Question: The unit circle {(x, y) : x2 +y2 = 1} is divided into three arcs by choosing three random points A, B, C on the
The unit circle {(x, y) : x2 +y2 = 1} is divided into three arcs by choosing three random
points A, B, C on the circle (independently and uniformly), forming arcs between A and
B, between A and C, and between B and C. Let L be the length of the arc containing
the point (1, 0). What is E(L)? Study this by working through the following steps.
(a) Explain what is wrong with the following argument: "The total length of the arcs is
2?, the circumference of the circle. So by symmetry and linearity, each arc has length
2?/3 on average. Referring to the arc containing (1, 0) is just a way to specify one of
the arcs (it wouldn't matter if (1, 0) were replaced by (0,
In the event that Xi, I = 1, 2, 3 are autonomous remarkable arbitrary factors with rates Ai = 1, 2, 3, find (a) P{Xi
(b) P{X1
(C) EIMaXXilKi
(d) ElmaxXil
Q14
A bunch of n urban areas is to be associated through correspondence joins. The expense to build a connection between urban communities I and j is Cap I r j. Enough connections ought to be built so that for each pair of urban areas there is a way of connections that interfaces them. Therefore, just n ? 1 connections need be developed. An insignificant expense calculation for tackling this issue (known as the negligible crossing tree issue) first develops the least expensive of all the (1 ) joins. At that point, at each extra stage it picks the least expensive connection that associates a city with no connections 3, , n to one with joins. That is, assuming the principal connect is between urban areas 1 and 2, the subsequent connection will either be somewhere in the range of 1 and one of the connections or somewhere in the range of 2 and one of the connections 3, .. , n. Assume that the entirety of the (11) costs are free remarkable irregular factors with mean 1. Track down the normal expense Cu of the former calculation
in the event that
(a) n = 3,
(b) n = 4
Q15
Leave X1 and X2 alone free outstanding irregular factors, each having rate p. Let X(i) = minimum(Xi, X1) and X(2) = IMU M( X , X>) Find
(a) EIX(1)1. (b) Var[Xi), (c) EIX1)], (d) Var[Xz],
Q16
Consider a two-worker framework where a client is served first by worker 1, at that point by worker 2,
