Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
these are the formulas SECTION A: PRACTICAL QUESTIONS TOTAL: 100 MARKS Answer FOUR (4) out of FIVE (5) questions. Question 1 a) Tom is a




these are the formulas 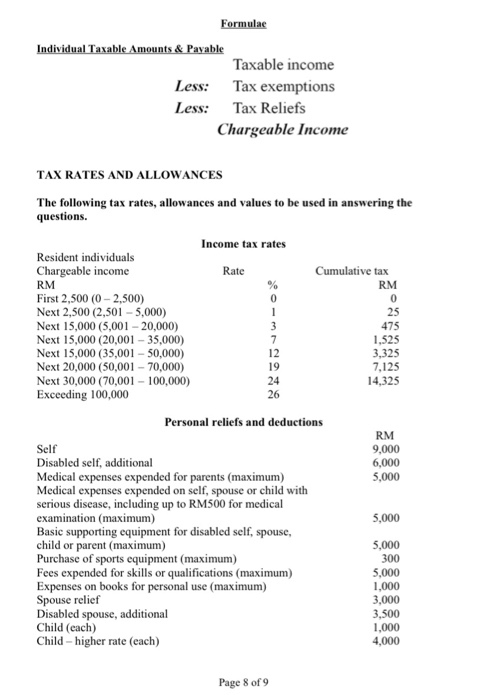

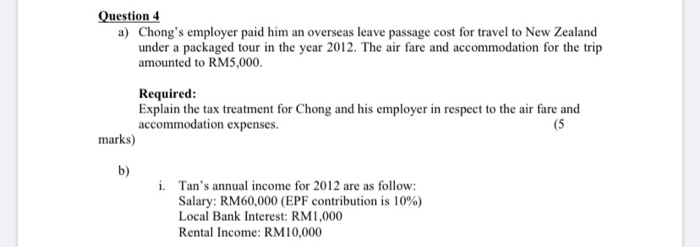
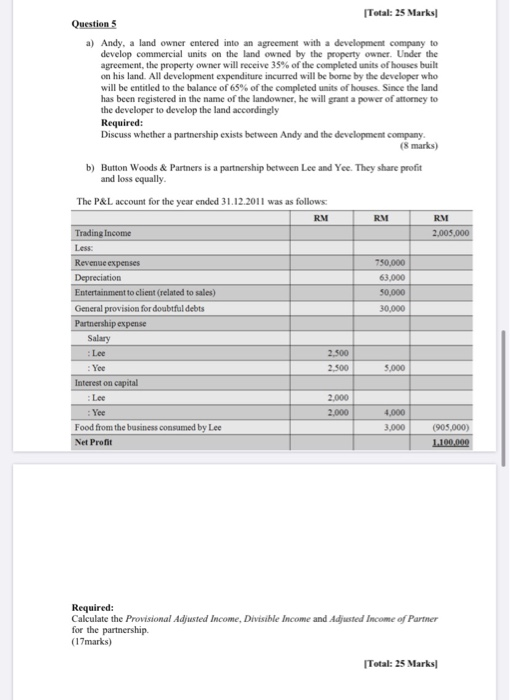
SECTION A: PRACTICAL QUESTIONS TOTAL: 100 MARKS Answer FOUR (4) out of FIVE (5) questions. Question 1 a) Tom is a builder, he bought an agricultural land near Senadin in 2009 for RM80,000. The purchase was financed by a bank loan. He did not develop the land nor did he advertised it for sale. In January 2011, he received an offer from a real estate company in which he had no interest). He sold part of the land to the company for RM80,000. Six months later, He sold the remainder of the land for RM120,000 to another real estate company in which he had a controlling interest. Required: Explain with reason, would the profit be considered as business income under S.4 of Income Tax Act? (7 marks) b) There are significant differences between employment and profession. Discuss the different tax treatments for each of the items below: i. Capital allowance ii. Losses carried forward iii. Basis of assessment iv. Deductions (12 marks) (6 c) Describe 3 inherent characteristics of employment Marks) [Total: 25 Marks) Question 2 a) Below listed are some of the common expenses incurred by businesses in various industries. State with reason(s) whether each of the mentioned expenses is deductible for corporate tax purposes. a) Provision for warranty claims charged to profit and loss account by an electrical appliances manufacturer. [4 Marks) b) Expenses incurred by a company for holding a Family Day" for the staffs and their families [4 Marks] c) Fines imposed on a transport company for repeated offences of overloading. Such practice is necessary to increase the profitability of the company. [4 Marks b) YKY provided the following information regarding the residential property for the year ended 31 Dec 2015 Receipts RM RM Rental: Jan - March 16,000 April-May June - December 24,000 Deposit (refundable) 26,000 Deposit for electricity, water & telephone 4.000 70,000 Payments Deposit refunded to ex-tenant 4,000 Assessment 4,200 Quit rent for 2014 - RM390 2015 - RM390 780 Interest on loan (Jan-Dec) 8,010 Penalty for late payment of quit rent 160 Repairs (carried out in May) Repainting 2,650 Renovation to kitchen & bathroom 7,660 Replacement of damaged tiles 3,750 Installation of air-conditioning unit 1.150 (32.360) Net Rental 37,640 Calculate the adjusted income from rental source of YKY. Explain your answers for any tax adjustment made for the YA2015. (13 marks) Question 3 Bunga Sdn Bhd is in the transportation and logistics business and closes its accounts to 31 December annually. The company has been in operations for more than five years. The company acquired the following assets during the year ended 31 December 2015: Cost RM (1) New passenger motor vehicle 120,000 Lorry 200,000 (iii) Company van (with commercial license) 160,000 (iv) Second-hand passenger motor vehicle 101,000 During the year ended 31 December 2015, the following assets were disposed of: Qualifying Disposal expenditure proceeds RM RM Assets acquired in 2011 Office equipment 10,000 11,000 Assets acquired in 2012 Furniture and fittings 20,000 12,000 Required: (a) Compute the capital allowances for the new assets acquired in 2015. (17 