Question: The provided programs should not be modified. Packing circles and rectangles Description In this assignment, you are asked to implement a program (named checkpack) that,
The provided programs should not be modified.
Packing circles and rectangles
Description
In this assignment, you are asked to implement a program (named checkpack) that, given a
rectangular domain and a list of circles and rectangles, can check if the packing configuration is
valid, in the sense that all shapes fit within the domain and there are no overlaps between shapes.
This problem occurs e.g. in electronic device design when packing electronic components on a
printed circuit board.
The program should create a visual representation of the domain and shapes as a scalable vector
graphics (svg) file. An svg file can be visualized using a browser such as Firefox, Safari, Chrome
or Internet Explorer. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scalable_Vector_Graphics .
The positions and sizes of the shapes are specified using integers. The domain is a rectangle of
fixed size (600x500). Circles of arbitrary position and radius are read from standard input.
Rectangles of arbitrary position and sizes are read from input. Circles and Rectangles can appear
in any order in the input.
The program should write on standard output the svg representation of all the shapes, and include
in addition the following diagnostic message:
- ok if the configuration is valid, i.e. all shapes fit in the domain and there are no overlaps
between shapes.
- overlap if the shapes fit in the domain but some of the shapes overlap
- does not fit if any of the shapes does not fit in the domain.
The diagnostic message should appear when rendering the svg file as in Figure 1.
HW3
Implementation
The implementation relies on the classes Domain, Point and Shape. The header files
Domain.h Point.h Shape.h are provided and must not be modified. The programs
testPoint.cpp , testShape.cpp and checkpack.cpp are provided and must not be
modified. All source files should compile without warning. The executables should build without
warning. You must implement the classes Domain (file Domain.cpp) Point (file
Point.cpp) and the classes Circle and Rectangle (file Shape.cpp).
You must provide a Makefile that builds all executables by using the command
$ make
Input
Input for the checkpack program is read from standard input. Each line of input defines a
shape to be added to the domain. The first character on each line determines whether the shape is
a circle (C) or a rectangle (R). The position and size of the shape is described by integers in
the rest of the input line.
A rectangle is specified by the position of its lower left corner, its width and its height.
Example: Rectangle with corners at (10,20), (40,20), (40,60), (10,60)
R 10 20 30 40
A circle is specified by the position of its center and its radius
Example: Circle centered at position (30,40) with radius 20
C 30 40 20
It can be assumed that input will consist of valid characters (only R or C) and the appropriate
number of positive integers.
The checkpack program should be used as follows:
$ ./checkpack test.svg
It must be possible to visualize the file test.svg using a browser (Firefox, Chrome, etc.)
The program checkpack should reproduce exactly the example svg files provided when using
the provided input files. Use the Unix diff function to check for differences.
Point
class
The Point class represents a point in the x-y plane, using integer coordinates x and y. Point
objects can be added and subtracted, and the square of the norm of a point can be calculated (the
square of the norm is computed rather than the norm, in order to perform all operations with
integer arithmetic, and avoid the use of a square root function).
operator>> should read two ints from an input stream to set the values of members x and y.
operator
x=3 and y=4): (3,4)
Domain
class
The Domain class defines the rectangular region of fixed size (600x500) in which the shapes are
packed.
void addShape(const Shape* p) is a function used to add a Shape pointer to the
vector of Shape pointers s.
void draw(void) is a function that generates the entire svg output. It first checks whether
all shapes fit into the Domain (hint: this can be done by defining a Rectangle object
representing the domain and using the Shapes fits_in functions). It checks whether there are
overlaps between shapes (using the Shapes overlaps functions). On the basis of these tests, it
determines the diagnostic message (ok, overlap or does not fit). It then prints the
svg header, the svg representations of all shapes (using the Shapes draw() functions), the
diagnostic message, and the svg trailer on standard output. See the example test output svg files
for details about the svg output format and the contents of the svg header and trailer.
Shape
class
The Shape class is an abstract base class from which Rectangle and Circle are derived.
bool fits_in(const Rectangle& r) is a pure virtual function that should return
true if the Shape fits in the Rectangle r.
void draw(void) is a pure virtual function that writes the svg description of the Shape on
standard output.
Rectangle
class
The Rectangle class is derived from Shape and represents a rectangle. The position of the
Rectangle is its lower left corner.
void draw(void) is a virtual function that writes the svg description of the Rectangle on
standard output, e.g.
Circle
class
The Circle class is derived from Shape and describes a circle. The position of the Circle is its
center.
void draw(void) is a virtual function that writes the svg description of the Circle on
standard output, e.g.
Create a tar file hw3.tar containing all source files and the Makefile. Submit your tar file
using $ handin cs40 hw3 hw3.tar
Notes
1) This problem is an example of use of the double dispatch technique described in Lecture 11.
2) When implementing the various overlaps virtual functions, use the fact that the
Circle::overlaps(const Rectangle& r) function does the same thing as the
Rectangle::overlaps(const Circle& c) function. You only need to implement one
of the two functions, and you can have the second function call the first one.
3) To determine whether a Circle of radius ?? centered at ??!, ??! overlaps with a Rectangle, use
the following algorithm:
a) Compute the coordinates ??!, ??! of the point of the Rectangle that is closest to the Circle
center ??!, ??! (note: this point is not necessarily a corner of the Rectangle). Use the formulas
??! = min (max ??!, ??! , ??! + ??)