and afterward withdraws. The assistance times at worker j are outstanding arbitrary factors vvith rates I =
1, 2. At the point when you show up, you discover worker 1 free and two clients at worker 2?customerA in
administration and client a holding up in line.
(a) Find PA, the likelihood that An is as yet in setuice vvhen you move over to worker 2.
(b) Find PS, the likelihood that B is as yet in the framework when you move over to worker 2.
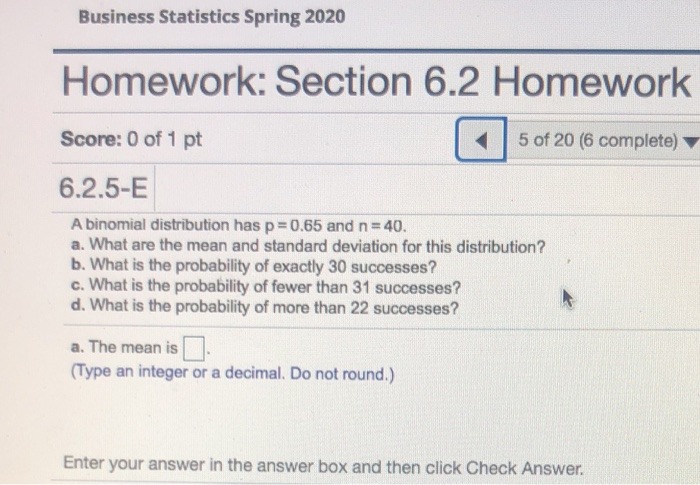
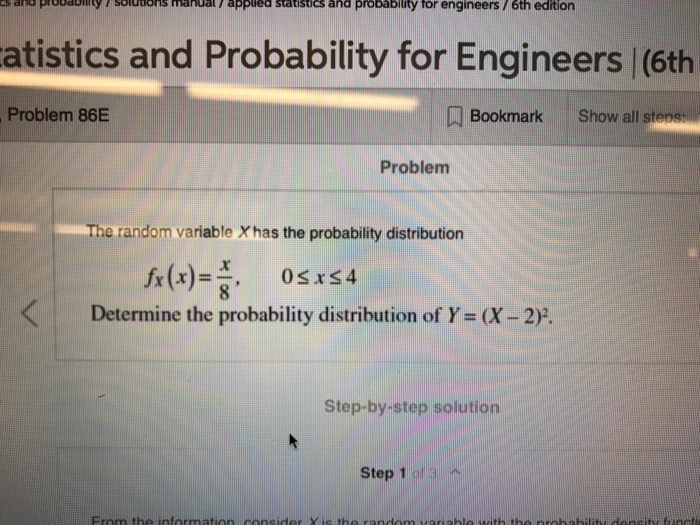
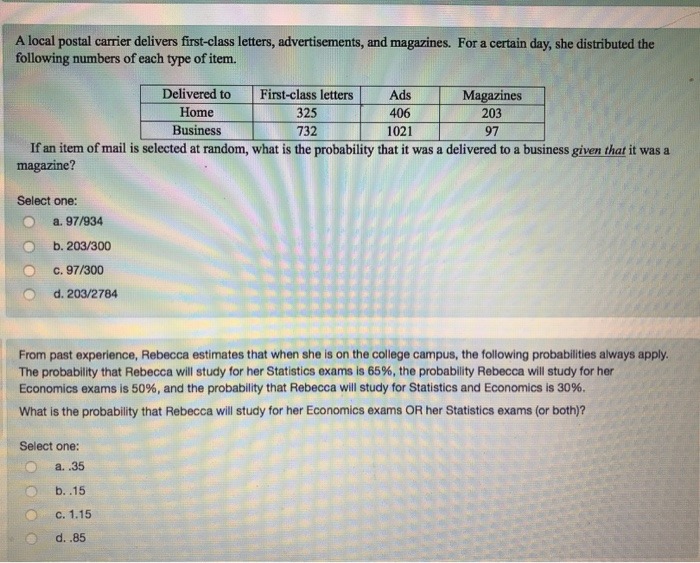
Business Statistics Spring 2020 Homework: Section 6.2 Homework Score: 0 of 1 pt 5 of 20 (6 complete) 6.2.5-E A binomial distribution has p =0.65 and n = 40. a. What are the mean and standard deviation for this distribution? b. What is the probability of exactly 30 successes? c. What is the probability of fewer than 31 successes? d. What is the probability of more than 22 successes? a. The mean is (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer.nd probability for engineers / 6th edition atistics and Probability for Engineers | (6th Problem 86E Bookmark Show all stepsill Problem The random variable X has the probability distribution fx (x) = OSX54 Determine the probability distribution of Y = (X- 2). Step-by-step solution Step 1A local postal carrier delivers first-class letters, advertisements, and magazines. For a certain day, she distributed the following numbers of each type of item. Delivered to First-class letters Ads Magazines Home 325 406 203 Business 732 1021 97 If an item of mail is selected at random, what is the probability that it was a delivered to a business given that it was a magazine? Select one: a. 97/934 O b. 203/300 C. 97/300 d. 203/2784 From past experience, Rebecca estimates that when she is on the college campus, the following probabilities always apply. The probability that Rebecca will study for her Statistics exams is 65%, the probability Rebecca will study for her Economics exams is 50%, and the probability that Rebecca will study for Statistics and Economics is 30%. What is the probability that Rebecca will study for her Economics exams OR her Statistics exams (or both)? Select one: O a. .35 O b. .15 C. 1.15 d. .85
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


