Question
The president of Solar Phasic Industries, Jayne Cash, is interested in buying the Hi Voltage Transformer Company. She sees the possibility of large profits occuring
The president of Solar Phasic Industries, Jayne Cash, is interested in buying the Hi Voltage Transformer Company. She sees the possibility of large profits occuring to Hi Voltage if business is good. If she purchases the company now, large returns can be made in 2 years, when it would be sold. Hi Voltage's stock is currently held by two families, the Edisons and Franklins. The Edisons and Franklins have agreed to sell all their stock now for $1 Million, or half now for $600.000 and the rest in 1 year based on the profit picture that time. Jayne Cash sees the following alternatives available to her.
One is to buy all the stock now and sell at the end of 2 years. On the other hand, if she buys only half now, she can purchase the rest in 1 year and sell at the end of 2 years.
Or she could hold her initial purchase initial purchase and not buy the second half, then sell at the end of the second year. A third alternative is not to purchase any stock and instead buy 2-year treasury bills.
Jayne's payoffs are influenced by business conditions. If business is good the company's first year, the price of the second 50% of the stock will be $800.000. If business is bad, the remainder of the stock will sell for $300.000. However, if business is good the first year, it may be bad during the second, and vice versa. All these events influence what payoffs could be when Jayne plans to sell her shares of Hi Voltage. To resolve the chances of these states of nature facing Jayne Cash, G.N. Potter, Solar's chief economist, was called in to develop estimates of future events.
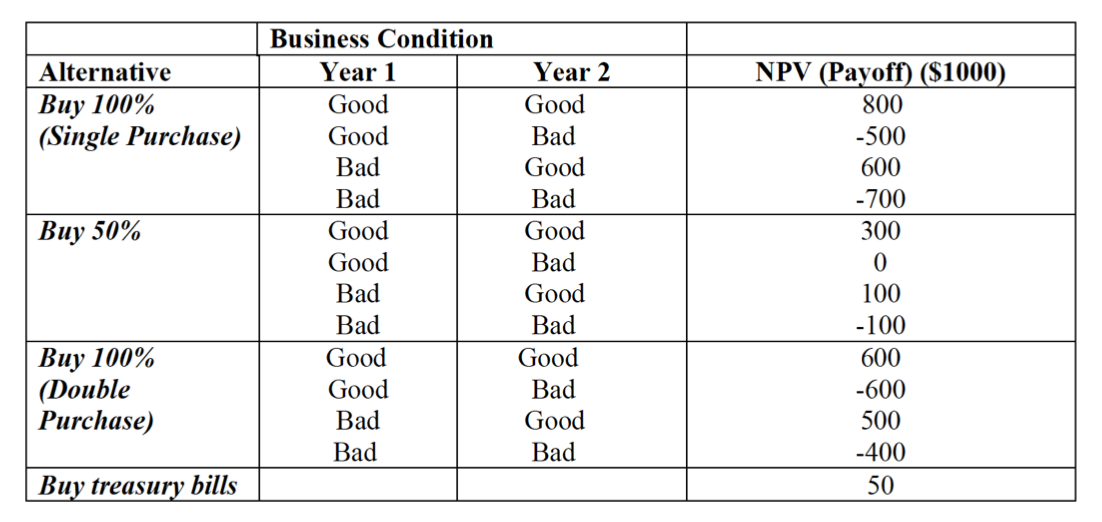
Potter gathered data and projected future events. He stated that in the first year, there would be a 60% chance of good business and 40% of bad. In the second year, if business were good in first, there would be a 70% chance it would be good in the second and 30% chance that it would be bad. If the first year were bad, there would be a 40% chance of good times and 60% of bad in the second year. Colleen Smart, Solar's chief system analyst, was also called on to help. She computed the net present value (NPV) of all possible alternatives available, based on the expected payoffs for each possible outcome. These are presented in Table 1.
Jayne Cash can reap up to $800.000 or lose $700.000, depending upon what decision she makes and the events that occur in the future. Jayne sat at her desk reviewing the information from Potter and Smart. She will have to make a decision in the next few days or lse the opportunity to buy into the company. The Edison and Franklin Families have received other inquiries about selling.
a) Develop a decision tree for Jayne Cash (you can use QM for Windows Decision Tree module or you can depict manually).
b) What do you recommend? What is the best solution for Jayne Cash? Explain.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