Marks) (b) Compute the residual expenditure and the balancing charge(s) and/or balancing allowance(s) in respect of the assets disposed of during the year of assessment 2015. (8 Marks) Question 4 a) Chong's employer paid him an overseas leave passage cost for travel to New Zealand under a packaged tour in the year 2012. The air fare and accommodation for the trip amounted to RM5,000. Required: Explain the tax treatment for Chong and his employer in respect to the air fare and accommodation expenses. (5 marks) b) i. Tan's annual income for 2012 are as follow: Salary: RM60,000 (EPF contribution is 10%) Local Bank Interest: RM1,000 Rental Income: RM10,000 Required: Compute the chargeable income and tax payable for Tan for YA2012. (10 marks) ii. Ali and his wife made the following EPF contribution and insurance premium payment in 2012: Ali - EPF: RM3,000 & Insurance Premium: RM7,000 Wife - EPF: RM4,000 & Insurance Premium: RM500 Number of children below 18-years old : 4 Required: Compute the total relief for Ali and his wife for the YA2012 under both joint and separate assessment. The wife has made an election to claim child relief. (10 marks) [Total: 25 Marks Total: 25 Marks Questions a) Andy, a land owner entered into an agreement with a development company to develop commercial units on the land owned by the property owner. Under the agreement, the property owner will receive 35% of the completed units of houses built on his land. All development expenditure incurred will be bome by the developer who will be entitled to the balance of 65% of the completed units of houses. Since the land has been registered in the name of the landowner, he will grant a power of attorney to the developer to develop the land accordingly Required: Discuss whether a partnership exists between Andy and the development company. (8 marks) b) Button Woods & Partners is a partnership between Lee and Yce. They share profit and loss equally The P&L account for the year ended 31.12.2011 was as follows RM RM RM Trading Income 2,005,000 Less: Revenue expenses 750,000 Depreciation 63.000 Entertainment to client related to sales) 50.000 General provision for doubtfuldebts 30,000 Partnership expense Salary : Lee 2.500 : Yee 2.500 5.000 Interest on capital Lee 2.000 : Yee 2.000 4,000 Food from the business consumed by Lee 3,000 (905,000) Net Profit 1.100.000 Required: Calculate the Provisional Adjusted Income, Divisible Income and Adjusted Income of Partner for the partnership (17marks) Total: 25 Marks Formulae Individual Taxable Amounts & Payable Taxable income Less: Tax exemptions Less: Tax Reliefs Chargeable Income TAX RATES AND ALLOWANCES The following tax rates, allowances and values to be used in answering the questions. Income tax rates Resident individuals Chargeable income Rate Cumulative tax RM RM First 2,500 (0 - 2,500) 0 0 Next 2,500 (2,501 - 5,000) 25 Next 15,000 (5,001 - 20,000) 3 475 Next 15,000 (20,001 - 35,000) 7 1.525 Next 15,000 (35,001 - 50,000) 12 3,325 Next 20,000 (50,001 - 70,000) 19 7.125 Next 30,000 (70,001 - 100,000) 24 14,325 Exceeding 100,000 26 Personal reliefs and deductions RM Self 9,000 Disabled self, additional 6,000 Medical expenses expended for parents (maximum) 5,000 Medical expenses expended on self, spouse or child with serious disease, including up to RM500 for medical examination (maximum) 5,000 Basic supporting equipment for disabled self, spouse, child or parent (maximum) 5,000 Purchase of sports equipment (maximum) 