and 8,000 on December 31, 2017 and 2016. 3. All sales are on credit. Print Done - i Requirements 1. Compute the following ratios for 2018 and 2017: a. Current ratio b. Cash ratio c. Times-interest-earned ratio d. Inventory turnover e. Gross profit percentage f. Debt to equity ratio g. Rate of return on common stockholders' equity h. Earnings per share of common stock i. Price/earnings ratio Decide (a) whether Panfield's ability to pay debts and to sell inventory improved or deteriorated during 2018 and (b) whether the investment attractiveness of its common stock appears to have increased or decreased. 2. Requirement 1a. Compute the current ratios for 2018 and 2017. Begin by selecting the formula to compute the current ratio. Current ratio Average merchandise inventory / Net sales revenue (Cash + Cash equivalents) / Total current liabilities (Cash + Accounts receivable, net) / Total current liabilities Cost of goods sold / Average merchandise inventory Gross profit / Net sales revenue Market price per share of common stock /Earnings per share (Net Income + Income tax expense + Interest expense) / Interest expense (Net income - Preferred dividends) / Average common stockholder's equity (Net income - Preferred dividends)/Weighted average number of common shares outstanding Total current assets/Total current liabilities Total equity / Total liabilities Total liabilities / Total equity i provided the charts with the values i need to be used
everything should be done the same as the examples but just use the new values i provided
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


