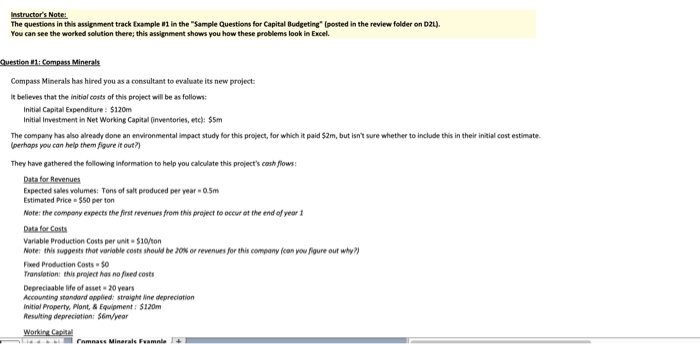
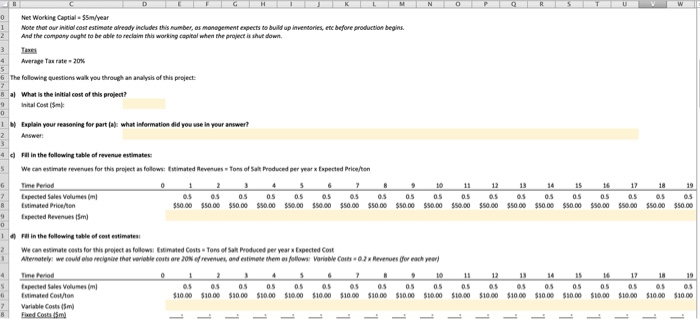
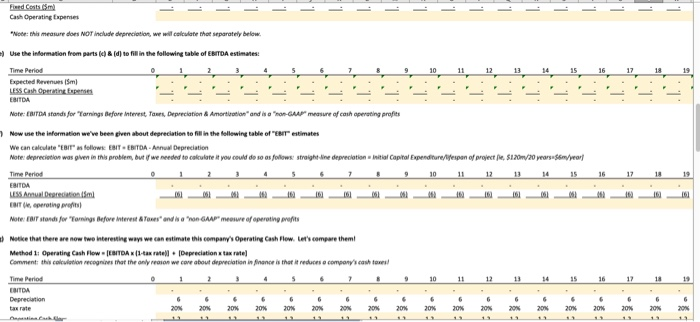
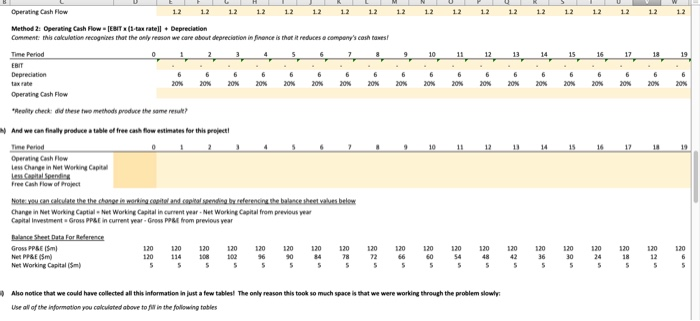
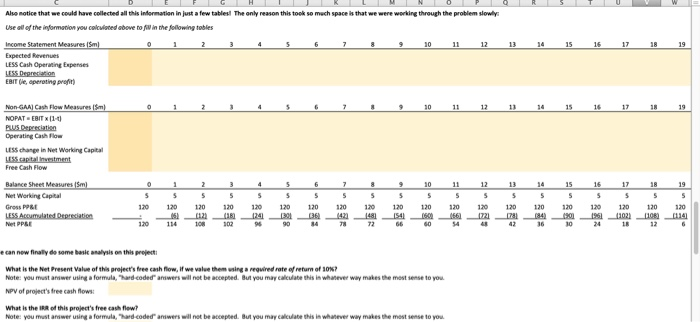
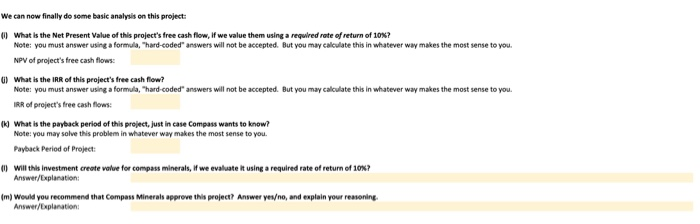
The questions in this assignment track txample "1 in the "Sample Questions for Capital Budgeting" (posted in the review folder on You can see the worked solution there; this assignment shows you how these problems look in Excel. Compass Minerals has hired you as a consultant to evaluate its new project t believes that the initial costs of this project will be as follows: nitial Capital Expenditure: $120m nitial Investment in Net Working Capital Onventories, etc) $5m The company has also already done an environmental impact study for this project, for which it paid $2m, but isn't sure whether to include this in their initial cost estimate (perhaps you can help them figure it out?) They have gathered the following information to help you calculate this project's cosh flows: Data for Revenues Expected sales volumes: Tons of salt produced per year-0.5m Estimated Price $50 per ton Note: the company expects the first revenues from this project to occur et the end of year Data for Costs Variable Production Costs per unit $10Mon Note: this suggests that variable costs should be 20% or revenues for this company (con Fixed Production Costs-$0 Translotion: this project has no flxed costs Faure out why?) Depreciaable life of asset 20 years Accounting standard applied straight Nne depreciation Initial Property, Plant,& Equipment: $120m Resulting depreciation: 36m/year Net Working Captial-$5m/year Noe tht our ineial cost estimate aready includes this umber, os monegement expects to build ap inventories, ene before production begins And the compony oughe to be ablie do reclaim this working copital when the projinct is shut down 3Tar Average Tax rate 20% 6 The followingquestions walk you through an analysis of this preject a) What is the initial cosofthis project? Inital Cost mk 1Explain your reasoning lor part (a)i what infermation did you sse in your answer? 2 Answer Fll in the following table of revenue estimates S We can estimate revenues for this project as follows: Estimated Revenues 6 Time Period 8 Estimated Priceon Tons of Salt Produced per year x Expected Price/o 7 Expected Sales Volumes (m Expected Revenues (Sm) #0 inthe following table of cost estimates: We can eimate cests for ts preject as folows: Eimated Cests Tors of Sal Produced per year x Expected Cot Alternately, we could ehorecgsre that venoble costs are 20% ef revenues, and estmete ehem os folows: vonable Cast.. 02 x Revenues each year Espected Sales Volumes 6imated Costo s1000 $1000 $30.0 $10.00 10.00 $10.00 s1000 $1000 $30.00 $10.00 $10.00 S10.00 S1000 $30.00 $30.00 %10.00 $10.00 s1000 s1000| 7 Variable Costs(5m Cash Operating Expenses Note: this measure dors NOT inelude deprecietm, we wacaklate thee separately below. ) Use the indarmation frem parts ()& (dj te fill