300 Fees expended for skills or qualifications (maximum) 5,000 Expenses on books for personal use (maximum) 1,000 Spouse relief 3,000 Disabled spouse, additional 3,500 Child (each) 1,000 Child - higher rate (each) 4,000 Page 8 of 9 5.000 4.000 6.000 1,000 Disabled chim (each) Disabled child - additional (each) Life insurance premiums and contributions to approved funds (maximum) Deferred annaty premiums (maximum) Medical and for education insurance premium for self, spouse or child (maximum) Purchase of a personal computer (maximum) Broadband subscription (maximum Deposit for a child into the National Education Savings Scheme (maximum) 3.000 3.000 3.000 Rebates Chargeable income not exceeding RM35,000 RM Individual 400 Individual entitled to a deduction in respect of a spouse or former wife 800 Value of benefits in kind Car scale Cost of car(when new) Prescribed annual value of private usage of car RM RM Up to 50,000 1.200 50,001 to 75.000 75.001 to 100,000 3.600 100,001 to 150.000 150,00 1 0 200,000 7000 200,001 to 250.000 9.000 250,001 to 350,000 15.000 350,001 to 500.000 21.250 500,001 and above 25.000 The value of the car benefit equal to half the prescribed annual value (above) is taken if the car provided is more than five (5) years old Where a driver is provided by the employer, the value of the benefit per month is fixed at RM600 RM per month Other benefits Household furnishings apparatus and appliances Semi-furnished with furniture in the lounge, dining room, or bedroom Semi-furnished with furniture as above plus air-conditioners and/or curtains and carpets 70 140 Fully furnished premises Domestic help Gardener 280 400 300 Capital allowances Annual allowance (AA) Rate Industrial buildings Plant and machinery - general Motor vehicles and heavy machinery Office equipment, furniture and fittings Initial allowance (IA) Rate 10 20 20 20 20 10 SECTION A: PRACTICAL QUESTIONS TOTAL: 100 MARKS Answer FOUR (4) out of FIVE (5) questions. Question 1 a) Tom is a builder, he bought an agricultural land near Senadin in 2009 for RM80,000. The purchase was financed by a bank loan. He did not develop the land nor did he advertised it for sale. In January 2011, he received an offer from a real estate company in which he had no interest). He sold part of the land to the company for RM80,000. Six months later, He sold the remainder of the land for RM120,000 to another real estate company in which he had a controlling interest. Required: Explain with reason, would the profit be considered as business income under S.4 of Income Tax Act? (7 marks) b) There are significant differences between employment and profession. Discuss the different tax treatments for each of the items below: i. Capital allowance ii. Losses carried forward iii. Basis of assessment iv. Deductions (12 marks) (6 c) Describe 3 inherent characteristics of employment Marks) [Total: 25 Marks) Question 2 a) Below listed are some of the common expenses incurred by businesses in various industries. State with reason(s) whether each of the mentioned expenses is deductible for corporate tax purposes. a) Provision for warranty claims charged to profit and loss account by an electrical appliances manufacturer. [4 Marks) b) Expenses incurred by a company for holding a Family Day" for the staffs and their families [4 Marks] c) Fines imposed on a transport company for repeated offences of overloading. Such practice is necessary to increase the profitability of the company. [4 