Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
The standard methods that apply to analytical chemistry still applies with radiochemical analytes. When the behavior of a radionuclide has to be taken into consideration
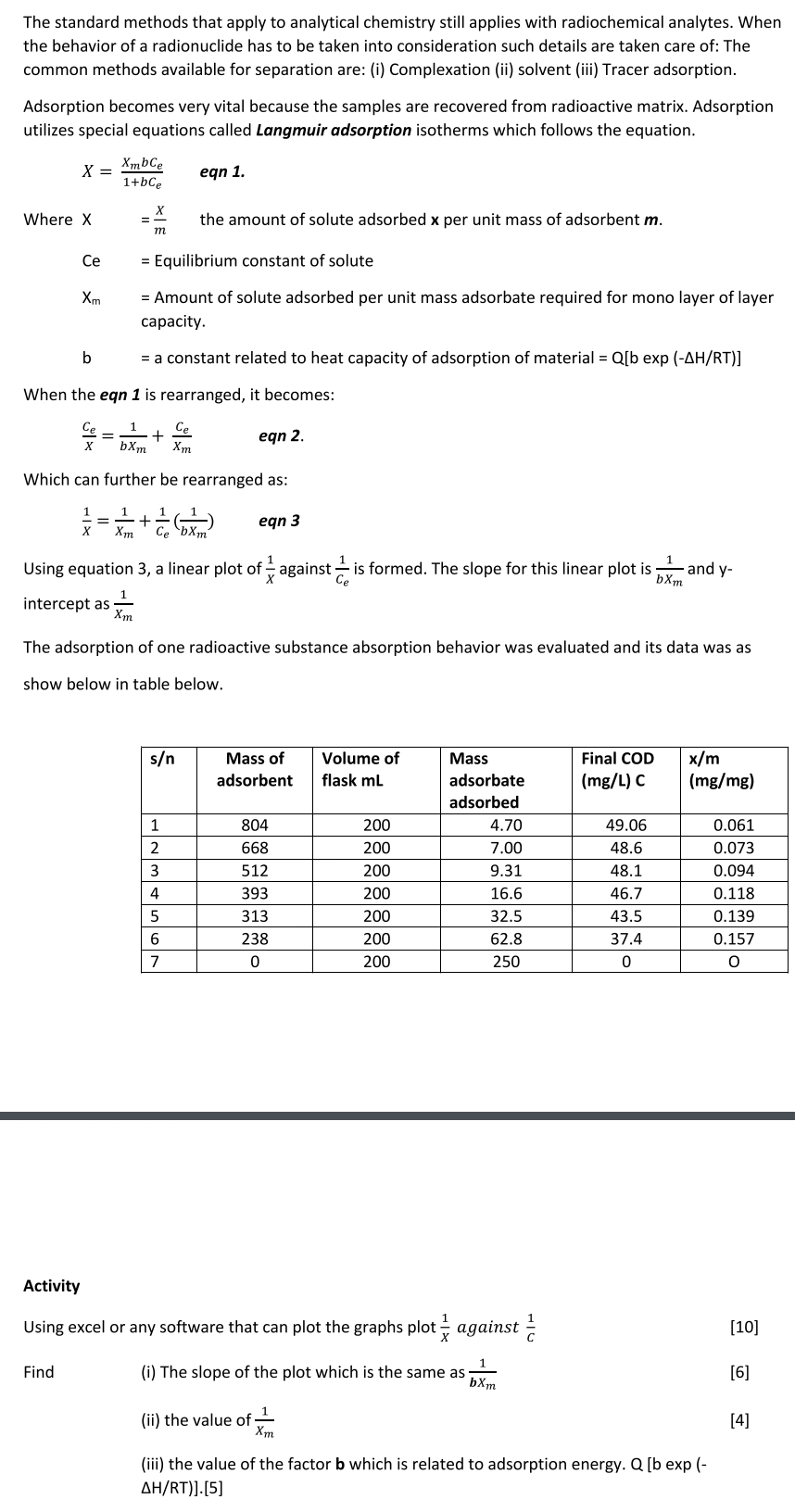
The standard methods that apply to analytical chemistry still applies with radiochemical analytes. When the behavior of a radionuclide has to be taken into consideration such details are taken care of: The common methods available for separation are: i Complexation ii solvent iii Tracer adsorption.
Adsorption becomes very vital because the samples are recovered from radioactive matrix. Adsorption utilizes special equations called Langmuir adsorption isotherms which follows the equation.
eqn
Where the amount of solute adsorbed per unit mass of adsorbent
Equilibrium constant of solute
Amount of solute adsorbed per unit mass adsorbate required for mono layer of layer capacity.
b a constant related to heat capacity of adsorption of material
When the eqn is rearranged, it becomes:
eqn
Which can further be rearranged as:
eqn
Using equation a linear plot of against is formed. The slope for this linear plot is and intercept as
The adsorption of one radioactive substance absorption behavior was evaluated and its data was as show below in table below.
tabletableMass ofadsorbenttableVolume offlask mLtableMassadsorbateadsorbedtableFinal CODmgL Ctable
The standard methods that apply to analytical chemistry still applies with radiochemical analytes. When the behavior of a radionuclide has to be taken into consideration such details are taken care of: The common methods available for separation are: i Complexation ii solvent iii Tracer adsorption.
Adsorption becomes very vital because the samples are recovered from radioactive matrix. Adsorption utilizes special equations called Langmuir adsorption isotherms which follows the equation.
eqn
Where the amount of solute adsorbed per unit mass of adsorbent
Equilibrium constant of solute
Amount of solute adsorbed per unit mass adsorbate required for mono layer of layer capacity.
b a constant related to heat capacity of adsorption of material
When the eqn is rearranged, it becomes:
eqn
Which can further be rearranged as:
eqn
Using equation a linear plot of against is formed. The slope for this linear plot is and intercept as
The adsorption of one radioactive substance absorption behavior was evaluated and its data was as show below in table below.
tabletableMass ofadsorbenttableVolume offlask
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