in the follewing table of EBITDA estimates: 17 Expected Revenues (Sm ESITDA Note: EBITDA stands for Tarnings Before Intenest, Tases, Depreciation&Amortiration and is o "mon-GAAP measure of cash operating profits Now une the isformation we've been given about depreciatien to fill in the fellewing table of "ENT estimates We can caleulate EBIT"as llow ESIT EBITDA-Asnual Depreciation Note deprecietion was geennNs problem, but we needed to cakalateityou could do so asyolows, stroghean, depreciationndial Capital EspendtureMeoen of projecte si20m/20 years-sevve Time Period Note: EBIT stands for Tomings Before interest&Toxes and is a "non GAAP meosure ofoperoting prefits Notice that there are now twe nteresting ways we can estimate this company's Operating Cash Flew Let's compare them Method 1: Operating Cash Flow [ESITDA(1-tax ratell [Depreciation tax rate Comment: this coluiation recognines mat the only reason we core about deprecilation in finance is that it reduces o compony's cash toxes Time Perio SITDA XN20% 20% 2 % 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% 20% Operating Cash Flow 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 Method 2: Operating Cash Flow-EBIT (1-tax rate]I + Depreciation Comment this caleulotion recognites that the oney reeson we (are obout depreciation n finence is that it reduces compony's cash tael Operating Cash Flow Reolity check: did these two methods produce the same resal And we can finaly produceatable of free cash flaw estimates for this prejectl Operating Cash Flew Less Change in Net Working Capital free Cash Flow of Project Change in Net Working Captial Net Working Capital in current year-Net Working Capital from previous ear Capital investment Gross PP&E in current year-Gress PP&t from previous year Gross PP&E ISm) Net PP&E (5m) Net Working Capital Gm anotice th w, could hav, collected all this infomationinjust a few tables, The on y reason this took so much space isnt w, were working through the problem slewew Use all of the information you colculated above to fil in the folowing tobies Also notice that we could have collected all this infenmatian in just a few tablesl The only reason this took so much space is that we were working through the problem slowly Use all of the informotion you colculoted above to jill in the folowing tobles Expected Revenues LESS Cash Operating Experses EBIT (ie, aperating prefit) NOPAT EBIT1- Operating Cash low LESS change in Net Working Capital Net Working Capital Gross PP& 120 120 120 120 120 120120 1210120 120010 120 10 120 120 12010 120 114 10802 e can new finally da some basic analysis on this prejert what is the Net Present Value of this project's foee cwsh flow, if we value them using required rate orretum of 30%? But you may calculate this Note: you must answer using a formula, ardeoded. answers will not be accepted NPV of project's free cash flows What is the IRR of this project's free cash flew whatever way makes the most sense to you Note: you must answer using a formala'd