Marks b) YKY provided the following information regarding the residential property for the year ended 31 Dec 2015 Receipts RM RM Rental: Jan - March 16,000 April-May June - December 24,000 Deposit (refundable) 26,000 Deposit for electricity, water & telephone 4.000 70,000 Payments Deposit refunded to ex-tenant 4,000 Assessment 4,200 Quit rent for 2014 - RM390 2015 - RM390 780 Interest on loan (Jan-Dec) 8,010 Penalty for late payment of quit rent 160 Repairs (carried out in May) Repainting 2,650 Renovation to kitchen & bathroom 7,660 Replacement of damaged tiles 3,750 Installation of air-conditioning unit 1.150 (32.360) Net Rental 37,640 Calculate the adjusted income from rental source of YKY. Explain your answers for any tax adjustment made for the YA2015. (13 marks) Question 3 Bunga Sdn Bhd is in the transportation and logistics business and closes its accounts to 31 December annually. The company has been in operations for more than five years. The company acquired the following assets during the year ended 31 December 2015: Cost RM (1) New passenger motor vehicle 120,000 Lorry 200,000 (iii) Company van (with commercial license) 160,000 (iv) Second-hand passenger motor vehicle 101,000 During the year ended 31 December 2015, the following assets were disposed of: Qualifying Disposal expenditure proceeds RM RM Assets acquired in 2011 Office equipment 10,000 11,000 Assets acquired in 2012 Furniture and fittings 20,000 12,000 Required: (a) Compute the capital allowances for the new assets acquired in 2015. (17 Marks) (b) Compute the residual expenditure and the balancing charge(s) and/or balancing allowance(s) in respect of the assets disposed of during the year of assessment 2015. (8 Marks) Question 4 a) Chong's employer paid him an overseas leave passage cost for travel to New Zealand under a packaged tour in the year 2012. The air fare and accommodation for the trip amounted to RM5,000. Required: Explain the tax treatment for Chong and his employer in respect to the air fare and accommodation expenses. (5 marks) b) i. Tan's annual income for 2012 are as follow: Salary: RM60,000 (EPF contribution is 10%) Local Bank Interest: RM1,000 Rental Income: RM10,000 Required: Compute the chargeable income and tax payable for Tan for YA2012. (10 marks) ii. Ali and his wife made the following EPF contribution and insurance premium payment in 2012: Ali - EPF: RM3,000 & Insurance Premium: RM7,000 Wife - EPF: RM4,000 & Insurance Premium: RM500 Number of children below 18-years old : 4 Required: Compute the total relief for Ali and his wife for the YA2012 under both joint and separate assessment. The wife has made an election to claim child relief. (10 marks) [Total: 25 Marks Total: 25 Marks Questions a) Andy, a land owner entered into an agreement with a development company to develop commercial units on the land owned by the property owner. Under the agreement, the property owner will receive 35% of the completed units of houses built on his land. All development expenditure incurred will be bome by the developer who will be entitled to the balance of 65% of the completed units of houses. Since the land has been registered in the name of the landowner, he will grant a power of attorney to the developer to develop the land accordingly Required: Discuss whether a partnership exists between Andy and the development company. (8 marks) b) Button Woods & Partners is a partnership between Lee and Yce. They share profit and loss equally