??! = min (max ??!, ??! , ??! + ?)
where ??!, ??! is the position of the lower left corner of the Rectangle, and ?? and ? are the
Rectangles width and height.
b) Compute the distance ?? between the point ??!, ??! and the Circle center ??!, ??! . If ??
there is overlap between the Circle and the Rectangle. When testing if ??
condition ??!
function.
4) Rectangles that share an edge do not overlap. For example, the rectangle defined by the points
(10,20), (40,20), (40,60), (10,60) does not overlap with the rectangle defined by the points
(40,30), (60,30), (60,70), (40,70). Likewise, rectangles can share edges with the domain
boundary.
5) This assignment requires you to write a program that verifies that a given packing of circles
and rectangles is valid. The problem of finding an optimal packing of a given set of circles and
rectangles is much more complex, and falls into the category of NP complete problems. See
e.g. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Packing_problems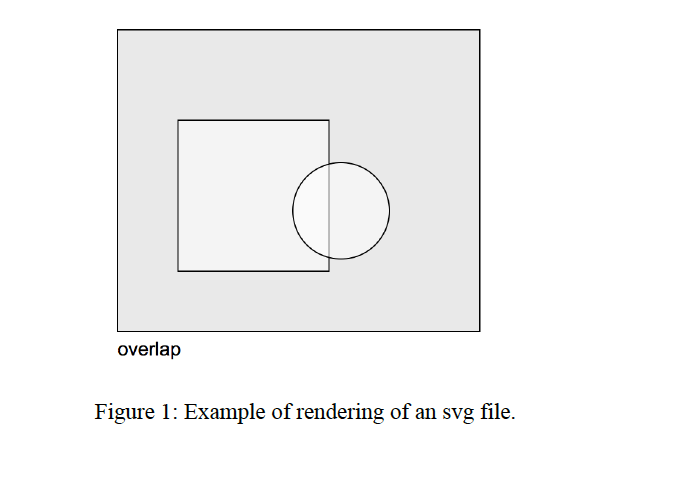
//
// Point.h
//
#ifndef POINT_H
#define POINT_H
#include
class Point
{
public:
Point(void) : x(0), y(0) {}
Point(int xin, int yin) : x(xin), y(yin) {}
int norm2(void) const { return x*x + y*y; }
Point operator+(const Point& rhs) const;
Point operator-(const Point& rhs) const;
int x, y;
};
std::ostream& operator
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& is, Point& p);
#endif
//
// Shape.h
//
#ifndef SHAPE_H
#define SHAPE_H
#include "Point.h"
#include
class Circle;
class Rectangle;
class Shape
{
public:
virtual ~Shape(void) {}
virtual bool overlaps(const Shape& s) const = 0;
virtual bool overlaps(const Circle& r) const = 0;
virtual bool overlaps(const Rectangle& r) const = 0;
virtual bool fits_in(const Rectangle& r) const = 0;
virtual void draw(void) const = 0;
};
class Rectangle : public Shape
{
public:
Rectangle(void): position(Point(0,0)), width(0), height(0) {}
Rectangle(Point p, int w, int h) :
position(p), width(w), height(h) {}
virtual ~Rectangle(void);
virtual bool overlaps(const Shape& r) const;
virtual bool overlaps(const Circle& r) const;
virtual bool overlaps(const Rectangle& r) const;
virtual bool fits_in(const Rectangle& r) const;
virtual void draw(void) const;
const Point position; // position of the lower left corner
const int width, height;
};
class Circle : public Shape
{
public:
Circle(void): center(Point(0,0)), radius(0) {}
Circle(Point c, int r) : center(c),radius(r) {}
virtual ~Circle(void);
virtual bool overlaps(const Shape& s) const;
virtual bool overlaps(const Circle& r) const;
virtual bool overlaps(const Rectangle& r) const;
virtual bool fits_in(const Rectangle& r) const;
virtual void draw(void) const;
Point center;
int radius;
};
#endif
//
// Domain.h
//
#include "Shape.h"
#include
#include
class Domain
{
public:
Domain(void);
~Domain(void);
void addShape(const Shape* p);
void draw(void);
private:
int sizex, sizey;
std::vector
};
//
// testPoint.cpp
//
#include "Point.h"
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Point a(1,2);
Point b(3,4);
cout
cout
cout
cout
cout
Point c = a;
c = c + b - a;
cout
cin >> c;
cout
}
//
// testShape.cpp
//
#include "Shape.h"
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Point center(10,30);
const int radius = 50;
Circle c(center,radius);
c.draw();
Point llcorner = Point(50,70);
const int width = 25;
const int height = 80;
Rectangle r1(llcorner,width,height);
r1.draw();
Rectangle r2(llcorner+Point(20,30),width,height);
r2.draw();
Circle c1(Point(60,160),10);
c1.draw();
Circle c2(llcorner-Point(5,-5),100);
c2.draw();
cout
cout
cout
}
//
// checkpack.cpp
//
#include "Domain.h"
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Domain d;
char type;
int x,y,w,h,r;
cin >> type;
while (cin)
{
if ( type == 'C' )
{
cin >> x >> y >> r;
Shape* p = new Circle(Point(x,y),r);
d.addShape(p);
}
else if ( type == 'R' )
{
cin >> x >> y >> w >> h;
Shape* p = new Rectangle(Point(x,y),w,h);
d.addShape(p);
}
cin >> type;
}
d.draw();
}
overlap Figure 1: Example of rendering of an svg file overlap Figure 1: Example of rendering of an svg file
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


