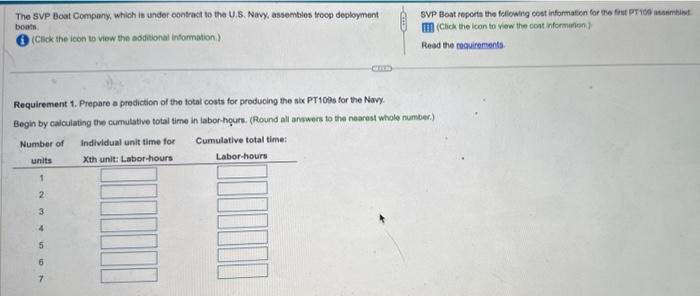
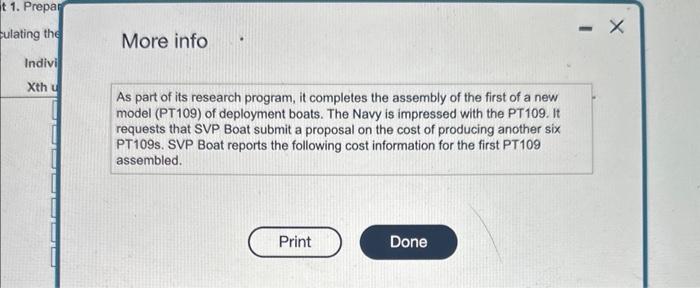
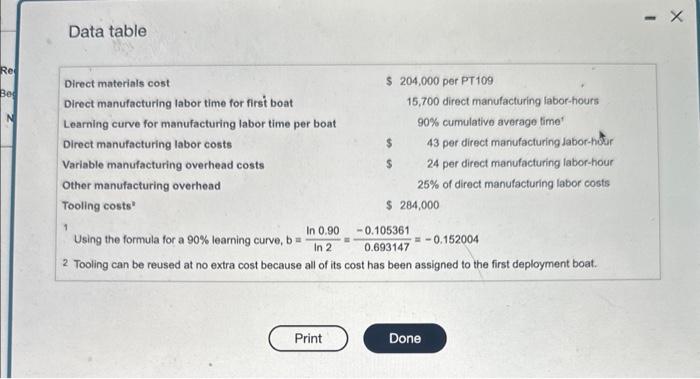
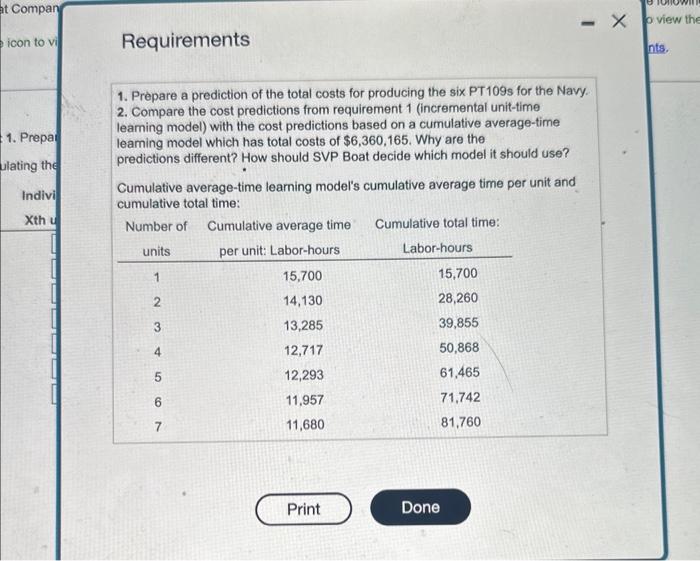
The SVP Boat Company, which is under oontract to the U.S. Navy, assembles troep deployment SVP Boat reporta the following cost informason for the fest pr iod atsembint. boats III (Click the icon to vew the cost information) (Csck the icon to view the aditional intormation.) Read the roguirements. Requirement 1. Prepare a prediction of the total costs for producing the sic PT109s for the Navy. Begin by caiculating the cumulative total time in labor-hours. (Round all answers to the nearest whole number.) As part of its research program, it completes the assembly of the first of a new model (PT109) of deployment boats. The Navy is impressed with the PT109. It requests that SVP Boat submit a proposal on the cost of producing another six PT109s. SVP Boat reports the following cost information for the first PT109 assembled. Data table Direct materials cost \$ 204,000 per PT 109 Direct manufacturing labor time for first boat 15,700 direct manufacturing labor-hours Learning curve for manufacturing labor time per boat 90% curmulative average time' Direct manufacturing labor costs 43 per direct manufacturing labor-hr Variable manufacturing overhead costs 24 per direct manufacturing labor-hour Other manufacturing overhead 25% of direct manufacturing labor costs Tooling costs $284,000 1 Using the formula for a 90% learning curve, b=ln2ln0.90=0.6931470.105361=0.152004 2 Tooling can be reused at no extra cost because all of its cost has been assigned to the first deployment boat. Requirements 1. Prepare a prediction of the total costs for producing the six PT 109s for the Navy. 2. Compare the cost predictions from requirement 1 (incremental unit-time leaming model) with the cost predictions based on a cumulative average-time leaming model which has total costs of $6,360,165. Why are the predictions different? How should SVP Boat decide which model it should use? Cumulative average-time learning model's cumulative average time per unit and cumulative total time: The SVP Boat Company, which is under oontract to the U.S. Navy, assembles troep deployment SVP Boat reporta the following cost informason for the fest pr iod atsembint. boats III (Click the icon to vew the cost information) (Csck the icon to view the aditional intormation.) Read the roguirements. Requirement 1. Prepare a prediction of the total costs for producing the sic PT109s for the Navy. Begin by caiculating the cumulative total time in labor-hours. (Round all answers to the nearest whole number.) As part of its research program, it completes the assembly of the first of a new model (PT109) of deployment boats. The Navy is impressed with the PT109. It requests that SVP Boat submit a proposal on the cost of producing another six PT109s. SVP Boat reports the following cost information for the first PT109 assembled. Data table Direct materials cost \$ 204,000 per PT 109 Direct manufacturing labor time for first boat 15,700 direct manufacturing labor-hours Learning curve for manufacturing labor time per boat 90% curmulative average time' Direct manufacturing labor costs 43 per direct manufacturing labor-hr Variable manufacturing overhead costs 24 per direct manufacturing labor-hour Other manufacturing overhead 25% of direct manufacturing labor costs Tooling costs $284,000 1 Using the formula for a 90% learning curve, b=ln2ln0.90=0.6931470.105361=0.152004 2 Tooling can be reused at no extra cost because all of its cost has been assigned to the first deployment boat. Requirements 1. Prepare a prediction of the total costs for producing the six PT 109s for the Navy. 2. Compare the cost predictions from requirement 1 (incremental unit-time leaming model) with the cost predictions based on a cumulative average-time leaming model which has total costs of $6,360,165. Why are the predictions different? How should SVP Boat decide which model it should use? Cumulative average-time learning model's cumulative average time per unit and cumulative total time