The P&L account for the year ended 31.12.2011 was as follows RM RM RM Trading Income 2,005,000 Less: Revenue expenses 750,000 Depreciation 63.000 Entertainment to client related to sales) 50.000 General provision for doubtfuldebts 30,000 Partnership expense Salary : Lee 2.500 : Yee 2.500 5.000 Interest on capital Lee 2.000 : Yee 2.000 4,000 Food from the business consumed by Lee 3,000 (905,000) Net Profit 1.100.000 Required: Calculate the Provisional Adjusted Income, Divisible Income and Adjusted Income of Partner for the partnership (17marks) Total: 25 Marks Formulae Individual Taxable Amounts & Payable Taxable income Less: Tax exemptions Less: Tax Reliefs Chargeable Income TAX RATES AND ALLOWANCES The following tax rates, allowances and values to be used in answering the questions. Income tax rates Resident individuals Chargeable income Rate Cumulative tax RM RM First 2,500 (0 - 2,500) 0 0 Next 2,500 (2,501 - 5,000) 25 Next 15,000 (5,001 - 20,000) 3 475 Next 15,000 (20,001 - 35,000) 7 1.525 Next 15,000 (35,001 - 50,000) 12 3,325 Next 20,000 (50,001 - 70,000) 19 7.125 Next 30,000 (70,001 - 100,000) 24 14,325 Exceeding 100,000 26 Personal reliefs and deductions RM Self 9,000 Disabled self, additional 6,000 Medical expenses expended for parents (maximum) 5,000 Medical expenses expended on self, spouse or child with serious disease, including up to RM500 for medical examination (maximum) 5,000 Basic supporting equipment for disabled self, spouse, child or parent (maximum) 5,000 Purchase of sports equipment (maximum) 300 Fees expended for skills or qualifications (maximum) 5,000 Expenses on books for personal use (maximum) 1,000 Spouse relief 3,000 Disabled spouse, additional 3,500 Child (each) 1,000 Child - higher rate (each) 4,000 Page 8 of 9 5.000 4.000 6.000 1,000 Disabled chim (each) Disabled child - additional (each) Life insurance premiums and contributions to approved funds (maximum) Deferred annaty premiums (maximum) Medical and for education insurance premium for self, spouse or child (maximum) Purchase of a personal computer (maximum) Broadband subscription (maximum Deposit for a child into the National Education Savings Scheme (maximum) 3.000 3.000 3.000 Rebates Chargeable income not exceeding RM35,000 RM Individual 400 Individual entitled to a deduction in respect of a spouse or former wife 800 Value of benefits in kind Car scale Cost of car(when new) Prescribed annual value of private usage of car RM RM Up to 50,000 1.200 50,001 to 75.000 75.001 to 100,000 3.600 100,001 to 150.000 150,00 1 0 200,000 7000 200,001 to 250.000 9.000 250,001 to 350,000 15.000 350,001 to 500.000 21.250 500,001 and above 25.000 The value of the car benefit equal to half the prescribed annual value (above) is taken if the car provided is more than five (5) years old Where a driver is provided by the employer, the value of the benefit per month is fixed at RM600 RM per month Other benefits Household furnishings apparatus and appliances Semi-furnished with furniture in the lounge, dining room, or bedroom Semi-furnished with furniture as above plus air-conditioners and/or curtains and carpets 70 140 Fully furnished premises Domestic help Gardener 280 400 300 Capital allowances Annual allowance (AA) Rate Industrial buildings Plant and machinery - general Motor vehicles and heavy machinery Office equipment, furniture and fittings Initial allowance (IA) Rate 10 20 20 20 20 10 

Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


